NA3155 - University of Brighton
advertisement
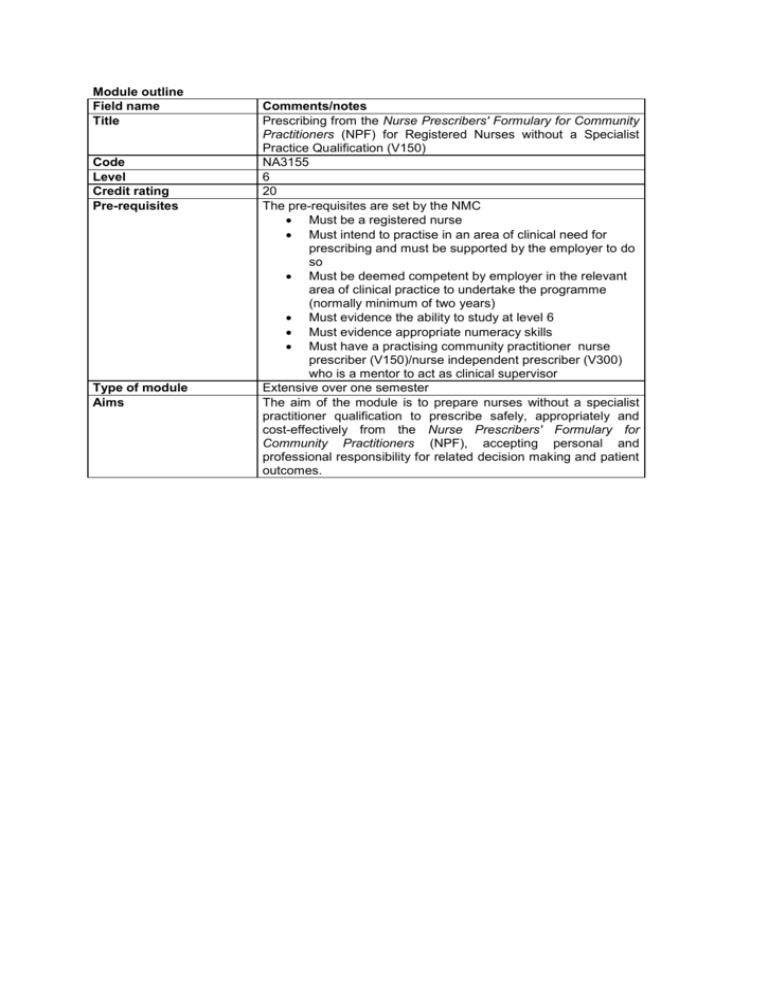
Module outline Field name Title Code Level Credit rating Pre-requisites Type of module Aims Comments/notes Prescribing from the Nurse Prescribers' Formulary for Community Practitioners (NPF) for Registered Nurses without a Specialist Practice Qualification (V150) NA3155 6 20 The pre-requisites are set by the NMC Must be a registered nurse Must intend to practise in an area of clinical need for prescribing and must be supported by the employer to do so Must be deemed competent by employer in the relevant area of clinical practice to undertake the programme (normally minimum of two years) Must evidence the ability to study at level 6 Must evidence appropriate numeracy skills Must have a practising community practitioner nurse prescriber (V150)/nurse independent prescriber (V300) who is a mentor to act as clinical supervisor Extensive over one semester The aim of the module is to prepare nurses without a specialist practitioner qualification to prescribe safely, appropriately and cost-effectively from the Nurse Prescribers' Formulary for Community Practitioners (NPF), accepting personal and professional responsibility for related decision making and patient outcomes. Learning outcomes/objectives Content The learning outcomes are dictated by the NMC (2007) and are as follows: On successful completion of the course students will be able to: 1. Assess and consult with patients, clients, parents and carers* 2. Undertake a thorough history, including medication history and current medication (including over-the-counter, alternative and complementary health therapies) to inform diagnosis* 3. Understand and apply the legislation relevant to the practice of nurse/midwife prescribing* 4. Critically appraise and use sources of information/advice and decision support systems in prescribing practice* 5. Understand the influences that can affect prescribing practice and demonstrate understanding by managing prescribing practice in an ethical way* 6. Understand and apply knowledge of drug actions in prescribing practice* 7. Demonstrate an understanding of the roles and relationships of others involved in prescribing, supplying and administering medicines 8. Prescribe safely, appropriately and cost-effectively 9. Practise within a framework of professional accountability and responsibility 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Teaching and learning strategies Student support The above learning outcomes will reflect, where implicated*, the intended scope of prescribing practice in specialist areas, such as neonates, infants, children & young people; pregnant and lactating women; and older people when indicated by the students area of clinical practice. This will be through specific theoretical sessions and frameworks and competencies in the portfolio of clinical practice. Consultation, decision-making and therapy, including referral Influences on, and psychology of, prescribing Prescribing in a team context Clinical pharmacology, including the effects of co-morbidity Evidence-based practice and clinical governance in relation to nurse prescribing Legal, policy and ethical aspects Professional accountability and responsibility Prescribing in the public health context Keynote lectures, self-directed learning, critical reflection, portfolio, case analysis of treatment scenarios, group discussion, problem-based learning. The students will be encouraged to use studentcentral. Teaching, supervision and support by lecturers and personal tutor (some of this support will be cohort-specific). Support from a mentor in order to enable the learning outcomes to be achieved in practice. Studentcentral and on-line learning materials. Learning resources are a central service of the university which provided learning support to all students. Reading list The core text for pharmacology is Rang and Pharmacology. 2012 7th edition. Churchill Livingstone. Dale’s Bickley, L.S. 2009 Bates’ Guide to Physical Assessment and History Taking. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Brookes, D. & A. Smith. 2006 Non-Medical Prescribing in Healthcare Practice: a Toolkit for Students and Practitioners. London: Palgrave. Beauchamp, T.L. & J.E. Childress. 2009 Principles of Biomedical Ethics. 