Medium-term-BTEC-sci-principles-unit
advertisement
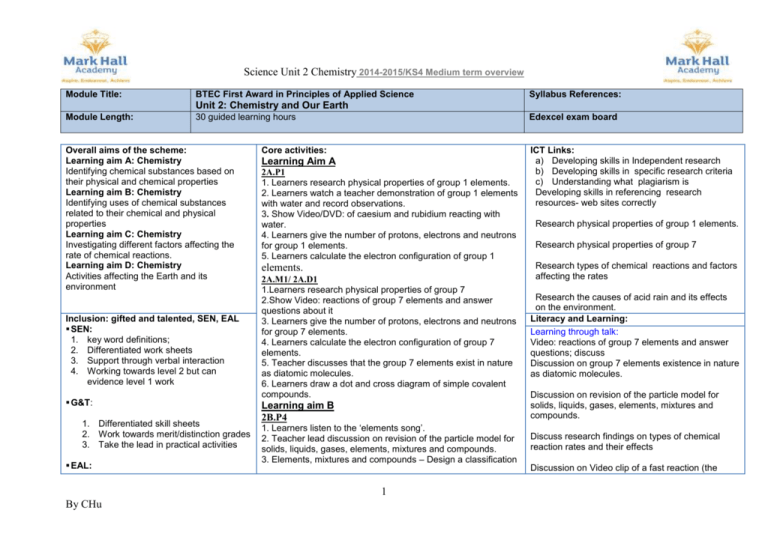
Science Unit 2 Chemistry 2014-2015/KS4 Medium term overview Module Title: BTEC First Award in Principles of Applied Science Syllabus References: Unit 2: Chemistry and Our Earth Module Length: Overall aims of the scheme: Learning aim A: Chemistry Identifying chemical substances based on their physical and chemical properties Learning aim B: Chemistry Identifying uses of chemical substances related to their chemical and physical properties Learning aim C: Chemistry Investigating different factors affecting the rate of chemical reactions. Learning aim D: Chemistry Activities affecting the Earth and its environment Inclusion: gifted and talented, SEN, EAL SEN: 1. key word definitions; 2. Differentiated work sheets 3. Support through verbal interaction 4. Working towards level 2 but can evidence level 1 work G&T: 1. Differentiated skill sheets 2. Work towards merit/distinction grades 3. Take the lead in practical activities EAL: Edexcel exam board 30 guided learning hours Core activities: Learning Aim A 2A.P1 1. Learners research physical properties of group 1 elements. 2. Learners watch a teacher demonstration of group 1 elements with water and record observations. 3. Show Video/DVD: of caesium and rubidium reacting with water. 4. Learners give the number of protons, electrons and neutrons for group 1 elements. 5. Learners calculate the electron configuration of group 1 elements. 2A.M1/ 2A.D1 1.Learners research physical properties of group 7 2.Show Video: reactions of group 7 elements and answer questions about it 3. Learners give the number of protons, electrons and neutrons for group 7 elements. 4. Learners calculate the electron configuration of group 7 elements. 5. Teacher discusses that the group 7 elements exist in nature as diatomic molecules. 6. Learners draw a dot and cross diagram of simple covalent compounds. Learning aim B 2B.P4 1. Learners listen to the ‘elements song’. 2. Teacher lead discussion on revision of the particle model for solids, liquids, gases, elements, mixtures and compounds. 3. Elements, mixtures and compounds – Design a classification 1 By CHu ICT Links: a) Developing skills in Independent research b) Developing skills in specific research criteria c) Understanding what plagiarism is Developing skills in referencing research resources- web sites correctly Research physical properties of group 1 elements. Research physical properties of group 7 Research types of chemical reactions and factors affecting the rates Research the causes of acid rain and its effects on the environment. Literacy and Learning: Learning through talk: Video: reactions of group 7 elements and answer questions; discuss Discussion on group 7 elements existence in nature as diatomic molecules. Discussion on revision of the particle model for solids, liquids, gases, elements, mixtures and compounds. Discuss research findings on types of chemical reaction rates and their effects Discussion on Video clip of a fast reaction (the 1. Use of visual aids- PP slides, images, practical work 2. Emphasis on key words use and meanings 3. Availability of a dictionary 4. Use of Google translate PP: 1. Regular assessment of student progress 2. Encouragement in class activities LAC: 1. Use of Collins differentiated work tasks available Boys underachievement: 1. Encourage full interaction in activities 2. Identify roles in group work 3. Peer supporting activities key. 4. Teacher led discussion on physical properties. 5.Learners examine the materials with the best physical properties to make a coffee cup 2B.P4; 2B.M4; 2B.D3 1. Teacher gives input on uses of chemicals based on chemical properties and links back to work on groups 1 and 7. 2. Learners research chemicals in unit content and their uses and produce a poster to present the information. Learning aim C 1, Teacher gives input on writing word equations. 2. Learners write simple word equations based on descriptions of chemical reactions. They label reactants and products. 3. Teacher gives input on writing balanced equations. 4. Learners write simple balanced equations based on word equations. 5. Learners research types of reactions and produce a poster to present the different types. 6. Teacher gives input on reversible and irreversible reactions. 7. Learners research some examples of reversible and irreversible reactions. 1. Learners watch a video clip of a fast reaction (the Hindenburg disaster) and then look at some slow reactions, e.g. rusting. Learners then answer questions on the differences between the reactions. 2. Teacher explains how to calculate reaction rate using graphs. 