MEng Engineering (Mechanical with Business Finance)
advertisement
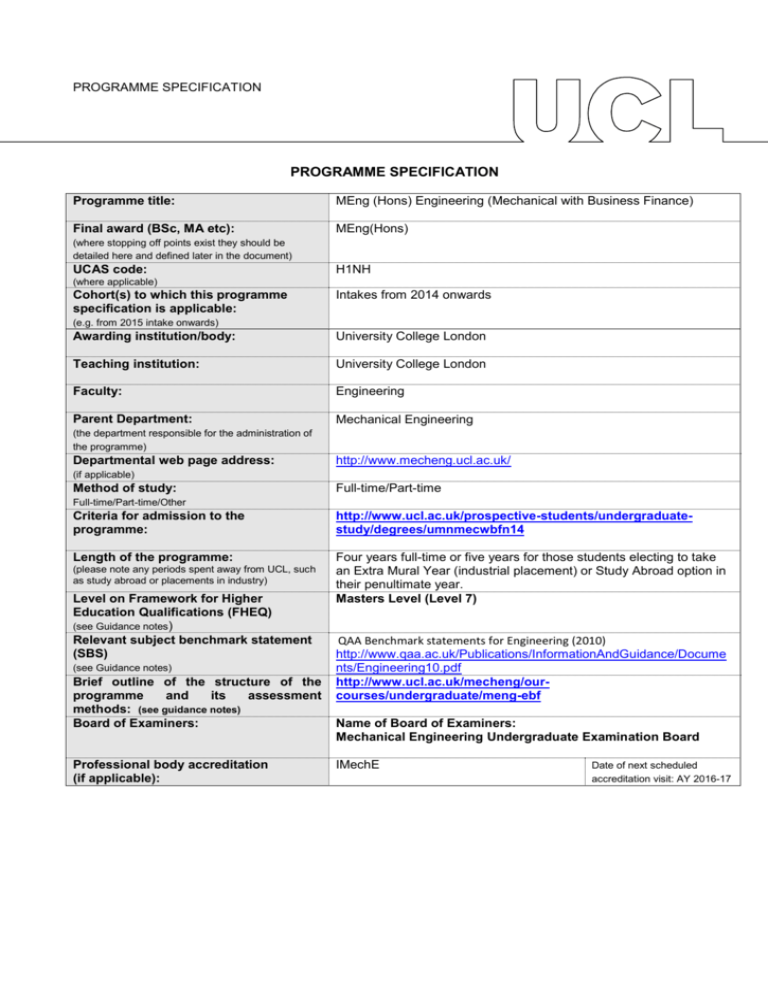
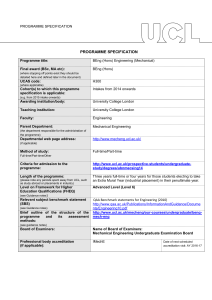
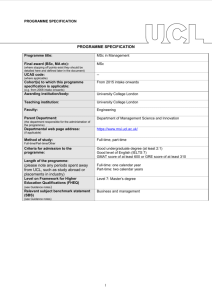
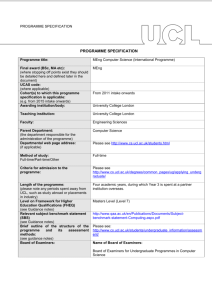
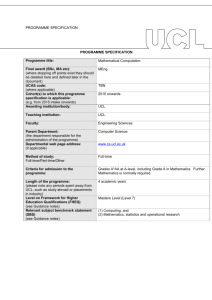
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION Programme title: MEng (Hons) Engineering (Mechanical with Business Finance) Final award (BSc, MA etc): MEng(Hons) (where stopping off points exist they should be detailed here and defined later in the document) UCAS code: H1NH (where applicable) Cohort(s) to which this programme specification is applicable: Intakes from 2014 onwards (e.g. from 2015 intake onwards) Awarding institution/body: University College London Teaching institution: University College London Faculty: Engineering Parent Department: Mechanical Engineering (the department responsible for the administration of the programme) Departmental web page address: http://www.mecheng.ucl.ac.uk/ (if applicable) Method of study: Full-time/Part-time Full-time/Part-time/Other Criteria for admission to the programme: http://www.ucl.ac.uk/prospective-students/undergraduatestudy/degrees/umnmecwbfn14 Length of the programme: Four years full-time or five years for those students electing to take an Extra Mural Year (industrial placement) or Study Abroad option in their penultimate year. Masters Level (Level 7) (please note any periods spent away from UCL, such as study abroad or placements in industry) Level on Framework for Higher Education Qualifications (FHEQ) (see Guidance notes) Relevant subject benchmark statement (SBS) (see Guidance notes) Brief outline of the structure of the programme and its assessment methods: (see guidance notes) Board of Examiners: Professional body accreditation (if applicable): QAA Benchmark statements for Engineering (2010) http://www.qaa.ac.uk/Publications/InformationAndGuidance/Docume nts/Engineering10.pdf http://www.ucl.ac.uk/mecheng/ourcourses/undergraduate/meng-ebf Name of Board of Examiners: Mechanical Engineering Undergraduate Examination Board IMechE Date of next scheduled accreditation visit: AY 2016-17 EDUCATIONAL AIMS OF THE PROGRAMME: The primary aim of this programme is to take well-qualified students and to equip them with the fundamental analytical and design skills necessary to become professional engineers in their chosen field. In addition, this programme provides graduates with a sound knowledge of management, finance, and business administration concepts and practices which are valuable in organisations within the engineering sector and more widely, for example in the financial sector and technology/information industries. Throughout, the programme integrates the transferable/employability skills defined by UK-SPEC which are so valued by employers of our graduates. The programme is designed to provide a rigorous and distinctive education emphasising the practical application of theory as widely as possible, providing exposure to the interdisciplinary nature of major engineering projects and the role of engineering in society through group challenges from 1st year onwards. This teaching is designed to exploit the major strengths of the Faculty in multi-disciplinary research. The enhanced treatment of the business and financial subjects within the programme is developed at the expense of the optional “Minor” component offered in the Engineering (Mechanical) programmes; the students are required to select the Engineering Finance Minor option. An individual 3rd year project provides a significant opportunity to develop and demonstrate their independent talent in