6th Math Ecofriendly
advertisement

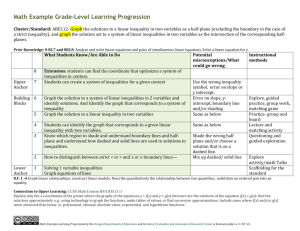
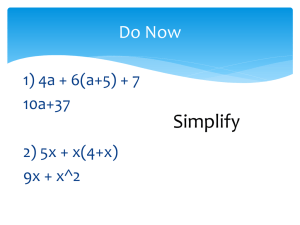
Unit Title: Eco-Friendly Two Weeks Math Lesson Plan Teacher: 6th Grade Math Teacher Grade: STEM Math IB Lesson Title: Environmental Research: Data Collection, Analysis, and Research STRANDS Equations and Expressions LESSON OVERVIEW Summary of the task, challenge, investigation, career-related scenario, problem, or community link. Students will be exploring inequalities. Through investigations and discussions, students will learn how to reason through inequalities, write inequalities for a given situation, and solve inequalities. Then students will look onto the 7th grade standards through solving two-step equations. During the project, students will take this knowledge to assist them in simplifying expressions and equations while using authentic data. Math will connect with Science through using the data collected during our watershed study. Math will collect to English Language Arts through writing written analysis of the data collected. Finally, Math and Social Studies will connect through using inequalities that involve topics such as elections and populations. Hook for the week unit or supplemental resources used throughout the week. (PBL scenarios, video clips, websites, literature) MOTIVATOR Our STEM Fair project has our students engineering recycling containers for our school. The video titled “Why Green Schools?” explains the need for schools to move towards being green schools. This will give the student a glimpse of where we are going at the end of the unit. DAY Objectives (I can….) Materials & Resources Instructional Procedures Differentiated Instruction Assessment 1 I can explain an inequality. Reasoning Through Inequalities Warm Up (See Resource Folder) Essential Question: What are inequalities? Reasoning Through Inequalities Guided Notes (See Resource Folder) Teaching Strategy: Have students open up the Guided Notes (See Resource Folder) for this lesson. This reviews with students the key vocabulary and symbols. Go through these notes with students. Model and discuss with students how to answer these questions. Set: Students will complete the Reasoning Through Inequalities Warm-Up. When all the students have completed the warm-up, ask the students to discuss this with their table groups and then discuss this as an entire group. Next, have students complete the Reasoning Through Inequalities Partner Practice (See Resource Folder) as a table group. Ask students assessing and advancing questions as they complete these practice problems. Discuss students responses to these questions. Reasoning Through Inequalities Partner Practice Finally, have students complete the Reasoning Through Inequalities Individual (See Resource Practice (See Resource Folder). Ask students assessing and advancing questions as Folder) they complete these practice problems. Reasoning Through Inequalities Independent Practice (See Resource Folder) Reasoning Through Inequalities Ticket Out the Door (See Resource Summarizing Strategy: Have students complete the ticket out the door. Differentiated Instruction – Remediation: Peer Tutoring Grouping Guided Notes Differentiated Instruction – Enrichment: Have students create inequalities for every day situations. Formative Assessment: Informal Observation Ticket out the Door Guided Notes Partner Practice Independent Work Summative Assessment: Homework Folder) Materials for Differentiated Instruction – Remediation: Guided Notes 2 I can write an inequality to describe a given situation. Writing Inequalities Warm Up (See Resource Folder) Writing Inequalities Guided Notes (See Resource Folder) Materials for Differentiated Instruction – Remediation: Guided Notes Essential Question: How do I write an inequality for a given situation? Set: Watch the LearnZillion video on writing inequalities. Peer Tutoring Teaching Strategy: Explain to the students that inequalities can be used to describe a situation. They are much like equations. The solution set is just larger. Ask students to fill out a chart similar to the one below. Have students identify key terms in a word problem that will tell them what operation they will be using. Addition Subtraction Multiplication Differentiated Instruction – Remediation: Division Ask students to fill out a chart similar to the one below. Have students identify key terms in a word problem that will tell them what inequality sign they will be using. Grouping Guided Notes Differentiated Instruction – Enrichment: Have students create inequalities for every day situations. Formative Assessment: Informal Observation Ticket out the Door Guided Notes Summative Assessment: Homework < > ≤ ≥ These tables can be found on Writing Inequalities Guided Notes for this lesson (See Resource Folder). After filling out the charts on the guided notes, model for students how to complete the examples on the guided notes. Then allow the students to work through some examples in partners, and finally, independently. Summarizing Strategy: Students will answer the following question as a Ticket Out the Door. Julia is saving for an iPad. The iPad will cost at least $600. She has $150 saved. She charges $8 an hour to babysit. Write an equality to find how many hours she must babysit in order to save for her iPad. 3 I can write and solve Materials for Differentiated Essential Question: How do I write and solve an inequality? Differentiated Instruction – Formative Assessment: inequality. Instruction – Remediation: Algebra Tiles Set: Students will watch the Virtual Nerd video on writing and solving an inequality from a word problem. Remediation: Teaching Strategy: Review with students how to solve one-step equations. Examples can include: Grouping Informal Observation Peer Tutoring Ticket out the Door Guided Notes Use algebra tiles, if needed. 