3. Teacher gives information on factors affecting rate. 4.Teacher explains how to calculate 2C.M5 Learners investigate effect of concentration on the reaction between magnesium ribbon and hydrochloric acid. 2C.M5 1. Learners investigate effect of temperature on the reaction 2 By CHu Discussion on the collision theory Discussion on concepts of yield and atom economy Discuss and collaborate on producing ideas about the ways that humans affect the Earth Small/large group activities – practical investigations- developing team work Use of roles within groups 2C.P7 2C.P6 Assessment for Learning Opportunities: 1. Students have targets which they know and understand 2. Students know regularly at what level they are working in relation to these targets 3. Students know how they can improve their working at level so as to achieve their targets 4. The students have access to level/grade descriptors, e.g. in their books or on classroom walls, and they understand them, and there is reference to them within lessons Hindenburg disaster) and then look at some slow reactions, e.g. rusting comparing them Learning from text: Use research and put information into own words Use of text books for research- students to gather appropriate information they required Use of library books Use of Principles Of science text books Learning through writing: Presenting work as: reports, leaflets, newspaper articles, posters Numeracy Links: Calculating the number of protons, electrons and neutrons for group 1 and 7 elements writing word equations then symbol equations then balancing them Calculating averages from practical results from chemical reaction rates Construct graphs lined/ bar/ curves from above results Constant temperature 5. There are exemplars of good work available of different types which we can show to students and which, in particular, illustrate level/grade requirements 6. Schemes of work/lesson plans all make specific reference to AFL 7. Learning objectives are differentiated and levelled/graded 8. Lesson observations show that each teacher is in “AFL mode”, i.e. always discussing their work with students and helping them see how they can improve in terms of level/grade descriptors and achieving targets. 9. There is evidence that teachers have the skill of asking the students the type of questions, both individually and to the whole class, that enables them to understand how they can progress, and where relevant lead them to see how they can move on to achieve higher levels/grades. 10. There is evidence that both peer and self assessment relating to the learning objectives are occurring in lessons as appropriate 11. There is the evidence of AFL comments in the marking of students’ work. 12. AFL is also being used to adjust schemes of work, lesson plans and overall teaching in the light of analysis of the ascertained responses of students between sodium thiosulphate and hydrochloric acid. 2. Learners investigate effect of catalyst on the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. 3. Teacher explanation of collision theory. 4. Learners use collision theory to explain their practical observations. Using the equation: The amount of energy transferred in a certain time as power. Measured in watts (W) (1W = 1j /s) Concepts of yield and atom economy. Earth’s atmospheric timeline gas levels 2C.P7; 2C.M6; 2C.D4 1. Teacher leads discussion on concepts of yield and atom economy. 2. Learners research Haber process. 3. Learners use collision theory to explain how the reaction between chlorine and sodium bromide can be speeded up. Cross-Curricular Links: Learning aim D 2D.P9 Local environment can be managed in a sustainable way. 1. Teacher leads discussion on tectonic plates using pictures of the effects of continental drift. 2. Learners watch videos of natural disasters as a lead into a teacher-led discussion. 3. Learners produce a newspaper article on earthquakes. 4. Learners produce a set of instructions for people to follow in the event of an earthquake or tsunami. 2D.P9 Teacher gives input on evolution of atmosphere. Learners will draw a poster of the Earth’s atmospheric timeline. Geography: looking at different areas within the country, then different countries on tectonic plates, volcanic eruptions/ earthquakes Art/Design Making a model of the atom Drama role play e.g. the particle model and the different properties of gases liquids and solids History local environment –management in a sustainable way- past present and future 2D.P8; 2D.M7 1.Learners collaborate on producing ideas about elements that can be extracted from the Earth, sea and air 2. Learners research the causes of acid rain and its effects on the environment. 2D.D5 Student Leadership Opportunities: . Group work roles- manager/ leader during practical activities Organising a small group for a presentation to the class on 1. Learners collaborate on producing ideas about the ways that humans affect the Earth. 