AQA AS Core section Rivers-Handout 1
advertisement

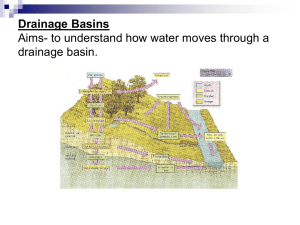
1 AQA AS Core section: Rivers 1- The drainage basin hydrological cycle TB page 2 Where slopes meet at the bottom of a valley, water is concentrated and forms a river channel. A drainage basin is an area of land drained by a river and its tributaries. Drainage basins are separated from each other by ridges of higher land called watershed. What is a watershed? Flash animation of how rain falling on to the landscape will drain into a river. A drainage basin is an open system- a system where there are inputs and/or outputs of energy and matter- with inputs (water and energy) and outputs of water. The water enters the system as precipitation and leaves as stream flow or as evaporation or transpiration. Inputs: energy from the sun/precipitation Stores such as glaciers, rivers, lakes and vegetation Transfers and flows move water through the system, such as infiltration. Outputs: moisture lost by evapotranspiration + runoff into the sea Key terms: 1- Precipitation (input): All forms of rainfall, snow, frost, hail and dew. It is the transfer of moisture in the atmosphere to the land. 2- Evaporation + Transpiration=Evapotranspiration (output) Evaporation: The change of state from liquid to gas from exposed water surfaces Transpiration: The loss of water from the leaves of plants Evapotranspiration: the combined losses 3- Surface stores such as glaciers and lakes 4- Interception (Storage): The process by which precipitation is trapped on the surface of vegetation. Interception loss (output): The proportion of water which evaporates from the surface of vegetation. After interception…transfers 5- Stemflow :Intercepted precipitation which runs down the stems of plants to reach the ground. 2 6- Throughfall: The precipitation which falls straight through the vegetation (or drips off leaves) and reaches the ground. 7- Overland flow/ surface runoff (transfers): Water that moves over the ground surface. Water moving as overland flow reaches the river channel much more quickly than water flowing through soil and rocks. The more overland flow that takes place, the faster the river level rises and the more likely flooding is to occur. Overland flow happens from a combination of the following reasons: - The ground surface is relatively impermeable and the water cannot infiltrate as a result of, foe example, urban development. - Vegetation cover has been removed, reducing the infiltration rates and the interception loss. The extra water runs over the ground surface. - When the soil store is already full of water, the term used is saturated overland flow. - The rainfall comes down faster than it can infiltrate the soil. This can occur with intense summer storms. 8- Infiltration (Transfer): process by which water soaks into or is absorbed by the soil. It is a very important process, because water entering the soil will move slowly through the drainage basin to the river channel, whereas water which does not infiltrate will flow relatively quickly over the surface to a river as overland flow. Infiltration rate: refers to how much water IS passing through in a certain time. Infiltration capacity: is the maximum rate at which water CAN enter the soil in a particular case [measured in cubic millimetres per hour]. 9- Throughflow (Transfer): The downslope flow of water within the soil. 10- Percolation (transfer): As water reaches the underlying soil or rock layers, which tend to be more compact, its progress is slowed. This slow movement , called percolation, creates groundwater storage. 11- Groundwater flow/baseflow (transfer): Groundwater refers to subsurface water. The upper layer of the permanently saturated zone is known as the water table and it varies seasonally. Groundwater flow is the slow movement of water through the underlying geology via cracks and joints below the water table and it varies seasonally. The slow flow through rock produces a steady input of water which varies relatively little in comparison with the discharge of the whole river. This explains why rivers can continue to flow even if it has not rained for weeks. 3 4 Question catcher (i) Identify flow X; (1) Explain why the drainage basin hydrological cycle can be described as an open system. (3 marks) -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Distinguish between the inputs and outputs of the drainage basin hydrological cycle. (2 marks) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 Describe how water reaches a river channel in a drainage basin. (4 marks) ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------The water balance TB page 4 The water balance or budget: balance between inputs and outputs of a drainage basin. - Dynamic relationship between temperature, precipitation and evaporation rates over the year. Water balance or budget P= Q+E = +/- change in storage P= precipitation Q= runoff E= evapotranspiration Shown using a water budget graph. What is potential evapotranspiration? For example, the actual evapotranspiration rate in Egypt is less than 250mm, because there is less than 250mm of rain annually. However, given the high temperatures experienced in Egypt, if the rainfall were as high as 2000mm, there would be sufficient heat to evaporate that water. Therefore, the potential evapotranspiration rate there is 2000mm. 6 Soil moisture is the total amount of water in a soil. Soil moisture recharge is the replenishment of stores of water used during warmer months when evapotranspiration has exceeded precipitation, when there is a net balance in favour of precipitation, water lost from the soil will be replaced. Temperate climate e.g. the UK Precipitation exceeds evapotranspiration Therefore positive budget over a year. During winter (high precipitation/low evapotranspiration) soil moisture surplus surface runoff/rise in river levels In summer, rates of evapotranspiration> precipitation and soil water may be utilised, reducing the amount remaining in the soil and river channels In autumn, the soil water will be replenished soil back to field capacity (the normal amount of water that can be held by soil) 7 Extremely arid and Mediterranean climates So much water can be there can be a soil moisture left in the soil to match the Figure Soil moisture deficit Question catcher removed from the soil in summer that deficit: that is, there is not enough water potential evapotranspiration. 