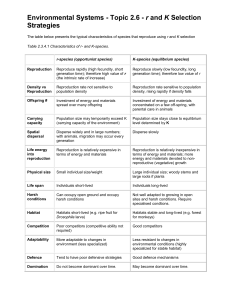
Filled in student notes for sexual and asexual reproduction
advertisement

Type of reproduction: Sexual reproduction in plants How it happens: Fusion of gametes Example species: Flowering plants, Ferns (fertilization) resulting in offspring genetically different from parents Advantages: Spread easily Genetic diversity Type of reproduction: Plant budding How it happens: Buds are cut off of an existing plant and grafted on to a new plant. Advantages: Budding requires less experience (than grafting) Only need a small part of the plant Type of reproduction: Binary fission How it happens: In unicellular organisms single cells divide into two new cells Advantages: Single organism (no need for a mate) Fast method of reproduction. Disadvantages: Requires insects or wind to pollinate, don’t spread as much as plants with seeds Example species: Fruit salad tree, potato Disadvantages: Weather adaptation may be poor. Example species: Protozoa, Cyanobacteria (bluegreen algae). Disadvantages: Cannot adapt to change. No genetic diversity. Type of reproduction: Grafting How it happens: Part of a plant is spliced onto another type of plant Example species: Rose, trees Advantages: Requires less time to grow. Cheap way to get desired traits. Disadvantages: May not live well in harsh environments. DNA may change suddenly. Type of reproduction: Spores How it happens: Build up pressure inside a plant, release seeds in the air. Example species: Algae, Fungi, puffball. Advantages: Spores can germinate after years. May travel large distances. Disadvantages: Spores may get buried and may not be viable. May require an insect or animal to help spread. Type of reproduction: Hermaphroditic species (animals) How it happens: Penis fencing in turbellaria. Example species: Turbellaria, earthworm. Both sexual organs are present so there is a fight to determine which is impregnated. Advantages: Ability to self replicate. Disadvantages: Limited genetic diversity. Less No need to find a mate in some cases. competition for a mate results in less fit organisms to pass down genes. Type of reproduction: Fragmentation How it happens: A portion breaks off, that portion can grow into new plants Advantages: Reproduce quickly. Identical copies can help maintain desirable traits. Type of reproduction: Vegetative reproduction How it happens: Offspring are generated from a single part of a parent plant. Advantages: cheap and fast Type of reproduction: Budding in animals How it happens: New organism from an outgrowth or bud due to cellular division. Advantages: less energy needed to find a mate Type of reproduction: Parthenogenesis How it happens: Different in different species. Achieved by different chromosome number of chromosome replication than normal sex cells. Advantages: Saves time and energy. Increase population size quickly. Example species: Lichen Disadvantages: No genetic diversity. Mutations passed down to all offspring. Example species: potatoes, onion, flower bulbs. Disadvantages: susceptibility to disease. Low biodiversity. Example species: jellyfish, flatworms Disadvantages: overcrowding can occur. Less ability to adapt. Example species: Stick insects, sharks. Disadvantages: Reduce genetic diversity. Harder to adapt.