2. Learners choose an environmentally damaging activity and prepare a leaflet explaining how individuals can reduce the impact of this activity. 3. Teacher gives explanation on what is ‘sustainable living’? 3 By CHu WrL / Enterprise: Extension/Enrichment Opportunities: Working at the higher distinction grades, to evaluate, synthesise learning 4. Learners produce a report containing suggestions on how the council and the local environment can be managed in a sustainable way. 5. Learners produce a concept map of the topics covered in Unit 2. 2D.D5 Responsible industry – Learners write an article about the likely environmental impact of a power station and how the impacts can be minimised. Week Learning Objectives 1 2A.P1 Describe trends in the physical and chemical properties of group 1 and 7 elements. 2A.M1, D1 explain and investigate the trends of group 1 and 7 elements explain what the reactivity series and displacement reactions are related to observations from investigations Natural disasters and effects on living species; Newspaper article on earthquakes. Acid rain and its effects on the environment. as man-made effects Responsible industry –an article about the likely environmental impact of a power station and how the impacts can be minimised. Tasks Annotate a periodic table group 1 and 7 elements State the meanings of physical and chemical properties and what a trend is Research the physical properties of group 1 and group 7 elements Watch demonstration of group 1 elements reacting with water and record observations about their physical properties and how they react. Investigate displacement reactions of group 7 and complete a full laboratory report Use your observations of the reaction of group 1 elements with water to describe the chemical properties of the group. Watch Video clip of caesium and rubidium reacting with water and describe and record observations. Draw a table with the numbers of protons, electrons and neutrons for group 1 elements. Calculate and draw the electron configuration of lithium, sodium and potassium, describe your method. Watch a Video Showing the reactivity of group 7 elements and answer questions about it. Draw a table with the number of protons, electrons and neutrons for group 7 elements. Calculate and draw the electron configuration of fluorine and 4 By CHu SMSC Differentiation A1.1 describe and Classify group 1 and 7 elements based on their physical properties Evidence of classification and categorising at least 2 elements from group 2 (based on their physical properties) Boiling points, melting points electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, solubility in water and non-polar viscosity (viscosity) M1.D1 Students to discuss the group 1 & 7 elements according to their melting, boiling points conductivity etc trends. Draw a table and identify any trends related to the elements position on the periodic table. Students to write a paragraph to explain this Research and interpret data and present information, developing an argument and drawing a conclusion using scientific technical and mathematical language conventions and symbols to apply the learning from chlorine. State how many electrons are found in the outer shell of group 1 and group 7 elements Describe trends in the physical properties of group 1 and group 7 elements (including melting, boiling points and electrical conductivity) Describe the trends in the chemical properties of group 1 and group 7 elements. Imagine you are a Head of Science in a school. Write a safety leaflet for technicians explaining which group 1 and group 7 elements may be used in school and which may not. Explain why those banned may not be used. Explain the trends in the chemical properties of group 1 and group 7 elements in terms of electronic structure and the forces of attraction between sub-atomic particles. 2 2A. P2 Compare properties of ionic and covalent substances. 2A.P3 Draw dot-and-cross diagrams of simple ionic and covalent substances 3 2A.M2 Explain the properties of ionic and covalent substances Recall unit 1 work on the structure of an atom Research and define the key words atom, molecule, ion, ionic bonding and covalent bonding 1A.2 Discuss then list the common properties of ionic and covalent 1. describe four typical properties of ionic substances substances. 2. Describe four typical properties of covalent Describe how to classify a substance as ionic or covalent present as a table. substances Complete investigations testing substances for solubility in water, conduction of electricity and the effect of temperature, Complete a laboratory report on your findings. Write a conclusion for the results from the investigation, identifying ionic and covalent substances by relating the results to the properties of ionic and covalent substances. a. Draw dot-and-cross diagrams for ionic bonding in sodium 1A.3 1. provide data through practical investigations chloride, magnesium oxide, and magnesium chloride. 