Printable Version
advertisement

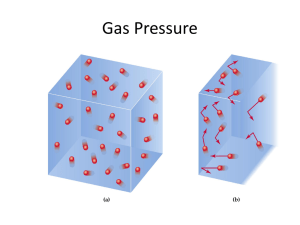
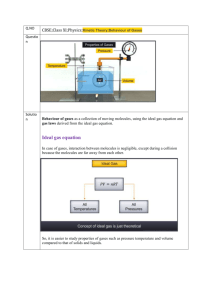
AP Chemistry Midterm Review: Gases 1 atm = 760 mmHg = 760 torr Ideal Gases are those in which come close to a low pressure at a high temperature. Gases begin to deviate from an “ideal” state when they are exposed to a low temperature and exhibit a high pressure. Gas Laws: The ideal gas law relates the variables of pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of gas within a closed system. The ideal gas law takes the form: PV = nRt______________________________________________________________________________ P = Pressure of the confined gas in atmospheres R = Gas Constant, 0.0821 L·atm/mol·K V = Volume of the confined gas, in liters T = Temperature in Kelvin n = Number of moles of gas________________ Boyles Law- The pressure exerted by a gas held at a constant temperature varies inversely with the volume of the gas. Gay-Lussac’s Law- If you increase the temperature of a container with fixed volume, the pressure inside the container will increase. Charles Law- When the temperature of a gas increases, the volume increases. Combined Gas Law- If the number of moles of gas are constant (No gas can get in or out) then we can combine the previous three gas laws. Calculating the Root Mean Square Speed of a Gas Calculating Kinetic Energy: Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures: Mole Fraction (X1)= Moles A/ Total Moles To calculate the actual partial pressure (In atm): P1= Total Pressure X (XA COMMON MISTAKES TO AVOID: 1. When using any gas laws, be sure you are dealing with gases! 2. In any laws be sure to express temperature in kevlin units. 3. Make sure your answer is reasonable. 4. Make sure your units cancel. 5. Be sure to use the correct molecular mass for those gases that exist as diatomic molecules. (BrINClHOF) 6. If value 22.4 L/mol is to be used, make sure that it is applied to a GAS at STP. AP Chemistry Midterm Review: Gases Recommended Free-Response questions to be completed for personal study: 1. A hydrogen gas sample is collected over water. The volume of the sample was 190.0 mL at 26°C, and the pressure in the room was 754 mm Hg. The vapor pressure of water at 26°C is 25.2 mm Hg. a. b. c. d. Calculate the number of moles of hydrogen in the sample. Calculate how many molecules of water vapor are present in the sample. Determine the density (in g/L) of the gas mixture. Determine the mole fraction of water. A sample containing 2/3 mole of potassium chlorate, KClO3, is heated until it decomposes to potassium chloride and oxygen gas. The oxygen is collected in an inverted bottle through the displacement of water. Answer the following questions using this information. 2. 3. 4. 5. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction. How many moles of oxygen gas are produced? The temperature and pressure of the sample are adjusted to STP. The volume of the sample is found to be slightly greater than 22.4 liters. Explain. An excess of sulfur is burned in the oxygen. Write a balanced chemical equation and calculate the number of moles of gas formed. Recommended Multiple-Choice questions to be completed for personal study: A sample of argon gas is sealed in a container. The volume of the container is doubled. If the pressure remains constant, what happens to the absolute temperature? A. B. C. D. E. It does not change. It is halved. It is doubled. It is squared. It cannot be predicted. A sealed, rigid container is filled with three ideal gases: A, B, and C. The partial pressure of each gas is known. The temperature and volume of the system are known. What additional information is needed to determine the masses of the gases in the container? A. B. C. D. E. the average distance traveled between molecular collisions the intermolecular forces the volume of the gas molecules the total pressure the molar masses of the gases Two balloons are at the same temperature and pressure. One contains 14 g of nitrogen and the other contains 20.0 g of argon. Pick the false statement from the following list. A. The density of the nitrogen sample is less than the density of the argon sample. B. C. D. E. The average speed of the nitrogen molecules is the same as the average speed of the argon molecules. The average kinetic energy of the nitrogen molecules is the same as the average kinetic energy of the argon molecules. The volume of the nitrogen container is the same as the volume of the argon container. The number of molecules in the nitrogen container is the same as the number of atoms in the argon container. An experiment to determine the molecular mass of a gas begins by heating a solid to produce a gaseous product. The gas passes through a tube and displaces water in an inverted, water-filled bottle. Which of the following necessary items may be determined after the experiment is completed? A. B. C. D. E. vapor pressure of water temperature of the displaced water barometric pressure in the room mass of the solid used volume of the displaced water The true volume of a particular real gas is larger than that calculated from the ideal gas equation. This occurs because the ideal gas equation does NOT correct for: A. B. C. D. the attraction between the molecules the shape of the molecules the volume of the molecules the mass of the molecules AP Chemistry Midterm Review: Gases E. the speed the molecules are moving Aluminum metal reacts with HCl to produce aluminum chloride and hydrogen gas. How many grams of aluminum metal must be added to an excess of HCl to produce 33.6 L of hydrogen gas, if the gas is at STP? A. B. C. D. E. 18.0 g 35.0 g 27.0 g 4.50 g 9.00 g A reaction produces a gaseous mixture of carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and water vapor. After one reaction, the mixture was analyzed and found to contain 0.60 mol of carbon dioxide, 0.30 mol of carbon monoxide, and 0.10 mol of water vapor. If the total pressure of the mixture was 0.80 atm, what was the partial pressure of the carbon monoxide? A. B. C. D. E. B. C. D. E. F. 760 mm Hg 41 mm Hg 715 mm Hg 797 mm Hg 756 mm Hg A sample of oxygen gas with a volume of 8.00 L at 127°C and 775 mm Hg is heated until it expands to a volume of 20.00 L. Determine the final temperature of the oxygen gas, if the pressure remains constant. A. B. C. D. E. 727°C 318°C 1000°C 160°C 45°C The average kinetic energy of nitrogen molecules changes by what factor when the temperature is increased from 30°C to 60°C? 0.080 atm 0.34 atm 0.13 atm 0.24 atm 0.48 atm A sample of methane gas was collected over water at 35°C. The sample was found to have a total pressure of 756 mm Hg. Determine the partial pressure of the methane gas in the sample (vapor pressure of water at 35°C is 41 mm Hg). _____________________________________________________________________________________ Free-Response Answers 1A.0.00742 mol H2 1B. 1.55 × 1020 molecules 1C. 0.103 g/L 1D. 0.0335 2A. 2 KClO3(s) → 2 KCl(s) + 3 O2(g) 2B. 2/3 mole KClO3) (3 moles O2/2 moles KClO3) = 1 mole O2 2C. At STP the volume of 1 mole of O2 should be 22.4 liters. The volume is greater because oxygen was not the only gas in the sample. Water vapor was present. The presence of the additional gas leads to a larger volume. 2D. 2 S(s) + 3 O2(g) → 2 SO3(g), (1 mole O2) (2 mole SO3/3 mole O2) = 2/3 mole SO2 2E. SO2 + H2O → H2SO3 Multiple Choice Answers: 1.C 2.E 3.B 4.A 5.C 6.C 7.D 8.C 9.A 10.A AP Chemistry Midterm Review: Gases NOTES: