Grade 4
advertisement
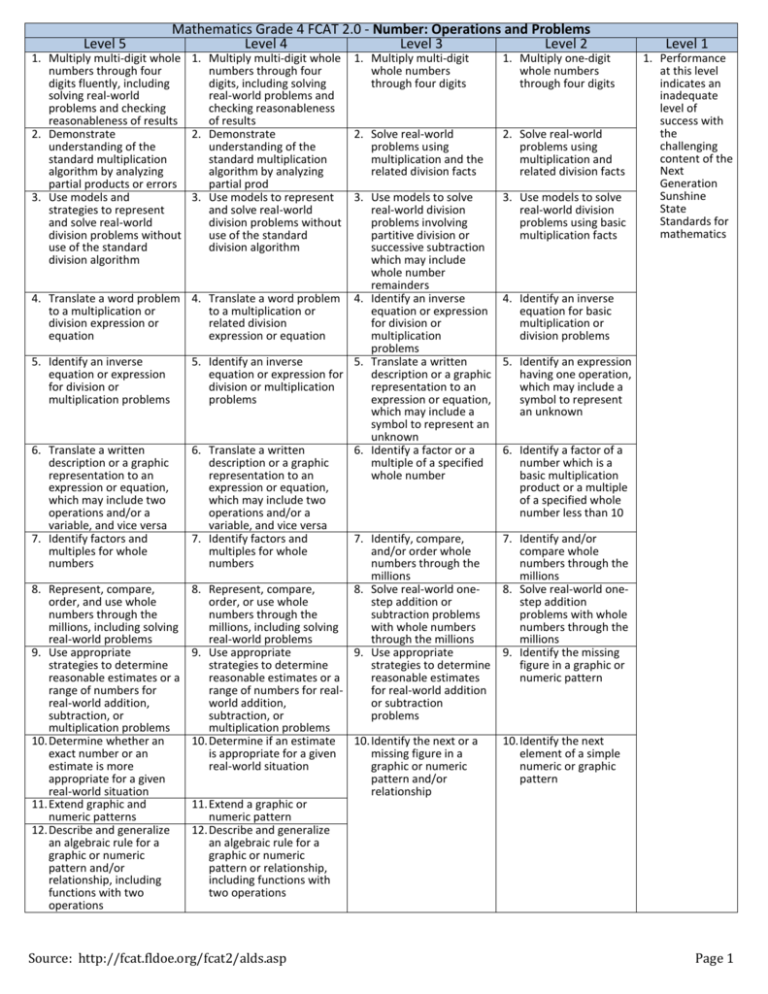
Level 5 Mathematics Grade 4 FCAT 2.0 - Number: Operations and Problems Level 4 Level 3 Level 2 1. Multiply multi-digit whole 1. Multiply multi-digit whole numbers through four numbers through four digits fluently, including digits, including solving solving real-world real-world problems and problems and checking checking reasonableness reasonableness of results of results 2. Demonstrate 2. Demonstrate understanding of the understanding of the standard multiplication standard multiplication algorithm by analyzing algorithm by analyzing partial products or errors partial prod 3. Use models and 3. Use models to represent strategies to represent and solve real-world and solve real-world division problems without division problems without use of the standard use of the standard division algorithm division algorithm 1. Multiply multi-digit whole numbers through four digits 1. Multiply one-digit whole numbers through four digits 2. Solve real-world problems using multiplication and the related division facts 2. Solve real-world problems using multiplication and related division facts 3. Use models to solve real-world division problems involving partitive division or successive subtraction which may include whole number remainders 4. Translate a word problem 4. Translate a word problem 4. Identify an inverse to a multiplication or to a multiplication or equation or expression division expression or related division for division or equation expression or equation multiplication problems 5. Identify an inverse 5. Identify an inverse 5. Translate a written equation or expression equation or expression for description or a graphic for division or division or multiplication representation to an multiplication problems problems expression or equation, which may include a symbol to represent an unknown 6. Translate a written 6. Translate a written 6. Identify a factor or a description or a graphic description or a graphic multiple of a specified representation to an representation to an whole number expression or equation, expression or equation, which may include two which may include two operations and/or a operations and/or a variable, and vice versa variable, and vice versa 7. Identify factors and 7. Identify factors and 7. Identify, compare, multiples for whole multiples for whole and/or order whole numbers numbers numbers through the millions 8. Represent, compare, 8. Represent, compare, 8. Solve real-world oneorder, and use whole order, or use whole step addition or numbers through the numbers through the subtraction problems millions, including solving millions, including solving with whole numbers real-world problems real-world problems through the millions 9. Use appropriate 9. Use appropriate 9. Use appropriate strategies to determine strategies to determine strategies to determine reasonable estimates or a reasonable estimates or a reasonable estimates range of numbers for range of numbers for realfor real-world addition real-world addition, world addition, or subtraction subtraction, or subtraction, or problems multiplication problems multiplication problems 10. Determine whether an 10. Determine if an estimate 10. Identify the next or a exact number or an is appropriate for a given missing figure in a estimate is more real-world situation graphic or numeric appropriate for a given pattern and/or real-world situation relationship 11. Extend graphic and 11. Extend a graphic or numeric patterns numeric pattern 12. Describe and generalize 12. Describe and generalize an algebraic rule for a an algebraic rule for a graphic or numeric graphic or numeric pattern and/or pattern or relationship, relationship, including including functions with functions with two two operations operations Source: http://fcat.fldoe.org/fcat2/alds.asp 3. Use models to solve real-world division problems using basic multiplication facts Level 1 1. Performance at this level indicates an inadequate level of success with the challenging