2. Classify at least six different substances as being b. Draw dot-and-cross diagrams for the covalent compounds methane, either ionic or covalent in nature water and carbon dioxide Extend your conclusion to investigation in task 2 to explain the M2, M3, .D2 different properties of ionic and covalent compounds. Students need to research and Use these diagrams to Add notes to the dot and cross diagrams drawn for task 2 to work out the formula for methane, water, chlorine, explain how the bonds have formed, including references to the carbon dioxide, hydrogen and oxygen. Then evaluate number of electrons in the outer shell. the formation of ionic and covalent substances 5 By CHu the lesson. To do this, students need to research and complete a set of instructions to explain the electron configurations and how to complete them. Then research how group 7 elements exist as diatomic molecules following the investigations 2A.M3 Explain the formation of ionic and covalent substances 2A.D2 apply knowledge of ionic and covalent substances 4 2B.P4 Describe how chemical substances are used based on their physical properties. Applying learning to plan a scientific test that Draw dot and cross diagrams for ammonia and sodium chloride Use these diagrams to work out the formula for chlorine, hydrogen can be used in industry to separate immiscible liquids and miscible liquids and oxygen Research and draw diagrams of silicon dioxide, diamond and graphite and explain how these form Sodium chloride can be used to produce chlorine. Explain how this is done and explain it using ideas about the properties of ionic skills/literacy/comprehension and thinking skills substances. Students to interpret the properties to explain and Research uses of silicon dioxide, diamonds and graphite. Relate relate the bonding to the uses in all bonding types. To these uses to structure, bonding and properties of these covalent substance Recall KS3 work on the particle model for solids, liquids, gases, elements, mixtures and compounds Complete a poster showing the particle model for solids, liquids and gases and giving the physical properties of each. Use/equipment Your chemical product Fire extinguisher Carbon dioxide Electrical wires Copper Welding Argon Lubricant Graphite Abrasive Silicon dioxide Paint Titanium dioxide Dehumidifier Calcium chloride Air bags Sodium azide Tools Iron Computer circuits Silicon To help the team find out more about some chemical products complete a table stating the physical properties a. Produce an information booklet/leaflet for each of four of those in the table b. Using appropriate websites and/or textbooks and/or chemical 6 By CHu do this they need to write an extended piece of work, added to activity 5 above 1B.4 1.Discuss different types of physical properties of some common chemical substances (Can complete a discussion sheet to show this evidence) 2. Provide evidence of a brief description of the above substances data books, research the following for each of the chemical products you chose: chemical properties –chemical reactivity; type of chemical bonding and structure; outer electron arrangement Physical properties – thermal and electrical conductivity; melting and boiling points; solubility in different solvents; viscosity etc. Other uses and applications 2B.P5 Describe chemical properties of chemical substances. 5 2B.M4 Explain how physical and chemical properties of chemical substances make them suitable for their uses. 2B.D3 Assess the suitability of different types of substance for a specified use. 6 2C.P6/P7 Identify the number and types of atoms in balanced chemical reactions. Explain how physical and chemical properties of chemical substances make the following suitable for their uses: a. sodium azide in airbags; b. argon in welding; c. silicon in computer–chip technology; d. carbon dioxide in fire extinguishers. Investigate the viscosity of different motor oils and write a lab report. Research the properties of motor oil and complete a worksheet your company could use to explain to the importance of keeping their car engine oil topped up. Extend your engine oil research further to give more technical information including boiling point and viscosity and relate these to the running temperature of a car engine and the conditions in which the engine is operating. Complete assessment activity 2.4 from Pearson Principles of Applied Science: Imagine you are a chemist