Animal Unit Review Sheet Test Friday November 13th Review Sheet
advertisement

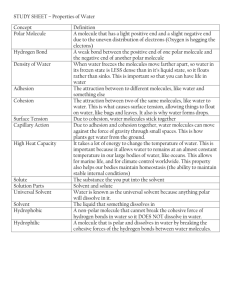
Animal Unit Review Sheet Test Friday November 13th Review Sheet DUE 11/13 (please use separate sheet to answer questions) Standards for Animals Unit Animal Standards for EOC Cellular I can describe cellular respiration as the process cells use to change the energy Respiration of glucose into energy in the form of ATP and/or the process that provides the in Cells energy source for most living organisms. I can compare cellular respiration to the burning of fossil fuels (e.g., large carbon-containing compounds are broken into smaller carbon compounds as chemical energy is transformed to different forms of energy in both cellular respiration and combustion of fossil fuels). I can describe the inputs and/or outputs of matter and/or energy in cellular respiration and/or in combustion (i.e., inputs include glucose or large carbohydrates and oxygen, outputs include carbon dioxide, water, and energy/ATP). Chemical I can describe that large molecules in food are broken down into smaller Reactions in molecules by cells to provide energy or building blocks (i.e., proteins into amino Cells acids, carbohydrates into simple sugars, fats into fatty acids, DNA into nucleotides). I can describe that cells build large molecules required for cell functions from smaller molecules (i.e., proteins from amino acids, carbohydrates from simple sugars, fats from fatty acids, DNA from nucleotides). I can describe that chemical energy stored in special molecules (i.e., ATP, fat, carbohydrate) is used by cells to drive cell processes. Cells and I can describe the essential function(s) of structures within cells (i.e., cellular Organelles* membrane, cell wall, nucleus, chromosome, chloroplast, mitochondrion, ribosome, cytoplasm). Cell I can describe the structure of the cell membrane as a bilayer with embedded Membrane* proteins capable of regulating the flow of materials into and out of the cell. *will be addressed throughout the Animal and Plant Units + √ STEP 1 - Reflect on the standards above to know where to spend your time studying. STEP 2 - Identify vocab/concepts that are unclear and review notes, worksheets, etc. STEP 3 - Select 6 of the following questions to answer: 1. We have two major ideas for the Food for Animal unit. Name, describe and explain each process. 2. Explain in your own words: How do we get energy from our food? 3. What are the three major groups of food molecules recognized by scientists? 4. Draw a picture of each food molecule and name the subunits of the major groups of food molecules. 5. What is the difference between the two major subdivisions of carbohydrates? (simple and complex) 6. Where is the energy stored in the molecules that we eat? 7. What process provides energy in animal cells? 8. What is the equation for cellular respiration? Words or formula=okay 9. Describe the transfer of energy in cellular respiration, including what percentage of the energy is transferred. 10. Is matter ever converted to energy? Explain your answer. 11. After a marshmallow was burned OR when sugar was used in our cells—where did the sugar go (the matter—the carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen)? _ STEP 4 EVERYONE ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS: 12. A cricket jumps around in its container. The cricket eats food that contains glucose. Use this information to answer the 2 questions below. A) Explain what happens to the matter (carbon) in the food as it is taken in by the cricket and used to power the jumping. Include any changes in the form of the matter. A diagram may be helpful. B) Explain what happens to the Energy in the food as it is taken in by the cricket and used to power the jumping. Include any changes in the form of the energy. A diagram may be helpful. 13. Answer True or False to these statements of what happened to the mass of the potato and/or mealworms when the potato was used as food a. _ ____ b. ____ The glucose and oxygen molecules were broken and rearranged into water molecules and carbon dioxide molecules. The glucose molecules combined with CO2 molecules and became water andO2. c. _____ Carbon dioxide is produced when glucose is used as food. d. _____ Oxygen is produced when glucose is used as food. e. _____ Water is produced when glucose is used as food. f. _____ The main purpose of eating the potato was to produce carbon dioxide g. _____ 40% of the mass (atoms) of the potato became ATP/Chemical Energy. STEP 5 - Animal Unit Vocabulary, complete the following table with a definition and picture WORD DEFINITION/EXPLANATION PICTURE/DIAGRAM CARBOHYDRATES PROTEINS FATS DIGESTION CIRCULATION BIOSYNTHESIS CHEMICAL ENERGY CELLULAR RESPIRATION ATP Food molecule made of simple sugars like glucose. Two major types – simple and complex. Simple – small not in chains (glucose). Complex – long chains (starch, glycogen and cellulose) GLUCOSE