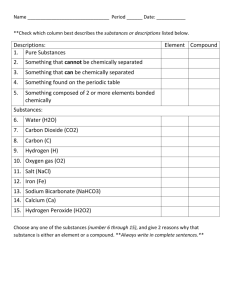
Worksheet
advertisement
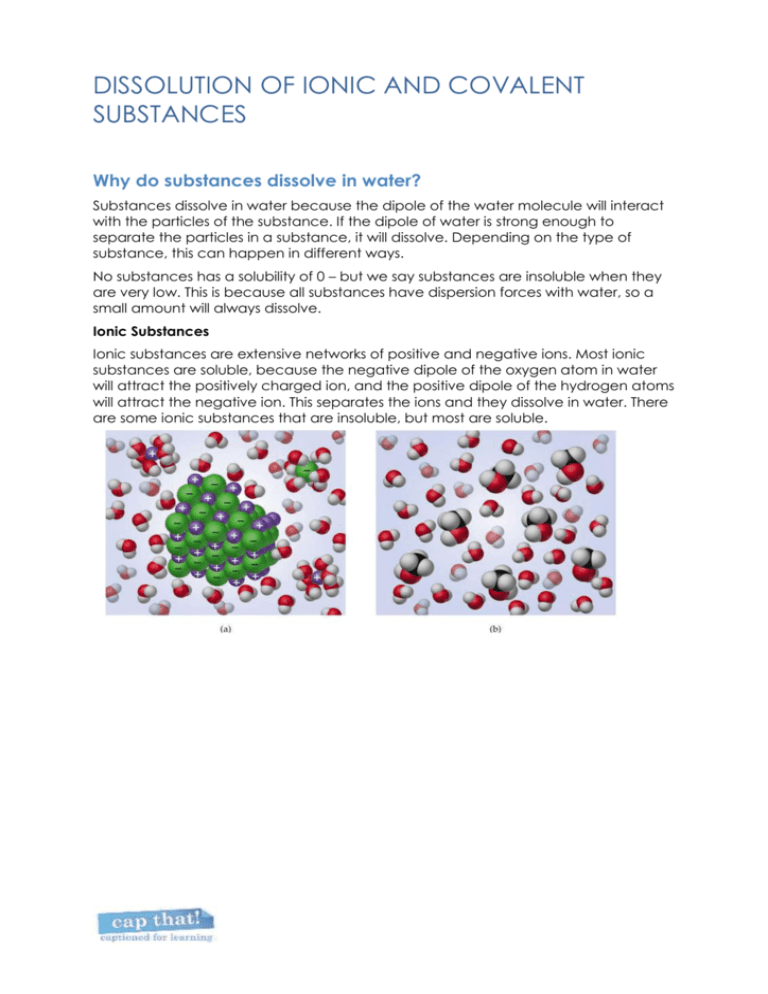
DISSOLUTION OF IONIC AND COVALENT SUBSTANCES Why do substances dissolve in water? Substances dissolve in water because the dipole of the water molecule will interact with the particles of the substance. If the dipole of water is strong enough to separate the particles in a substance, it will dissolve. Depending on the type of substance, this can happen in different ways. No substances has a solubility of 0 – but we say substances are insoluble when they are very low. This is because all substances have dispersion forces with water, so a small amount will always dissolve. Ionic Substances Ionic substances are extensive networks of positive and negative ions. Most ionic substances are soluble, because the negative dipole of the oxygen atom in water will attract the positively charged ion, and the positive dipole of the hydrogen atoms will attract the negative ion. This separates the ions and they dissolve in water. There are some ionic substances that are insoluble, but most are soluble. DISSOLUTION OF IONIC AND COVALENT SUBSTANCES Covalent Substances A covalent substance will dissolve in water if it has a dipole. For example, a glucose molecule has –OH groups. These –OH groups form hydrogen bonds with the –OH in water molecules, because they both have dipoles. This causes the glucose molecules to be dispersed throughout the water, and so they dissolve. Iodine is a covalent molecule that does not dissolve in water. Because it is a linear, symmetrical molecule, it has no dipole. The dipole in water has nothing to attract to to separate the molecules, and so iodine will not dissolve. This means that only covalent molecules with a dipole such as –OH will dissolve in water. Another type of covalent dissolution is ionisation. When hydrogen chloride gas is bubbled into water, the water actually reacts with it. The hydrogen is attracted to water to form hydronium, H3O+, and a negative chlorine atom forms. Covalent network substances do not dissolve because water is relatively weak compared to the strong network of covalent bonds holding them together. Questions 1. Are ionic or covalent substances more likely to dissolve in water? Why? 2. What is another name for a solution with water as the solvent? 3. Based on the shape of a molecule of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), is it soluble or insoluble? Why? 4. Explain why sand doesn’t dissolve in water. 5. Why does oxygen gas have a low solubility in water? 6. Sucrose will dissolve well in water because it can form hydrogen bonds with water.