engineering, and a 4 th year group project provides extensive training and experience of group work in design, analysis, construction, testing and evaluation. The MEng programme is designed to give additional depth and breadth over the BEng programme. Advanced engineering concepts are covered, giving an insight into current research and innovation. The final year of the MEng is designed to strengthen group project work and management skills in order that graduates may step seamlessly into a professional environment. PROGRAMME OUTCOMES: The programme provides opportunities for students to develop and demonstrate knowledge and understanding, qualities, skills and other attributes in the following areas: A: Knowledge and understanding Knowledge and understanding of: the fundamental mathematics, mechanical, electrical and thermal sciences to an advanced level appropriate for a Professional Engineer. engineering principles, quantitative methods, mathematical and computer models used in contemporary engineering and more widely. codes of practice, standards and quality issues as applicable to a an engineering career, including an awareness of intellectual property issues and of environmental, legal and ethical issues within the modern industrial world. design processes and methodologies as applied to technical engineering problems, including the appropriate integration of engineering within large and multidisciplinary challenges. management and business practices appropriate for a career in engineering management and/or business administration and an awareness of the commercial, economic and social context of business, in particular engineering practice. the characteristics of common engineering materials, the capabilities and limitations of manufacturing techniques an awareness of mechanical workshop practices. specific advanced and emerging technologies and associated research; applications of engineering in a range of areas peripheral to mechanical engineering. Teaching/learning methods and strategies: The knowledge and understanding outlined above is acquired through a combination of lectures, tutorials, individual project and group projects, design projects, practical laboratory work and coursework assignments, (this may be supplemented by industrial experience by taking an Extra Mural Year) Assessment: Assessment is through a combination of written examinations and assessed coursework. In some courses, the assessment is entirely based on the assessment of coursework through term-time; in others the assessment is a final written examination paper. Coursework assessment varies from course to course and includes the evaluation of laboratory reports, technical reports, problem solving exercises, design reports, design and testing of prototypes, assessment of computational skills, tests and oral presentations and, where necessary, viva-voce examinations. B: Skills and other attributes Intellectual (thinking) skills: the skill to identify and define an engineering or financial problem and generate innovative solutions. the ability to select and apply appropriate methods to model such solutions. the ability to plan and manage the design process of an engineering project taking account of constraints such as time, cost, health and safety as well as environmental issues. the ability to structure and plan communications clearly and accurately in formal report writing and oral presentations. skills associated with the analysis of cost drivers in management and accounting practices as well as marketing and entrepreneurship. the ability to make general evaluations of commercial risk. Teaching/learning