The Excellent Egg Edited
advertisement
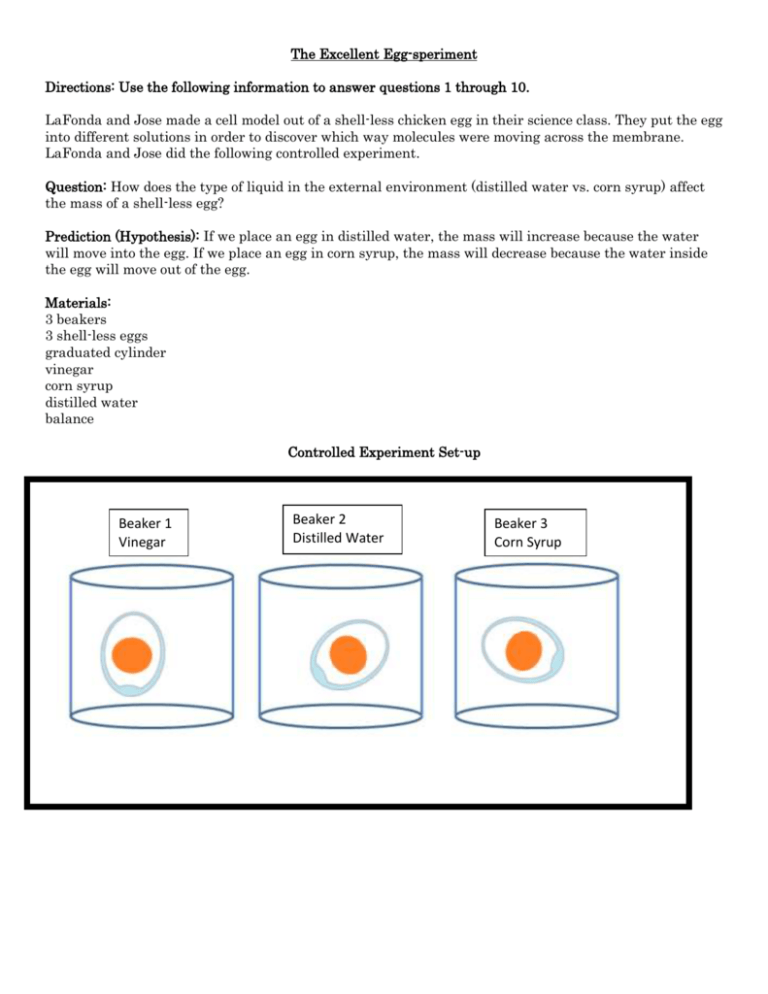
The Excellent Egg-speriment Directions: Use the following information to answer questions 1 through 10. LaFonda and Jose made a cell model out of a shell-less chicken egg in their science class. They put the egg into different solutions in order to discover which way molecules were moving across the membrane. LaFonda and Jose did the following controlled experiment. Question: How does the type of liquid in the external environment (distilled water vs. corn syrup) affect the mass of a shell-less egg? Prediction (Hypothesis): If we place an egg in distilled water, the mass will increase because the water will move into the egg. If we place an egg in corn syrup, the mass will decrease because the water inside the egg will move out of the egg. Materials: 3 beakers 3 shell-less eggs graduated cylinder vinegar corn syrup distilled water balance Controlled Experiment Set-up Beaker 1 Vinegar Beaker 2 Distilled Water Beaker 3 Corn Syrup Procedure: 1. Label one beaker “Vinegar”, one beaker “Distilled Water” and one beaker “Corn Syrup”. 2. Measure 200 mL of vinegar and pour it into the “Vinegar” beaker. 3. Measure 200 mL of distilled water and pour it into the “Distilled Water” beaker. 4. Measure 200 mL of corn syrup solution and pour it into the “Corn Syrup” beaker. 5. Mass one shell-less egg and record the mass. Place this egg into the beaker labeled “Vinegar”. 6. Mass one shell-less egg and record the mass. Place this egg into the beaker labeled “Distilled Water”. 7. Mass a different shell-less egg and record the mass. Place this egg into the beaker labeled “Corn Syrup”. 8. Allow the eggs to sit for 24 hours. 9. Remove the egg from the “Vinegar” beaker, and mass it. Record the mass in the data table. 10. Remove the egg from the “Distilled Water” beaker, and mass it. Record the mass in the data table. 11. Remove the egg from the “Corn Syrup” beaker, and mass it. Record the mass in the data table. Data: LaFonda and Jose Solution vs. Mass Trial 1 Trial 2 Type of Initial Final Initial Final Solution Mass Mass Mass Mass Vinegar 97.9 g 102.9g 78.6 g 80.3g Corn 110.7g 101.7 97.4 g 82.1 Syrup g g Distilled 98.6 g 106.2 111.4 123.8 Water g g g Ms. Love’s eggs 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 AVG Mass Change Cristostomo’s Eggs 1 2 3 4 5 Average Mass Change Water Mass g Day 1 Day 2 74.9 79.4 73.5 77.7 78.4 81.2 76.9 79.0 75.8 78.2 83.72 83.72 77.8 70.5 77.28 78.53 +1.25 Trial 3 Initial Final Mass Mass 84.2g 85.7g 107.6 99.8 g g 76.9 g 88.4 g Corn Syrup Mass g Day 1 Day 2 79.4 79.4 73.0 66.1 75.3 67.2 79.2 70.5 77.4 70.8 73.08 64.4 77.7 70.7 76.44 69.87 -23.34 Distilled Water Initial Mass Final Mass 95.82g 98.37g 97.99g 98.55g 92.45g 96.76g 94.12g 95.87g 90.83g 92.11g 94.24g 96.33g +2.09g Average Initial Final Mass Mass 86.9 g 105.2 g 95.6 g 89.6g 94.5 g 106.1 g Average Mass Change +2.7g -10.7g +10.5g Vinegar Control Mass g Day 1 Day 2 79.9 46.1 75.8 59.3 75.6 56.0 78.9 63.7 76.7 66.1 77.84 45.92 79.4 43.4 77.7 54.36 -6.57 Corn Syrup