HND Applied Chemistry MidKent College Title of the module
advertisement

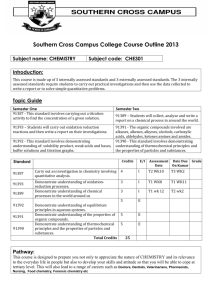
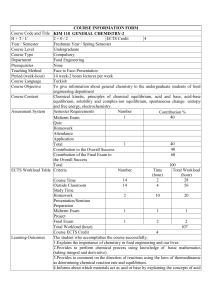
HND Applied Chemistry MidKent College 1. Title of the module Physical Chemistry 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Department responsible for management of the module SPS Start date of the module September 2012 The number of students expected to take the module 15 Modules to be withdrawn on the introduction of this proposed module? None The level of the module I Number of credits which the module represents 15 Which term(s) the module is to be taught in (or other teaching pattern) Year 2 Prerequisite/co-requisite modules none Programme of study to which the module contributes HND/C Applied Chemistry 11. The intended subject specific learning outcomes At the end of this module the student will be able to: 1. Apply the concept of chemical equilibrium 2. Understand physical equilibria in one and two component systems 3. Understand the origins and applications of molecular spectroscopy 4. Understand properties of surface chemistry. These will contribute to the following programme learning outcomes: A 1, 2, 3, 6 B 1, 2 C 1, 3, 4 D 1,2 ,3 ,4, 5 12. The intended generic learning outcomes and, as appropriate, their relationship to programme learning outcomes At the end of the module the learner will be able to demonstrate: a) decision making skills b) Critical thinking skills c) Ability to work with complex material d) Communication and report writing skills e) Ability to scan and organise data, abstract meaning from information and share knowledge with others f) Effective self-management skills These will contribute to the following programme learning outcomes: A 6 B 1, 2 C 1, 4 D 1,2, 3, 4, 5 13. A synopsis of the curriculum This module covers the kinetic theory of gases, chemical equilibrium, phase equilibria, spectroscopy, surface chemistry and colloids through a programme of related practical and assignment work. The module involves interpretation of phase diagrams, calculations involving chemical and phase equilibria and understanding models used to explain spectroscopy and the properties of surfaces. Understanding equilibria is important in chemical engineering applications. Spectroscopic models are useful in explaining how matter interacts with electromagnetic radiation and the information that may be gained from spectroscopic measurement. Understanding surface chemistry is important in catalysis, the detergent industry and polymer industry. April 2011 HND Applied Chemistry MidKent College 14. Indicative Reading List Atkins P W – The Elements of Physical Chemistry – 3rd Ed (Oxford University Press, 1992) ISBN 0198792905 Avery H E and Shaw D J – Work Out Physical Chemistry (Macmillan, 1989) ISBN 0333458699 Barrow G M – Physical Chemistry – 6th Ed (McGraw-Hill, 1996) ISBN 0070051119 Moore W – Physical Chemistry – 5th Ed (Longman, 1972) ISBN 0582442346 Silby R and Alberty R – Physical Chemistry (John Wiley & Sons, 2000) ISBN 0471383112 Burrows, Holman, Parsons, Pilling, Price – Chemistry3 (Oxford University Press, 2009) ISBN 978-0-19-927789-6 Websites: Royal Society of Chemistry 15. Learning and Teaching Methods, including nature and number of contact hours and total study hours which will be expected of students, and how these relate to achievement of the intended learning outcomes The total learning time for the module will be 150 hours. The module will be delivered by means of lectures, seminars, and practical work. Learners will be expected to undertake approximately 90 hours of independent study, including research, required reading and answering assignments. There will be 32 one hour lectures, 4 one hour supervision/problem sessions one per learning outcome and 8 half day laboratory sessions (total 60 hours). This will include a variety of tasks, discussions, study materials and case studies, practical’s, as appropriate to the topics being covered, with the focus being on the learning outcomes. 16. Assessment methods and how these relate to testing achievement of the intended learning outcomes Laboratory practical reports and questions 20% (learning outcomes 1-4, generic outcomes d, e and f) Problems for each learning outcome 20% (learning outcomes 1-4, generic outcomes a, b and c) Coursework 60% (learning outcomes 1-4, generic outcomes a to f) Learning outcome To achieve this outcome a student must demonstrate the ability to: Apply the concept of chemical equilibrium Account for the relationships between the variables in the ideal gas equation in terms of the kinetic theory of gases Calculate terms in the ideal gas equation Write expressions for calculating chemical equilibrium constants Solve problems involving chemical equilibrium Understand physical equilibria in one and two component systems Analyse pressure/temperature phase diagrams for simple, one-component systems Perform calculations using the Clapeyron and ClausiusClapeyron equations Explain liquid-vapour equilibria and distillation in terms of vapour pressure/composition and boiling point/composition plots for two component systems Analyse phase diagrams for solid-liquid equilibria which form a simple eutectic mixture Understand the origins and applications of molecular spectroscopy Examine the relationship between spectroscopic techniques and electromagnetic radiation Review theoretical models used in spectroscopy Explain the applications of practical spectroscopic April 2011 HND Applied Chemistry MidKent College techniques Understand properties of surface chemistry. Explain the solid-gas interface. Explain the nature and properties of surface active agents Discuss features of the solid-liquid interface Discuss the behaviour of colloidal systems 17. 18. Implications for learning resources, including staff, library, IT and space This is an existing module and there are no new implications for learning resources. As far as can be reasonably anticipated, the curriculum, learning and teaching methods and forms of assessment do not present any non-justifiable disadvantage to students with disabilities Statement by the Director of Learning and Teaching: "I confirm I have been consulted on the above module proposal and have given advice on the correct procedures and required content of module proposals" ................................................................ .............................................. Director of Learning and Teaching Date Statement by the Head of Department: "I confirm that the Department has approved the introduction of the module and will be responsible for its resourcing" ................................................................. Head of Department April 2011 .............................................. Date