Long-Term Plan - Muinteoir Valerie
advertisement

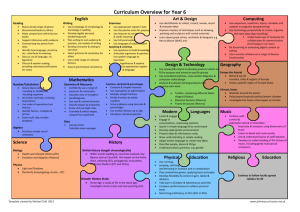
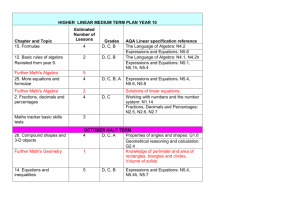
Long-Term Plan Subject: Maths Aims General or overall aims to develop a positive attitude towards mathematics and an appreciation of both its practical and its aesthetic aspects to develop problem-solving abilities and a facility for the application of mathematics to everyday life to enable the child to use mathematical language effectively and accurately to enable the child to acquire an understanding of mathematical concepts and processes to his/her appropriate level of development and ability to enable the child to acquire proficiency in fundamental mathematical skills and in recalling basic number facts Content (a) Strands and strand units Number Place value Operations Fractions Decimals and percentages Number theory Algebra Directed numbers Rules and properties Variables Equations Shape and space 2-D shapes 3-D shapes Lines and angles Measures Length Area Weight Capacity Time Money Data Representing and interpreting data Chance (b) An overview of the content objectives to be taught and/or examples of learning activities September Focus Objectives Look Back- Revision Big Numbers- Place value Revise and review material covered in 5th class Read, write and order whole numbers Identify place value in whole numbers Round whole numbers Operations- Addition and Subtraction Data-Representing and interpreting data Add and subtract whole numbers, without and with a calculator. Apply to word problems collect, organise and represent data using trend graphs read and interpret trend graphs compile and use simple data sets explore and calculate averages of data sets October Focus Objectives Multiplication- Operations Multiply a decimal by a whole number, without and with a calculator Apply to problems Lines and Angles Division 1 Fractions 1 Mental strategies November Fractions 2 Recognize, classify and describe angles and relate angles to shape Recognize angles in terms of a rotation Measure and construct angles in degrees Divide a four-digit number by a two-digit number, without and with a calculator. Divide a decimal by a whole number Apply to problems Compare and order fractions and identify equivalent fractions and forms of fractions Express improper fractions as mixed numbers and vice versa and position them on the number line Add and subtract simple fractions and simple mixed numbers Multiply a fraction by a fraction Express tenths, hundredths and thousandths in fractional form. Addition, subtraction, estimation Focus Objectives 2 Divide a whole number by a unit fraction Understand and use simple ratios 2-D shapes Make deductions about 2-d shapes and their properties Use angle and line properties to classify and describe triangles and quadrilaterals Construct triangles from given sides or angles Tessellate combinations of 2-D shapes Classify 2-D shapes according to their lines of symmetry Plot simple co-ordinates and apple where appropriate Use 2-D shapes and properties to solve problems. Decimals Identify place value in decimals Round decimals Relate decimals to fractions Estimate sums and differences of decimals Add and subtract decimals to three places. Puzzles Problem- Solving December Number theory Focus Objectives Look back Identify simple and composite numbers Identify and explore square numbers Explore and identify simple square roots Identify common factors and multiples Write whole numbers in exponential Review place value, operations, data Review place value, money, length, weight, angles Review angles, fractions, decimals, operations January Multiplication 2 Focus Objectives Length Multiply a decimal by a decimal, without and with a calculator Select and use appropriate instruments of measurement Rename measures of length Estimate and measure the perimeter of regular and irregular shapes Use and interpret scales on maps and plans. Division 2 February Divide a decimal by a decimal without and with a calculator. Focus Objectives 3 Fractions, decimals and percentages 1 Time Mental strategies 2 March Fractions, decimals and percentages 2/3 Use percentages and relate them to fractions and decimals. Compare and order percentages of numbers Explore the relationship between time, distance and average speed Explore international time zones Mental strategies: Multiplication, division, place value. Focus Objectives Area Use percentages and relate them to fractions and decimals Compare and order percentages of numbers. Solve problems involving percentages. Profit and loss. Solve problems involving discount, increases and decreases. Explore relationship between area and perimeter Calculate area of regular and irregular shapes Measure surface area of 3-D shapes Calculate area using ares and hectares Identify relationship between square metres and square centimetres. Find area using a scale plan Problem-solving 3 Problem-solving using R.U.D.E and group tasks Directed Numbers Identify positive and negative numbers on the number line, add simple positive and negative numbers on the number line. April Money Focus Objectives Explore value for money Convert currencies to euro and vice versa Solve problems relating to VAT and interest The circle Identify the properties of the circle Construct a circle of given radius or diameter Calculate the area of a circle by counting squares Rules and properties Know simple properties and rules about brackets and priority of operations Identify relationships and record symbolic rules for number patterns Revision of material covered in Term 2 Term assessment Variables Explore the concept of a variable in the context of simple patterns, tables and simple formulae and substitute values for variables 3-d shapes Identify and examine 3-D shapes and explore relationships Draw nets of simple 3-D shapes and construct the shapes May Look Back 2 Capacity 4 select and use appropriate instruments of measurement rename measures of capacity find the volume of a cuboid Standardised testing use of Sigma-T test to test pupils June Chance identify and list all possible outcomes of simple random processes estimate the likelihood of occurrence of events construct and use frequency charts and tables collect, organise and represent data using pie charts and trend graphs read, interpret trend graphs and pie charts compile and use data sets explore and calculate averages of simple data sets use data sets to solve problems Data 2 Equations Look Back 3 Use of relevant maths websites Problem solving every Fri when possible Maths games-ICT Maths stations every Friday Tables games (c) Skills and concepts to be developed Applying and problem-solving Communicating and expressing Integrating and connecting Reasoning Implementing Understanding and recalling Approaches and Methodologies Review of material covered during the year The children will complete tasks from workbook daily. Mental strategies discussed and used to solve these problems Class based tests Translate word problems with a variable into number sentences Solve one-step number sentences and equations Use of concrete materials 5 Modelling: Skills, strategies and language Oral approach to mental maths Estimation strategies Use of calculators Active learning Guided discovery Talk and discussion Problem solving Using the environment Skills through content Use of ICT Direct teaching Linkage and Integration Differentiation Learning process (a) Variety of level and sequence Learning content (a) Teaching style (b) Task (c) Pace (d) Interest (e) Choice (f) Support (g) Resource Learning outcome (a) Allow for different methods of response Assessment Assessment for learning Assessment of learning (a) Self assessment (b) Conferencing (c) Portfolio assessment (d) Concept mapping (e) Questioning (f) Teacher observation (g) Teacher designed tasks and tests (h) Wilf and Walt Resources Planet maths Figure it Out 6 Teacher textbooks and resources 6