working for a company producing rocket fuel. Assess and write a fully referenced report on the suitability of hydrogen, hydrazine and gunpowder as rocket fuels. Say which one you would recommend and justify your choice with reference to their chemical and physical properties. Research and describe the factors that affect rates of chemical reactions. a. Investigate the effect of temperature on the reaction between sodium thiosulphate and hydrochloric acid. Describe how increasing temperature changes the rate of reaction. b. Write the word and symbol equations for the reaction then identify the types and numbers of each atom present in the products and in the reactants. Give the state of each substance 7 By CHu 1B.5 1. Evidenced by practical work or secondary data provided or research, looking at chemical changes involving common substances 2. Must show evidence of classification of at least two changes that are chemical (e.g. interaction with water) D3 Complete an information leaflet to give to customers looking at buying oil for their car Complete a formal Witten report with audience and purpose 7 2C.P7 Describe the factors that can affect the rates of chemical reactions. involved. a. Investigate effect of catalyst solid manganese dioxide on the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. b. Describe how the catalyst changes the rate of reaction. Write the word and symbol equations for the reaction then identify the types and numbers of each atom present in the products and in the reactants. Give the state of each substance involved. a. Carry out an investigation to find out how the rate of reaction between calcium carbonate or magnesium and hydrochloric acid is affected by changing the concentration of acid. Plot a graph of your results. Describe how concentration changes the rate of reaction. Write the word and symbol equations for the reaction then identify the types and numbers of each atom present in the products and in the reactants. Give the state of each substance involved. For the range of chemical reactions investigated in task 1 identify the reactants and products, state if the reactions are reversible or irreversible. Identify if the reactants and products are solids liquids, gases or in aqueous solution. (include decomposition, displacement, combustion and neutralisation reactions 1C. 6 1. Discuss factors affecting the rates of reaction, to establish what the possible factors could be (Can complete a discussion sheet to show this evidence and after carrying out some practical investigations. Can be reported in the form of a table) 2. Must describe these factors, covering effects of concentration, particle size, temperature, the presence of catalyst on the rates of chemical reactions, and show that e.g. increasing the temperature increases the rate of reaction 1C.7 1. Can be given (at least three) balanced equations 2. They must identify the reactants and products in each equations 3. They must include their symbols, and state if the reaction is reversible 8 By CHu 8 9 10 2C.M5, Explain plan complete an investigation independently to look at effects of catalyst a solid manganese dioxide on the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. Identify the reactants and products state if the reactions are reversible or irreversible Research and write a report on the industrial manufacture of bromine, the hydration of ethene and the Contact process. 2C.M6 explain writing the word and symbol equations for the reaction then identifying the types numbers of each atom in the products and reactants, state if they are gases or in aqueous Solution and if the reaction is decomposition, displacement combustion or neutralisation reaction Research the Haber process and describe it. Include an explanation of the terms ‘yield’ and ‘atom economy’ in relation to this process 2C.D4 Apply learning to look at the factors that could change the rate of reaction in each case and Explain why they affect the rate by considering collision theory. To analyse how different factors affect the rate and yield of an industrial reaction imagine that you are a chemist working for a company manufacturing ammonia. Your line manager wants to cut the cost of the Haber process by doing the reaction at 200 0C and 100 atm and also use less catalyst. 