Initial Mass Final Mass 88.69g 59.15g 98.85 64.16 94.37g 60.67g 98.41g 60.87g 95.39 g 58.08g 95.12g 60.59g -34.53g Vinegar Initial Mass Final Mass 93.09g 99.36g 94.86g 98.97g 93.98 99.17 +5.19g 1. Which cell part produces proteins? o A. ribosome o B. nucleus o C. mitochondria o D. vacuole 2. What is the main function of the cell wall? o A. To store carbohydrates for later use o B. To give the cell a rigid structure o C. To package proteins for export o D. To carry out photosynthesis 3. Which part of the cell produces ATP for the egg to grow? o A. nucleus o B. ribosome o C. cytoplasm o D. mitochondria 4. How can Jose and Lafonda increase the reliability of their experiment? o A. Repeat the same procedure using a different cell model. o B. Repeat the same procedure to conduct more trials. o C. Add another controlled variable. o D. Add another dependent variable. 5. What is the manipulated variable of their experiment? o A. The Change in mass of the eggs. o B. 200mL of liquid in each beaker. o C. The shells removed from all eggs. o D. The different liquids the eggs were in. 6. What is the responding variable of their experiment? o A. The Change in mass of the eggs. o B. 200mL of liquid in each beaker. o C. The shells removed from all eggs. o D. The different liquids the eggs were in. 7. Write a conclusion for this controlled experiment. In your conclusion, be sure to: Answer the experimental question. Include supporting data from the Type of Solution vs. Mass table. Explain how these data support your conclusion. Provide a scientific explanation for the trend in the data. Question: What is the effect of type of solution on mass of the egg? Conclusion: 8. Which of the following processes occurs when water moves through the cell membrane? o A. Osmosis o B. Replication o C. Active transport o D. Protein Synthesis 9. Which cell part is responsible for photosynthesis? Write your answer in the box. 10. Animal cells absorb nutrients from the environment around them. What cellular process moves nutrients across cell membranes from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration? o A. Facilitated diffusion o B. Passive Transport o C. Active Transport o D. Osmosis 11. Which cell part contains genetic information for the egg cell? o A. Chloroplast o B. Cytoplasm o C. Vacuole o D. Nucleus 12. Which cell organelle is selectively permeable to materials entering and exiting the cytoplasm? o A. Chloroplast o B. Plasma Membrane o C. Vacuole o D. Nucleus 13. Which organelle is not present in an animal cell? o A. Mitochondria o B. Cell Membrane o C. Chloroplast o D. Microtubules 14. Plan a controlled experiment to answer the question in the box. You may use any materials and equipment in your procedure. Be sure your procedure includes: Logical steps to do the experiment Two controlled (kept the same) variables One manipulated (independent) variable One responding (dependent) variable How often measurements should be taken and recorded Question: What is the effect of Kool-Aid on the mass of the egg? Procedure: MV: CV: RV:






