Consumers?
advertisement

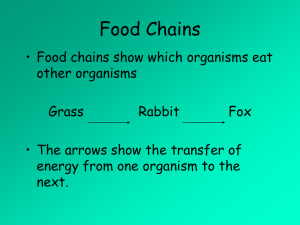
Topic 5: Ecology and evolution (16 hours) 5.2 Ecosystems and Communities March 27th/2011 Adapted from: Taylor, S. (2010). Ecosystems and Communities (Presentation). Science Video Resources. [Online] Wordpress. Retrieved from http://ibiology.net/ibdpbio/05-ecology-and-evolution/02-communities-ecosystems/ Ecology from Greek: οἶκος, "house“ λογία, "study of" http://gabiecologia.blogspot.com/ 5.1.1 Define species, habitat, population, community, ecosystem and ecology. 5.1.2 Distinguish between autotroph and heterotroph. 5.1.3 Distinguish between consumers, detritivores and saprotrophs. Consumers? Primary consumers? Secondary consumers? Producers? Autotrophs? Heterotrophs? Detritivores? Saprotrophs? http://dbg-englishclassroom.blogspot.com/2011/11/animals_17.html Consumers? Producers? Autotrophs? Heterotrophs? Detritivores? Saprotrophs? http://guides.wikinut.com/img/23pyri.8.frh-6iy/Classification-of-Organisms 5.1.6 Define trophic level. 5.1.4 Describe what is meant by a food chain, giving three examples, each with at least three linkages (four organisms). http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/esp/2001_gbio /folder_structure/ec/m3/s2/ecm3s2_6.htm 5.1.4 Describe what is meant by a food chain, giving three examples, each with at least three linkages (four organisms). 5.1.5 Describe what is meant by a food web. The diagram below shows an ocean food web. The arrows indicate the energy flow. [Source: www.ciesin.org/docs/011-558/fig4-3.gif] (a) Indicate the three producers of this food web. (1) (b) Identify the trophic level of each organism named below. On the diagram opposite, mark clearly the arrows of energy flow that support your choice. (i) Macrozooplankton (1) (ii) Weddell seal (1) (c) Determine the maximum percentage of energy that may reach emperor penguins from primary producers. 5.1.7 Deduce the trophic level of organisms in a food chain and a food web. (a) nanophytoplankton, bacteria, phytoplankton 1 All three needed to receive [1]. (b) (i) 1° / primary or 2° / secondary consumer (depending on chain marked) 1 (ii) 2° / secondary, 3° / tertiary or 4° / quaternary consumer (depending on chain marked) 1 Marks may not be given if the arrows are not marked on the diagram. (c) 1 / 2% 1 (d) more macrozooplankton / phytoplankton eaten / numbers fall; natural selection for small / camouflaged / fast growing / fast swimming plankton; competition between small fish is more intense; natural selection among small fish for faster swimming / more skill in feeding; more food for predators of small fish / named predator of small fish; natural selection among predators for feeding on small fish / not on other prey; changes in the gene pool / allele frequencies; 3 max [7] 5.1.8 Construct a food web containing up to 10 organisms, using appropriate information. 5.1.9 State that light is the initial energy source for almost all communities. 5.1.10 Explain the energy flow in a food chain. 5.1.11 State that energy transformations are never 100% efficient. 5.1.12 Explain reasons for the shape of pyramids of energy. http://www.nodvin.net/snhu/SCI219/demos/Chapte r_3/Chapter_03/Present/animations/32_2_1a.html 5.1.13 Explain that energy enters and leaves ecosystems, but nutrients must be recycled. 5.1.14 State that saprotrophic bacteria and fungi (decomposers) recycle nutrients.