content of the Next Generation Sunshine State Standards for mathematics 4. Identify an inverse equation for basic multiplication or division problems 5. Identify an expression having one operation, which may include a symbol to represent an unknown 6. Identify a factor of a number which is a basic multiplication product or a multiple of a specified whole number less than 10 7. Identify and/or compare whole numbers through the millions 8. Solve real-world onestep addition problems with whole numbers through the millions 9. Identify the missing figure in a graphic or numeric pattern 10. Identify the next element of a simple numeric or graphic pattern Page 1 Level 5 Mathematics Grade 4 FCAT 2.0 - Geometry and Measurement Level 4 Level 3 Level 2 Level 1 1. Describe and determine the 1. Describe and determine area of a figure or region the area of a figure or on a plane by counting region on a plane by units with or without grid counting units with or lines shown through the without grid lines shown figure or region through the figure or region 2. Justify the formula for the area of a rectangle 2. 3. Identify or describe a 3. situation that requires the use of the area formula in a real-world context 4. Determine the area of a rectangle or a composite shape composed from rectangles by multiplying the base times the height 4. 5. Use appropriate tools and square units to estimate and solve real-world area problems 5. 1. Determine the area 1. Determine the area 1. Performance of a rectangle or a of a rectangle or a at this level composite shape composite shape indicates an made only from made only from inadequate rectangles on a plane rectangles on a plane level of success by counting whole by counting whole with the units with or without units with grid lines challenging grid lines shown content of the through the rectangle Next or composite shape Generation Sunshine State Identify or describe a 2. Recognize that the 2. Recognize that the Standards for situation that requires the number of square number of square mathematics use of the area formula in units inside a units inside a a real-world context rectangle is equal to rectangle is equal to the base times the the base times the height height using a grid or concrete materials Determine the area of a 3. Recognize that area is 3. Determine the area rectangle or a composite measured in square of a rectangle by shape composed from units multiplying the base rectangles by multiplying times the height the base times the height when both dimensions are given on a grid or graphic Use appropriate tools and 4. Determine the area 4. Identify acute, square units to estimate of a rectangle by obtuse, and right and solve real-world area multiplying the base angles problems times the height when both dimensions are given Use properties of 5. Identify acute, 5. Identify the rectangles to deduce the obtuse, right, or benchmark angle of lengths of a side or sides straight angles 90° of a rectangle given the area and/or the lengths of the remaining sides of the rectangle Identify and classify angles 6. Identify benchmark 6. Identify a shape that using benchmark angle angles of 45°, 90°, is the result of one measurements that may 180°, or 360° rotation of the given include geometric shape notation 6. Use properties of 6. rectangles to deduce the lengths of a side or sides of a rectangle given the area and/or the lengths of the remaining sides of the rectangle 7. Identify and classify angles 7. Identify acute, obtuse, using benchmark angle right, or straight angles measurements that may include geometric notation 8. Identify acute, obtuse, right, or straight angles 9. Identify and describe a shape that is the result of one or more translations, reflections, or rotations of the given shape 10. Identify and build a threedimensional object from a two-dimensional representation of the object and vice versa 11. Identify two-dimensional views of a threedimensional object 8. Identify a shape that is the result of one or more translations, reflections, or