BSc Theoretical Physics - University College London
advertisement

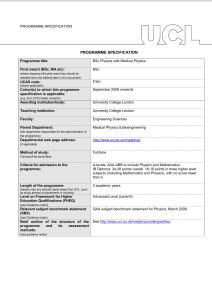
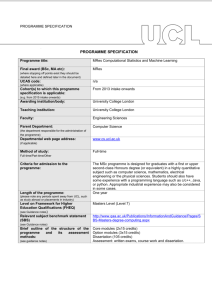
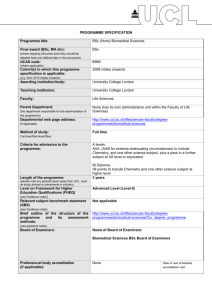
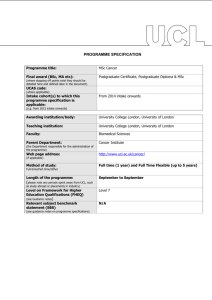
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION Programme title: BSc Theoretical Physics Final award (BSc, MA etc): BSc (where stopping off points exist they should be detailed here and defined later in the document) UCAS code: F340 (where applicable) Cohort(s) to which this programme specification is applicable: September 2003 onwards (e.g. from 2015 intake onwards) Awarding institution/body: University College London Teaching institution: University College London Faculty: MAPS Parent Department: Physics and Astronomy (the department responsible for the administration of the programme) Departmental web page address: www.phys.ucl.ac.uk (if applicable) Method of study: Full time Full-time/Part-time/Other Criteria for admission to the programme: AAA-AAB including A in Maths, A in Physics and A-B in Theoretical Physics Length of the programme: 3 academic years (please note any periods spent away from UCL, such as study abroad or placements in industry) Level on Framework for Higher Education Qualifications (FHEQ) (see Guidance notes) Relevant subject benchmark statement (SBS) (see Guidance notes) Brief outline of the structure of the programme and its assessment methods: (see guidance notes) Advanced Level (Level 6) http://www.qaa.ac.uk/en/Publications/Documents/Subjectbenchmark-statement-Physics-astronomy-and-astrophysics.pdf 8 1/2 units per year, made up of core courses, practicals and a choice of optional courses in years 2 & 3. Assessment by unseen examinations, coursework problems, laboratory reports, essays, reports and oral presentations. Board of Examiners: Name of Board of Examiners: Boards of Examiners in Physics and Astronomy Professional body accreditation (if applicable): Institute of Physics Date of next scheduled accreditation visit: Nov. 2016 EDUCATIONAL AIMS OF THE PROGRAMME: To encourage students to develop critical modes of thought and study, to acquire an in-depth knowledge of the subject and to develop a range of technical and inter-personal skills. They should be prepared for a wide variety of careers, both within professions connected directly with physics or in a wide range of other activities. PROGRAMME OUTCOMES: The programme provides opportunities for students to develop and demonstrate knowledge and understanding, qualities, skills and other attributes in the following areas: A: Knowledge and understanding Knowledge and understanding of: 1. Theoretical structure of the core topics in Physics, with a selection of advanced research topics, sufficient to allow informed choice of a field of postgraduate study. 2. The mathematical basis of Physics. 3. Mathematics of relevance to Physics. 4. The structure of compiled computer programmes. Teaching/learning methods and strategies: 1 and 2. Lectures with associated problem sheets and tutorials. Access to recommended textbooks and web material. 3. Lectures and workstation-based courses in first year and (optionally) third year. Assessment: 1 and 2. Unseen examinations. Continuous assessment marks from problem sheets. 3. Online testing of computing knowledge. B: Skills and other attributes Intellectual (thinking) skills: 1. Application of their knowledge to unseen problems. 2. Ability to combine mathematics and verbal explanation in a coherent rigorous argument. Teaching/learning methods and strategies: 1 and 2. Fortnightly problem-sheets on all courses, supported by tutorial discussion. Special problem solving classes with staff and postgraduate supervision in the first two year. Assessment: 1 and 2. Unseen written examination. In-course assessment problem sheets used in coursework mark. C: Skills and other attributes Practical skills (able to): 1. Carry out laboratory experiments to demonstrate physical principles and measure constants of nature. 2. Use spreadsheet package to present and calculate physics results. 3. Present results with appropriately calculated errors. 4. Report experimental results clearly and methodically. 5. Use computer packages for word processing, webpage management and manipulation of mathematical functions. 6. Use compiled or interpreted computer languages to write original programs. 7. Use Mathematical techniques to solve problems in Theoretical Physics. Teaching/learning methods and strategies: 1. Set experiments, starting simply in first year; more open ended in later years. Close advice and supervision. 2, 5 and 6. Workstation-based hands-on courses; first year, Python and Mathematica; second year Mathematica and third year object oriented programming option (Java). 3. Supplementary lectures linked to set experiments. 4. Preparation of workbooks and detailed reports. 7. 1.5-unit final-year project. Assessment: 1, 3 and 4. Grading of Lab. reports. 2, 5 and 6. Online testing and written exercises. 7. Observation of progress. Written and oral reports. D: Skills and other attributes Transferable skills (able to): Write clear accounts of scientific subjects at a level appropriate to audiences ranging from complete lay-people to fully qualified colleagues. Teaching/learning methods and strategies: Communications Skills course, involving essays, reports and oral presentations running over the first two years. Assessment: Essays, reports and presentations marked and included separately in the scheme for award of honours The following reference points were used in designing the programme: the Framework for Higher Education Qualifications (http://www.qaa.ac.uk/en/Publications/Documents/Framework-Higher-Education-Qualifications-08.pdf); the relevant Subject Benchmark Statements (http://www.qaa.ac.uk/assuring-standards-and-quality/the-qualitycode/subject-benchmark-statements); the programme specifications for UCL degree programmes in relevant subjects (where applicable); UCL teaching and learning policies; staff research. Please note: This specification provides a concise summary of the main features of the programme and the learning outcomes that a typical student might reasonably be expected to achieve and demonstrate if he/she takes full advantage of the learning opportunities that are provided. More detailed information on the learning outcomes, content and teaching, learning and assessment methods of each course unit/module can be found in the departmental course handbook. The accuracy of the information contained in this document is reviewed annually by UCL and may be checked by the Quality Assurance Agency. Programme Organiser(s) Dr S Zochowski Name(s): Programme Tutor, Physics and Astronomy Date of Production: January 2011 Date of Review: November 2014 Date approved by Head of Department: November 2014 Date approved by Chair of Departmental Teaching Committee: Date approved by Faculty Teaching Committee November 2014 February 2015