8 3- The storm hydrograph Discharge: total volume of water in a river channel passing at any giving point every second. To find the discharge of a river, we multiply the velocity of the river, measured in metres per second by the cross-sectional area of the river measured in square metre. This gives the discharge in cumecs passing any given point. (Cubic metres per second). Figure How to find the discharge of a river The storm hydrograph shows variations in a river’s discharge over a short period of time, usually a storm. Figure The storm hydrograph 9 Lag time: the time period between peak rainfall and peak discharge Base flow: the constant part of a river’s discharge produced by groundwater and slow throughflow seeping slowly into the river. It is the main contributor to river flow during dry weather. The rising limb shows the increase of the discharge. The highest flow is shown by the peak discharge. This occurs some time after the peak of the input because the water takes time to move through the system to the measuring point of the basin. The falling or receding limb shows the fall in the discharge back to the base level. Runoff or storm flow: Combination of overland flow and rapid throughflow Figure Type of flows and storm hydrograph The processes operating in the drainage basin transfer water to the channel. However, they transfer water at different speeds. Most hydrographs are controlled by the interaction of several variable factors. 10 Factors affecting the shape of the storm hydrograph Factor Climatic factors Precipitation (Intensity and duration of the storm) Snow (Water stored as snow) Evapotranspiration (temperature) Soil characteristics Soil moisture (Antecedent /pre-existing conditions) Permeability Drainage basin characteristics Drainage density Size of drainage basin Slopes Shape of drainage basin Hydrograph dominated by quickflow processes Hydrograph dominated by slowflow processes High-intensity rainfall which exceeds the infiltration capacity of the soil. Large amount of rainfall Fast snow melt as temperatures suddenly rise above zero Low rates of evapotranspiration outputs due to low temperatures e.g. winter in Britain Low-intensity rainfall which is less than the infiltration capacity of the soil Small amounts of rainfall Slow snow melt Basin already wet from previous rain, water table high, soils saturated and so low infiltration/percolation Impermeable soil Dry soil-the soil store can hold much more water. Low water table. High infiltration/percolation Permeable soil High drainage density (large number of streams per km).The higher the density the faster the water reaches the main river channel. Low drainage density (small number of streams per km) means few streams and rivers and so water is more likely to enter the ground and move slowly through the basin. Small drainage basin tends to respond more rapidly to a storm than larger one, so the lag time is shorter. Steep slopes promote surface runoff. Rainfall reaches the river more quickly from a round basin than from an elongated basin. High rates of evapotranspiration outputs due to high temperatures e.g. summer in Britain Gentle slopes allow infiltration and percolation. 11 Rock type Vegetation cover Impermeable rocks- e.g. clay, granite, restrict percolation and encourage rapid runoff Little vegetation cover Lack of interception and root development to open up the soil. Rapid movement through the system. Deciduous trees in winter. Soil depth Thin soil- e.g. upland areas allow little infiltration Water stores Lack of lakes and backwater swamps Human activity Forests Urban development Agricultural practices Question catcher Deforestation Urban development creates impermeable concrete and tarmac surfaces and water quickly reaches the channel via storms drains. Low infiltration/percolation Poor agricultural practices – poor soil structure, trampling by animals. Permeable rocks-e.g. chalk and limestone, allow infiltration and percolation Forest and woodland intercept much rainfall, and root development encourages infiltration. More water lost to evaporation from vegetation surfaces. Deciduous trees in summer. Deeper soils provide a large soil store –e.g. slope bottoms and lowland areas. Lakes and backwater swamps act as water stores, and slow the movement to the channel. Reforestation Rural land uses intercept more precipitation and have more permeable land surfaces. High infiltration and percolation. Good agricultural practices which encourage soil aeration and protect the soil surface. 12 (i) Draw sketch hydrographs on Figures 1a and 1b to show the contrasting effects of each of the two rainfall periods on river discharge. (3 marks) (ii) Suggest reasons for the differences in the shapes of the hydrographs that you have drawn in 1(b)(i). (3 marks) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 13 Explain likely effects of the forest on river discharge. (5 marks) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Extra space -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Study Figure , which shows a storm hydrograph. 14 (i) determine the lag time for this event (1) (ii) estimate the contribution of surface run-off at the time of the peak discharge (1) Explain why the rising limb is steeper than the falling llimb. (4) How is the discharge of a river calculated? (2) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------State and give reasons for the relationship between run-off and vegetation within a drainage basin. (3 marks) Infiltration is the movement of water from the ground surface into the soil. Explain why rates of infiltration vary from place to place and from time to time. (6) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Extra space -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 15 How might human activity modify the drainage basin hydrological cycle? (7 marks) ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Extra space -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1- Graded assessment 1 Our first essay question: TB page X Physical factors are more important than human factors in affecting river discharge. Discuss this view. (15) 2- Answer ONE of the following essay questions: Examine the factors that influence river discharge. (15 marks) (PAST AS) Using a systems approach, explain how different components of the drainage basin hydrological cycle are linked. (15 marks) (PAST AS)