Lesson 1 diversity of living things classification student wksht
advertisement

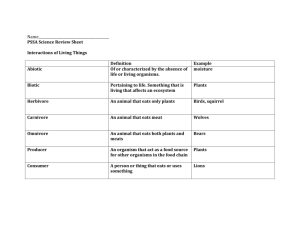
Unit 1: Diversity Activity 1: Classification of Living Things Imagine you had to empty out all the contents of your pencil case and try to organize them into specific categories and then identify them. Depending on the items you have, it may take you a few moments, but in time, you will probably develop groups of items that have similar features. Perhaps you separated pens from pencils and erasers from white out. Or maybe you grouped all the writing tools (pens, pencils, etc.) together and separated them from non-writing tools (erasers, paperclips, glue stick, etc.) Now imagine trying to classify all the organisms on Earth into specific groups. This task began long before you were born. In fact, it began 2300 years ago with Greek philosopher Aristotle identifying 1 000 different types of organisms. At that time, Aristotle grouped organisms according to their habitat. There were land dwellers, water dwellers and air dwellers. Aristotle also arranged species by their complexity and arranged them in order from least complex to highly complex. As we will learn, the hierarchy arrangement that Aristotle proposed is similar to the system we use today. Swedish botanist __________________(1707 1778) created our current classification system. Over 300 years ago, Linnaeus arranged organisms based upon their __________ and ______________ features. Thus, began the process of taxonomy. ______________ is the science of classifying organisms into similar groups so that when a new organism is found it can be identified. It also illustrates the relationship between similar organisms. Aristotle as a young philosopher. Linnaeus Similar to Aristotle's hierarchy, Linnaeus also developed levels of organization: kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Individual groups are called a _____________(plural taxa). Kingdom represents the highest level and the most number of organisms, whereas, species contain only one type of organism in its taxa. The chart below shows the order from highest to lowest and a mnemonic that you can use to help you remember the hierarchy. King Peter Came Over For Good Spaghetti Linnaeus also developed a tool, which is currently used today, to name specific organisms. ________________________assigns each organism a two word name in either Latin or Greek. This naming system only represents the __________ and __________ classification of the organism and omits the other five levels. For example, the scientific name for humans is Homo sapiens. Hopefully you notice that the names are written in __________. The genus name is always written in italics and is capitalized, and the species is also written in italics, but it is not capitalized. Here is a sample of common names for familiar organisms. Let's see if you are able to match up the correct scientific name. Practice Question 1. Match the organisms in the left hand column with their correct scientific names in the right hand column. Common Names Scientific Names Taraxacum officinale Acer palmatum Japanese Maple Rangifer tarandus Reindeer Dandelion At first, there were two main kingdoms: _________ and ____________. As time went on, it became apparent that more kingdoms were needed to correctly identify and name organisms. Currently there are five kingdoms: Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, and Bacteria. In addition, a new taxa ___________ was recently introduced to distinguish between the different types of bacteria, which we will explore in greater detail at a later time. The three domains are__________, __________, and _____________. Here is the complete classification of humans: Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Order Primates Family Hominidae Genus Homo Species sapiens Remember the opening problem of identifying and classifying the contents of your pencil case? You probably completed it without the use of a dichotomous key. A _____________________is a classification manual that provides the user with a series of options to choose from and then a link to follow based on that choice. For example, if we go back and explore the contents of your pencil case: pen, pencil, eraser, paper clip, scissors, and glue stick, we can create a dichotomous key. Simply follow the steps until you have been able to identify each item. 1.a.circular shape……….go to 2. b.irregular shape ……..go to 3. 2.a.thin body……………..go to 4. b.thick body ……………glue stick. 3.a.Metallic lustre…………… go to 5. b.Non-metallic lustre……... eraser. 4.a.wooden body…………..pencil b.plastic body…………… pen 5.a.malleable…………….. paper clip b.non-malleable ……..…scissors A Phylogenetic Tree A ________________tree can be used to show the evolutionary history of a particular organism. It resembles a tree with a trunk and many branches that diverge. A phylogenetic tree will show a common ancestor and the many different organisms that have branched away. This phylogenetic tree shows the evolution of all living things. Each branch contains organisms that have diverged from the common ancestor. As you can see, each group diverges at different times when their characteristics changed and no longer resemble their ancestor. Assignment Complete the following assignment and submit your work to your teacher. Using a Dichotomous Key 1. Use the illustrations of flowering plants and the dichotomous key to identify each flower. Image 1 Image 2 Image 3 Image 4 Image 5 Image 6 2. 1.a.Flower has more than six petals……..go to 2. b.Flower has less than six petals………go to 3. 3. 2.a.Petals are arranged tightly…………….Taraxacum officinale b.Petals are spread out…………………..go to 4. 4. 3.a.White petals……………………………...Geranium richardsonii b.Petals are purple………………………...Geranium viscosissimum 5. 4.a.Petals are pointed……………………….go to 5. b.Petals are rounded………………………Sphaeralcea coccinea 6. 5.a.Petals are thin and yellow……………… Balsamorhiza sagittata b.Petals are short and purple…………….Symphyotrichum novi-belgii 7. Determine the common name of each of the flowers and arrange your solutions into an organized table as shown below. Image Scientific Name Common Name 1 2 3 4 5 6 8. Create your own dichotomous key for the following images. Remember to choose distinguishing features to separate each organism. Atractosteus spathula Alosa pseudoharengus Ictalurus punctatus Acipenser oxyrhynchus Pomoxis nigromaculatus Esox niger