docx
advertisement

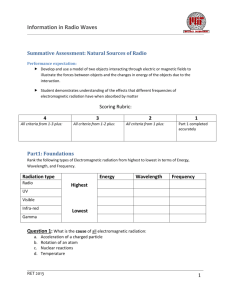
Information in Radio Waves Summative Assessment: Information Theory Performance expectation: Communicate technical information about how remote sensing uses the principles of wave behavior and wave interactions with matter to capture electromagnetic radiation providing information about the source and medium it travels through. Scoring Rubric: 4 3 2 1 All criteria from 1-3 plus: All criteria from 1-2 plus: All criteria from 1 plus: Part 1 completed accurately Ideas about remote sensing, the nature of the data used, and the information it provides are communicated accurately and are supported by evidence from the resource material. Discusses technical details about the structure of the atom resulting in spectral emission lines. Discusses details about the study of spectral emission lines observed in stars, nebula, and galaxies. primary differences between active and passive remote sensing are explained accurately Part 1: Demonstrate a basic understanding of the ways in which electromagnetic radiation can be modified in order to transfer information. Place the letter of each statement/example in the correct box for the type of EMR modification: a. Laboratory based measurements of atomic and molecular emission spectra can be used to match observed spectra from remote sources like stars and nebulae. b. AM radio stations contain much more interference or noise during the day due to the Sun’s natural variations in power output. c. Differences in phase can be used to correlate two signals from the same source and therefore achieve high angular resolution of a radio source. d. The ability of a satellite to send two separate signals on a carrier wave of the same frequency. Wavelength RET 2013 Amplitude Phase Polarization 1 Information in Radio Waves Part 2. Compare and Contrast Active and Passive remote sensing Active Both Passive Part 3: Describe how discoveries of the quantum mechanical model of atoms and molecules allowed for more information to be derived from remote observation of light sources in space. RET 2013 2 Information in Radio Waves Extension Case study: Pathways to the building blocks of life Instructions: Read one of the following articles about the discovery of a molecule in an interstellar dust cloud using radio astronomy methods. Consider how our study of information theory can be applied to the research project that was conducted. Write a reflection on the article and in your reflection provide an explanation of the following: A summary of the observational strategy Specifying, o The physical quantity being observed o How information was ‘encoded’ in the observed physical quantity Describe the discovery made Figure 1 Structure of cyanomethanimine, newly discovered in interstellar space. Credit: NRAO/AUI/NSF (http://www.nrao.edu/pr/2013/newchem/gra phics.shtml) News Publication (non-technical): https://public.nrao.edu/news/pressreleases/icy-cosmic-start-for-amino-acids-and-dna Research publication (Technical description): http://iopscience.iop.org/2041-8205/765/1/L9/article Astrophysical Journal Publication (peer reviewed academic journal): http://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1302/1302.0909.pdf Description of student team’s discovery: http://phys.org/news/2012-08-student-team-interstellar-molecule-summer.html You may submit your reflection as a google doc to turnitin for assessment. RET 2013 3