Land and Water Test Study Guide
advertisement

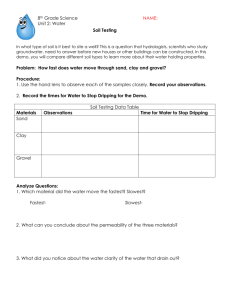
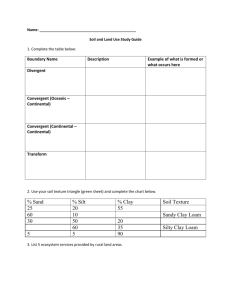
In this review, material that is underlined is what everyone should know for this unit. There will be opportunity on the test to share about other material shared in this review. Understanding of extra material will give students opportunity to show advanced understanding of the Land and Water Unit. The Water Cycle You should be able to describe precipitation, condensation and evaporation. To show advanced, you should be able to describe transpiration, infiltration, and groundwater flow. Are the following forms of water a solid, a liquid, or a gas? Rain = liquid clouds = liquid ice = solid River = liquid steam = gas snow = solid WHAT IS A RIVER SYSTEM? Every river is part of a larger system-a watershed, which is the land drained by a river and its tributaries. Rivers are large natural streams of water flowing in channels and emptying into larger bodies of water. This diagram shows some common characteristics of a river system. Every river is different, however, so not all rivers may look exactly like this illustration. The river source, also called the head, is the beginning of a river. Often located in mountains, the source may be fed by an under- ground spring, or by runoff from rain, snowmelt, or glacial melt. The mouth is the place where a river flows into a larger body of water, such as another river, a lake, or an ocean. Upstream is in the direction of or nearer to the source of a river. Downstream is in the direction of or nearer to the mouth of a river. Wetlands are low-lying areas saturated with water for long enough periods to support vegetation adapted to wet conditions. Wetlands help maintain river quality by filtering out pollutants and sediments, and regulating nutrient flow. A fully-developed floodplain is relatively flat land stretching from either side of a river, which may flood during heavy rain or snowmelt. Built of materials deposited by a river, floodplain soil is often rich in nutrients and ideal for growing food. A tributary is a smaller stream or river that joins a larger stream or main river. A watershed boundary, also called a drainage divide, marks the outer- most limit of a watershed. A watershed is a tract of land drained by a river and its tributaries. Anything that affects a watershed may eventually impact its tributaries and river as well as the water body at the mouth of the river. People's actions within a watershed can affect the overall quality of its rivers. The main river is the primary channel and course of a river. A meander is a loop in a river channel. A meandering river winds back and forth, rather than following a straight course. The delta is the buildup of deposited soil at the mouth of the river. You should be able to draw a river and label the head, the mouth and the tributaries. For advanced you will be able to add labels of other parts of rivers. An area that has gone a long period of time without rain is suffering from a drought. An area that has received too much rain in a short period of time may be suffering from a flood. What is in soil? Pieces of Gravel are often found in soil. Gravel are rock fragments that can be anywhere from 2 mm to 6.4 cm long. Components of Soil Sand is the largest particle in the soil other than gravel. When you rub it, it feels rough. This is because it has sharp edges. Sand doesn't hold many nutrients. Silt is a soil particle whose size is between sand and clay. Silt feels smooth and powdery. When wet it feels smooth but not sticky. Clay is the smallest of particles. Clay is smooth when dry and sticky when wet. Soils high in clay content are called heavy soils. Clay also can hold a lot of nutrients, but doesn't let air and water through it well. Particle size has a lot to do with a soil's drainage and nutrient holding capacity. To better understand how big these three soil particles are, think of them like this. If a particle of sand were the size of a basketball, then silt would be the size of a baseball, and clay would be the size of a golf ball. Line them all up, and you can see how these particles compare in size. Also in soil… There is also humus in soil. Humus is organic material – made from decaying plant and animal material. It is generally very dark, and holds lots of nutrients. It will often float when a lot of water is added. There is also air and water in soil. What is erosion? The process by which earth materials are broken down and moved from place to place. In our stream tables, we saw that water moved the soil from one end of the table to the other. The larger streams moved the bigger particles of gravel and sand. The smaller stream mainly moved the sand and clay. Erosion changed our flat surface of soil into a canyon, or rivulet, Why do humans build dams? To create electricity Provide water for farmers To provide a water supply for large cities To create habitats for fish and wildlife. To restore beaches when water is released. To prevent flooding. How does slope effect the way water moves? What happens to the water and the land? A lentic system Land is mostly flat… the water will move very slowly or be still. The land soaks up the water or the water evaporates into the sky. When land is mostly flat, a pond, lake or wetlands area may often form. A lotic system Land has a steep hill… the water will move very fast down the hill, perhaps creating a waterfall. The fast moving water will erode the land and pull the land down toward the bottom of the hill. Rivers and streams have formed due to water flowing down hills that have a slope rather than flat land. People plant grass and trees on sloped hills to help protect the land from erosion. Erosion makes canyons, caves and sinkholes. Deposition makes beaches and deltas.