2D.P8 Describe the human activities that affect the Earth and its environment Plan and Investigate and Researching how limestone is quarried, copper extracted, oil For each process include and explain the equations. Describe the factors that could change the rate of reaction in each case and explain why they affect the rate by considering collision theory. Write a detailed report to explain why this would not be a good idea by analysing how different factors affect the rate of production and yield of ammonia Research and list human activities that affect the environment. Research and list natural factors that have changed the surface of our Earth and its atmosphere 9 By CHu D4 Research examples of rates and yields in industry. Relate these to the substance of ammonia. Outline in a budget report how the manufactures can be cost effective 1D.8 1. Must identify at least two human activities that have environmental consequences (obtaining materials from the sea, land, air (e.g. coal natural gas oil, metal ores, salt, nitrogen, oxygen) extracted, nitrogen and oxygen extracted, biofuels grown and nuclear energy generated. State ways in which these activities lead to changes in the environment 2D.M7 Discuss the extent to which human activity has changed the environment. In comparison to natural activity Explain natural factors that have changed the surface and atmosphere of the Earth by; Research and describe the causes of volcanic eruptions and how this may change the Earth’s crust and its atmosphere. Identify some of the effects of a named volcanic eruption. Research two mountain ranges explain how they have been formed by the movement of tectonic plates, (the Andes and the Himalayas.) Research and describe the causes of earthquakes Identify how this may change the Earth’s crust and affect the environment. Describe some of the effects of a the 2011 earthquake near Japan that led to problems in the Fukushima Explain on a poster a timeline of changes Earth’s composition, atmosphere and identify natural and human activities that have led to these changes Describe the human activities that affect the environment by; a. Researching how limestone is quarried, copper extracted, oil extracted, nitrogen and oxygen extracted, biofuels grown and nuclear energy generated b. State ways in which these activities lead to changes in the environment Describe natural factors that have changed the surface and atmosphere of the Earth by; a. Research and describe the causes of volcanic eruptions and how this may change the Earth’s crust and its atmosphere. b. Identify some of the effects of a named volcanic eruption. c. Research two mountain ranges and explain how they have been formed by the movement of tectonic plates, for examples the Andes and the Himalayas. d. Research and describe the causes of earthquakes e. Identify how this may change the Earth’s crust and affect the environment. f. Describe some of the effects of a the 2011 earthquake near Japan that led to problems in the Fukushima Draw a poster showing the timeline of changes to the composition of Earth’s atmosphere and identify the natural and human activities that have led to these changes. 10 By CHu 11 2D.P9 Describe the natural factors that have changed the surface and atmosphere of the Earth. 1D.9 Research and describe the problems facing the Fukushima region of Japan following the 2011 earthquake. Identify the natural and human activities that led to the problems. 12 2D.D5 Apply learning to Evaluate possible solutions to changes in the environment, occurring from natural or human activity by: Evaluating if the need for copper can be met by recycling. Explain how the copper extraction could affect the local and global environment and explain steps the company will take to minimise these effects. Explain at least two methods of reducing the environmental impact of copper extraction and the burning of fossil fuels used in the process. Evaluate how successful these steps are likely to be. Discuss whether human or natural activities have had most impact on the region and write down and explain your conclusion Imagine you are an environmental scientist working for a copper extraction company building a new extraction plant. Environmental campaigners have been writing to the newspaper describing how damaging the plant could be. You have been asked to write an article for a newspaper to make a case for why the plant should be built. Evaluate if the need for copper can be met by recycling. Explain how the copper extraction could affect the local and global environment and explain steps the company will take to minimise these effects. You must explain at least two methods of reducing the environmental impact of copper extraction and the burning of fossil fuels used in the process. Evaluate how successful these steps are likely to be. 11 By CHu Must identify at least two natural factors that have environmental consequences ( e.g. volcanic eruption or movement of tectonic plates) 2D.5 Research data from surveys conducted on recycling rates, in the UK and another country of your choice. Compare the two sets of data, and evaluate; include past and recent data for your recycling, outline improvements