rotations of the given shape 9. Identify and build a threedimensional object from a two-dimensional representation of the object 7. Identify a shape that is the result of one rotation or one reflection of the given shape 8. Identify a twodimensional front or top view of a given three-dimensional figure 9. Build a threedimensional figure from a twodimensional representation 10. Identify two-dimensional views of a threedimensional object Source: http://fcat.fldoe.org/fcat2/alds.asp Page 2 Mathematics Grade 4 FCAT 2.0 - Number: Base 10 and Fractions Level 4 Level 3 Level 2 Level 5 1. Identify place value of 1. Identify place value of 1. Identify place value of decimals through the decimals through the decimals through the thousandths place, and thousandths place, and thousandths place recognize the recognize the relationship between relationship between place values place values 2. Identify a decimal, 2. Identify a decimal, 2. Identify a decimal, fraction, or mixed fraction, or mixed fraction, or mixed number between two number between two number between two numbers numbers numbers 3. Identify decimals 3. and/or fractions from a graphic representation or a number line 4. Relate equivalent 4. fractions and decimals with and without models 5. Compare and order 5. fractions, mixed numbers, and decimals in the same or different forms 6. Estimate fractions, 6. mixed numbers, and/or decimals in the same or different forms in real-world situations 7. Generate equivalent fractions or simplify fractions to lowest terms 7. 8. Rename fractions as 8. mixed numbers, or vice versa 9. Relate halves, fourths, tenths, and hundredths to percents, and vice versa 1. Identify the place value of decimals through the hundredths place 2. Identify commonly used fractions or decimals (equivalent to halves or fourths only) between two consecutive numbers Identify decimals 3. Identify decimals 3. Identify decimals and/or fractions from a and/or fractions from a and/or fractions from graphic representation graphic representation a graphic or a number line or a number line representation Identify decimals that 4. Identify decimals that 4. Identify decimals that are equivalent to are equivalent to are equivalent to commonly used commonly used fractions (halves and fractions or mixed fractions or mixed fourths only) when numbers, including numbers, including given a graphic halves, fourths, tenths, halves, fourths, tenths, representation and hundredths and hundredths Compare and order 5. Compare and order 5. Compare decimals, fractions, mixed decimals that have the that have the same numbers, and decimals same place value place value, through in the same or different hundredths forms Estimate fractions, 6. Compare and order 6. Compare commonly mixed numbers, or commonly used used fractions decimals, in the same fractions or different forms, to the nearest half or whole when given a graphic representation of the numbers being estimated Generate equivalent 7. Estimate fractions, 7. Estimate fractions or fractions or simplify mixed numbers, or decimals, in the same fractions to lowest decimals, in the same form, to the nearest terms form, to the nearest whole when given a half or whole when graphic given a graphic representation of the representation of the numbers being numbers being estimated estimated Relate halves, fourths, 8. Identify an equivalent 8. Entify an equivalent tenths, and hundredths fraction when the fraction when the to percents, and vice given fraction is in given fraction is a versa simplest form commonly used fraction in simplest form 9. Identify the simplest 9. Relate halves to form of a given fraction percents and percents to halves 10. Identify the simplest form of a given fraction 11. Relate halves and fourths to percents and percents to halves or fourths Source: http://fcat.fldoe.org/fcat2/alds.asp Level 1 1. Performance at this level indicates an inadequate level of success with the challenging content of the Next Generation Sunshine State Standards for mathematics Page 3