6th ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Courtenay, M. & Griffiths, M (eds) 2010. Medication safety: an essential guide. Cambridge University press. Dale, M.M. & Haylett, D.G. 2009 Pharmacology Condensed 2nd ed. Churchill Livingstone; Elsevier. Department of Health. 2006. Improving Patients’ Access to Medicines: A Guide to Implementing Nurse and Pharmacist Independent Prescribing within the NHS in England. London: DOH. Dimond, B. 2008. Legal Aspects of Nursing. 5th ed. Harlow: Longman. Dimond, B. 2005. Legal Aspects of Medicines. Quay. Jones, M. & Guatam, N. 2004 The hands-on guide to practical prescribing. Blackwell. Jones, A. 2009 Nurse Prescribing in mental health. WileyBlackwell. Kumar, P. & Clark, M. (eds). 2009. Clinical Medicine. 7th ed. Saunders Elsevier. Jevon, P. Et al (eds). 2010 Medicines Management; a guide for nurses. Wiley-Blackwell. Lymn, J., Bowskill, D., Bath-Hextall, F., Knaggs, R. (eds) 2010 the new Prescriber. An integrated approach to medical and nonmedical prescribing. Wiley-Blackwell. Merrills, J. & Fisher, J. 2006 Pharmacy law and practice. Elsevier. Neal, M.J. 2005 Medical Pharmacology at a glance. 5th ed. London: Blackwell Porth, C.M. & Matfin, G. 2009. Pathophysiology: concepts of altered health states. 7th ed. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins Robinson, D. 2002. Clinical Decision-Making, a case study approach 2nd ed. Lippincott Rutter, P. 2005 Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment: a guide for pharmacists and nurses. Elsevier Churchill Livingstone Swage, T. 2004. Clinical Governance in Health Care Practice. 2nd ed. Butterworth-Heinemann Tingle J. & McHale, J. 2007 Law and Nursing. 3rd ed. Elsevier. Assessment tasks The assessment regulations will conform to the University of Brighton General Examination and Assessment Regulations. The assessment is in two parts: Theoretical (50% of mark) 1. Written examination consisting of a short answer paper (pass mark 40%) and a multi-choice question paper (pass mark 80%) to test pharmacological knowledge and its application to practice Practice component (50% of the total mark) 2. Portfolio which demonstrates an understanding of legal and ethical issues, team-working, record-keeping, writing a prescription and numeracy, and how these apply to prescribing practice (pass mark 40%) All assessments (which overall will test the attainment of the NMC standards and learning outcomes for the module) must be passed in order to pass the module. The NMC requires that nurses undertaking preparation as a community practitioner nurse prescriber (V150 route) must complete the programme within one year from the identified start of the programme. If a registrant has not completed all assessments within the allocated time, they must undertake the whole programme again, including all assessments, to ensure that competence has been maintained. For the purpose of this standard, interruption means any absence from a programme of education other than annual leave, statutory and public holidays. Brief description of module content and/or aims (maximum 80 words) Area examination board to which module relates Module team/authors/ coordinator Semester offered, where appropriate Site where delivered Date of first approval Date of last revision Date of approval of this version Version number Replacement for previous module Field for which module is acceptable and status in that field Please note that it is ONLY after successful completion of all elements of the module and it has been annotated on the professional register with the Nursing and Midwifery Council that the individual will have the authority to prescribe AND only from the Nurse Prescribers’ Formulary for Community Practitioners. This module aims to equip registered nurses, without a Specialist Practitioner qualification, with the knowledge, skills and competence to prescribe from the Nurse Prescribers' Formulary for Community Practitioners (NPF) and to become safe, effective and cost-effective prescribers within the community team. BSc(Hons) Professional Practice Stevan Monkley-Poole, Penny Lindley, Michelle Dryden Two only (must be completed within a year) Falmer January 2009 October 2011 Jan 2012 2 Nursing Course(s) for which module is acceptable and status in course School home External examiner BSc (Hons) Professional Practice May be taken as a stand alone module School of Nursing and Midwifery Louise Hales (2012 – 2015)