Food chains notes with gaps (2)
advertisement

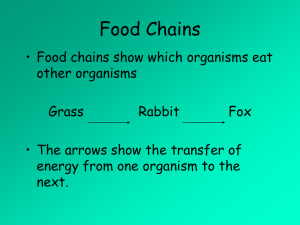
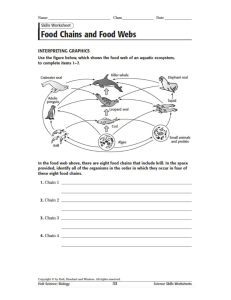
Food chains, food webs and food pyramids. Ecology is the study of the interactions of organisms with other organisms and with their ____________environment. Food chains and food webs are often used to show these producing interactions. detritivores Plants are known as producers because they use _________ and phytoplankton inorganic materials to produce organic compounds. This occurs chemical through the process of photosynthesis, where light energy is consumers converted into _____________ energy. Animals that fed upon primary plants are called _____________consumers while animals that eat energy other animals are known as secondary or tertiary____________. zooplankton Scavengers feed on dead organisms. Decomposers and food web ___________break down non-living organic matter into materials herbivore that are then available to enter the food chain as nutrients. consumers A food chain shows how each living organism gets its food. A sunlight __________ ___consists of many food chains which are interrelated trophic and divided into separate feeding groups or __________levels. The physical trophic level of an organism is usually its position in the energy flow predator pyramid of an ecosystem. The food pyramid helps us to visualise the fact that in an ecological system there need to be many _______________organisms at the bottom level of the pyramid in order to sustain fewer organisms at the top level. Energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next trophic level in a food chain and food web. When one organism consumes another, about 5 – 10% of the chemical energy is transferred to the ____________ . 90% of energy is lost as heat energy to the environment. A food chain shows how each living organism gets its food. A simple food chain starts with a producer. The producer is eaten by a primary consumer (_____________) which is eaten by a secondary consumer (carnivore). A tertiary consumer eats the secondary consumer. Most food chains have no more than four or five links so that the animals at the end of the chain can get sufficient____________. _________________are small microscopic producers found on the top layer of the ocean (where there is light) __________________are organisms that feed on phytoplankton. Some zooplankton are herbivores and others are carnivorous, feeding on smaller organisms. The sun is the ultimate source of energy for a food chain. The producers act as “translators” for this energy. Without them the ________________on earth could not use this energy. Use the organisms in the table below to construct a marine food web. Put the producers at the bottom and arrange the consumers in their different trophic levels from primary consumer to fifth order consumer. Organisms in a Marine Food Web Organisms Trophic Prey/food Predators/grazers level Phytoplankton Photosynthesis Krill and herbivorous zooplankton Herbivorous phytoplankton fish zooplankton Carnivorous krill Fish, blue whales and birds. zooplankton Krill phytoplankton Fish, blue whales, birds, penguins, leopard seal, other seals and baleen whale. Squid Krill, fish and herbivorous Fish, penguin, elephant seal, sperm zooplankton whale, and small toothed whale. Fish Krill and squid Penguin, leopard seal and elephant seal Other birds Krill and fish Leopard seal Other seals Krill and carnivorous Small toothed whale zooplankton Elephant seal Fish and squid Small toothed whale Leopard seal Krill, fish, other birds and small toothed whale penguins Penguin krill, fish and squid Leopard seal and small toothed whale Baleen whale krill Small toothed whale Small toothed Other seal, leopard seal, None whale elephant seal and baleen whale Sperm whale. Squid None 1. Fill in the “trophic level” column. Is it possible to be in more than one trophic level in a food web? 2. Which is the top predator in this community? 3. Where would humans fit in? 4. What might happen if krill was removed from the food web? 5. What might happen if the small-toothed whale was removed from the food web?

![S.7.SCA.5TH.TEST1.11-12 [5919] Student Class Date Soil](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006975137_1-fb9bddb56ef9a782b7ffb648a65768de-300x300.png)