2𝑥 = 12 𝑥 − 5 = 13 𝑥 = 63 7 6 𝑥 = 42 7 Explain to the students that solving inequalities is similar to solving equations. Have students make a conjecture on how to solve the following inequality: 3𝑥 ≥ 18 Model for students how to solve this inequality. Model how to graph the inequality. Compare and contrast this with the equation 3𝑥 = 18. Have students discuss the difference between the solution set for the equation and the solution set of the inequality. Work through more examples with students. Model some, work some in partners, and finally work some independently. Examples can include: 𝑏 − 10 ≤ 12 14 ≤ 2𝑑 12 > 𝑐 4 3 𝑥 > 16 4 Differentiated Instruction – Enrichment: Solve an inequality with a coefficient that is negative. Summative Assessment: Homework In order to win the class president election, Carol must earn at least 55% of the vote of the student body. There are 120 students. Write an solve an inequality to determine the minimum number of votes Carol must get to become class president. Summarizing Strategy: Have students write, solve, and graph their own inequality as a ticket out the door. 4 Project Day 1 – refer to Unit Plan Topic – Watershed Study 5 Project Day 2 – refer to Unit Plan Topic – Watershed Study 6 I can use the data from my field journal to create graphs and draw conclusions. Data from the Stream Flow Essential Question: How do I create graphs and analyze my data from my field journal? Materials for Differentiated Instruction – Remediation: Computers with Excel Set: Differentiated Instruction – Remediation: Peer Tutoring Teaching Strategy: Ask the students to take out their field journals from our project days. Have students turn to their table groups and discuss the types of data they collected during these two days. This will serve as a review for students who may not remember the data that was collected. Explain to the students that their task for the data is to create graphs for their data. Pass out supplies to the students. Allow students to work individually on their graphs. When students have finished their graphs, ask students to interpret what their graph means. Summarizing Strategy: When the students are done with creating their graphs, allow them to post one of their graphs. Do a gallery walk and ask students to make a conclusion based on the data of at least two other students’ graphs. Differentiated Instruction – Enrichment: Peer Tutoring Formative Assessment: Informal Observation Ticket out the Door Summative Assessment: Homework 7 I can solve multi-step equations. Algebra Tiles Matts Paper Pencil Colored Pencils Two-Step Equation Examples (See Resource Folder) Two-Step Equation Word Problems Examples (See Resource Folder) Materials for Differentiated Instruction – Remediation: Algebra Tiles Calculator Materials for Differentiated Instruction – Enrichment: Two-Step Inequalities Essential Question: How do I solve a multi-step equation? Set: Put 2x+5=15 on the board. Have students make a conjecture on how to solve this equation. Teaching Strategy: Pass out the algebra tiles and the matts. Remind students of the concept of a zero pair. Model for the students a simple two-step equation using the zero pair concept to solve the equations. Express the importance of what you do to one side, you must do to the other side. Otherwise the equation will not be balanced. First, just have students get used to using the Algebra Tiles. After a few models, show students how draw a picture of the models in their notes. Finally, show students how to show their work using just paper and pencil. See Resource Folder for examples. Along each step, allow students to create problems for each other in their table groups and for the class. After the students have gotten the hang of it, give them some real-world world problems. Summarizing Strategy: Students will write a Dear Teacher note. This note will include what they already know about equations, what they liked/disliked, and what they are unclear about. Differentiated Instruction – Remediation: Peer Tutoring Formative Assessment: Informal Observation Ticket out the Door Grouping Algebra tiles Calculator Differentiated Instruction – Enrichment: Solve two-step inequalities. Summative Assessment: Homework (See Resource Folder) 8 Project Day 3 – refer to Unit Plan Topic –Engineering Fair 9 Project Day 4 – refer to Unit Plan Topic –Engineering Fair 10 Project Day 3 – refer to Unit Plan Topic – Engineering Fair STANDARDS Identify what you want to teach. Reference State, Common Core, ACT College Readiness Standards and/or State Competencies. 6.EE. 5. Understand solving an equation or inequality as a process of answering a question: which values from a specified set, if any, make the equation or inequality true? Use substitution to determine whether a given number in a specified set makes an equation or inequality true. 6.EE.9 Use variables to represent two quantities in a real-world problem that change in relationship to one another; write an equation to express one quantity, thought of as the dependent variable, in terms of the other quantity, thought of as the independent variable. Analyze the relationship between the dependent and independent variables using graphs and tables, and relate these to the equation. For example, in a problem involving motion at constant speed, list and graph ordered pairs of distances and times, and write the equation d = 65t to represent the relationship between distance and time. 7.EE.3. Solve multi-step real-life and mathematical problems posed with positive and negative rational numbers in any form (whole numbers, fractions, and decimals), using tools strategically. Apply properties of operations to calculate with numbers in any form; convert between forms as appropriate; and assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies. For example: If a woman making $25 an hour gets a 10% raise, she will make an additional 1/10 of her salary an hour, or $2.50, for a new salary of $27.50. If you want to place a towel bar 9 3/4 inches long in the center of a door that is 27 1/2 inches wide, you will need to place the bar about 9 inches from each edge; this estimate can be used as a check on the exact computation. 7.EE.4.Use variables to represent quantities in a real-world or mathematical problem, and construct simple equations and inequalities to solve problems by reasoning about the quantities. a. Solve word problems leading to equations of the form px + q = r and p(x + q) = r, where p, q, and r are specific rational numbers. Solve equations of these forms fluently. Compare an algebraic solution to an arithmetic solution, identifying the sequence of the operations used in each approach. For example, the perimeter of a rectangle is 54 cm. Its length is 6 cm. What is its width?