methods and strategies: The skills outlined here are acquired through a combination of lectures, tutorials, major individual and group projects, design projects, practical laboratory work and coursework assignments, (this may be supplemented by industrial experience by taking an Extra Mural Year). Assessment: As indicated in section A above. C: Skills and other attributes Practical skills (able to): undertake engineering laboratory tests using a range of facilities and processes with due regard to issues of safety of the personnel involved. identify and implement appropriate ICT solutions. successfully undertake a design or research project, taking account of constraints such as time, cost, health and safety as well as environmental and societal issues. make general evaluations of commercial risk. Teaching/learning methods and strategies: These practical skills are acquired through, unseen written examinations, workshop practice, individual projects and group projects, design projects, practical laboratory work and coursework assignments, which may be supplemented by industrial experience by taking an Extra Mural Year. Assessment: These skills are evaluated from the assessment of laboratory reports, technical reports, problem solving exercises, design reports, design and testing of prototypes, assessment of computational skills, tests and oral presentations and, where necessary, vivavoce examinations. D: Skills and other attributes Transferable skills (able to): communicate technical, financial and contextual information and clearly and accurately in written and oral presentations as appropriate for a professional engineering career. understand individual strengths and capabilities to collaborate effectively as a member of a small team. plan appropriate work schedules to meet specified deadlines. apply the elements of financial accounting and bookkeeping in a variety of commercial situations. Teaching/learning methods and strategies: These skills are acquired through, individual projects and group projects, design projects, practical laboratory work and coursework assignments, which may be supplemented by industrial experience by taking an Extra Mural Year. Assessment: As indicated in section C above. The following reference points were used in designing the programme: the Framework for Higher Education Qualifications: (http://www.qaa.ac.uk/en/Publications/Documents/Framework-Higher-Education-Qualifications-08.pdf); the relevant Subject Benchmark Statements: (http://www.qaa.ac.uk/assuring-standards-and-quality/the-quality-code/subject-benchmark-statements); the programme specifications for UCL degree programmes in relevant subjects (where applicable); UCL teaching and learning policies; staff research. Please note: This specification provides a concise summary of the main features of the programme and the learning outcomes that a typical student might reasonably be expected to achieve and demonstrate if he/she takes full advantage of the learning opportunities that are provided. More detailed information on the learning outcomes, content and teaching, learning and assessment methods of each course unit/module can be found in the departmental course handbook. The accuracy of the information contained in this document is reviewed annually by UCL and may be checked by the Quality Assurance Agency. Programme Organiser(s) Dr B Hanson Name(s): Date of Production: September 2014 Date of Review: October 2014 Date approved by Head of Department: October 2014 Date approved by Chair of Departmental Teaching Committee: Date approved by Faculty Teaching Committee 14th Oct 2014 November 2014