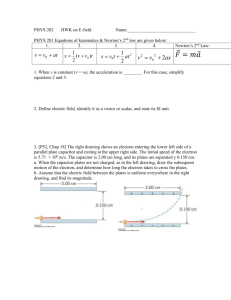
Electrostatics Multiple Choice Review
advertisement
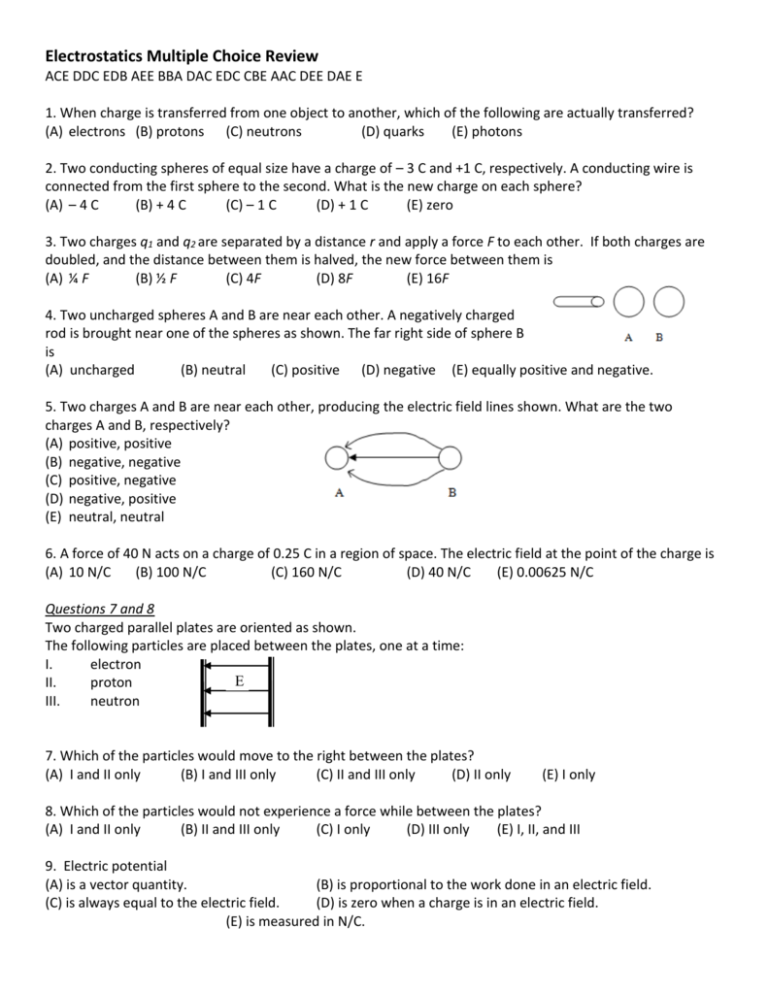
Electrostatics Multiple Choice Review ACE DDC EDB AEE BBA DAC EDC CBE AAC DEE DAE E 1. When charge is transferred from one object to another, which of the following are actually transferred? (A) electrons (B) protons (C) neutrons (D) quarks (E) photons 2. Two conducting spheres of equal size have a charge of – 3 C and +1 C, respectively. A conducting wire is connected from the first sphere to the second. What is the new charge on each sphere? (A) – 4 C (B) + 4 C (C) – 1 C (D) + 1 C (E) zero 3. Two charges q1 and q2 are separated by a distance r and apply a force F to each other. If both charges are doubled, and the distance between them is halved, the new force between them is (A) ¼ F (B) ½ F (C) 4F (D) 8F (E) 16F 4. Two uncharged spheres A and B are near each other. A negatively charged rod is brought near one of the spheres as shown. The far right side of sphere B is (A) uncharged (B) neutral (C) positive (D) negative (E) equally positive and negative. 5. Two charges A and B are near each other, producing the electric field lines shown. What are the two charges A and B, respectively? (A) positive, positive (B) negative, negative (C) positive, negative (D) negative, positive (E) neutral, neutral 6. A force of 40 N acts on a charge of 0.25 C in a region of space. The electric field at the point of the charge is (A) 10 N/C (B) 100 N/C (C) 160 N/C (D) 40 N/C (E) 0.00625 N/C Questions 7 and 8 Two charged parallel plates are oriented as shown. The following particles are placed between the plates, one at a time: I. electron E II. proton III. neutron 7. Which of the particles would move to the right between the plates? (A) I and II only (B) I and III only (C) II and III only (D) II only (E) I only 8. Which of the particles would not experience a force while between the plates? (A) I and II only (B) II and III only (C) I only (D) III only (E) I, II, and III 9. Electric potential (A) is a vector quantity. (B) is proportional to the work done in an electric field. (C) is always equal to the electric field. (D) is zero when a charge is in an electric field. (E) is measured in N/C. Questions 10 – 12: A hollow metal sphere has a radius R and a charge Q placed on it. 10. The electric field inside the sphere is KQ KQ KQ (A) zero (B) (C) 2 (D) 2 r r R 11. The electric potential at the surface of the sphere is KQ KQ KQ (A) zero (B) (C) 2 (D) 2 r r R 12. The electric potential at the center of the sphere is KQ KQ KQ (A) zero (B) (C) 2 (D) 2 r r R (E) KQ R (E) KQ R (E) KQ R 13. Two unequally sized metal spheres are each charged. A wire is connected from one sphere to the other. When the wire is removed, (A) the spheres will be equally charged (B) the spheres will have the same potential (C) the spheres will have the same electric field at their surfaces (D) the spheres will be oppositely charged (E) all of the above are true. 14. Equipotential lines are always (A) parallel to electric field lines (B) perpendicular to electric field lines (C) perpendicular to charged surfaces (D) circular (E) positive Questions 15 - 18 Two parallel conducting plates each of area 0.004 m2 are separated by a distance of 0.001 m. A 9 V battery is connected across the plates. 15. The electric field between the plates is (A) 9000 V/m (B) 900 V/m (C) 9 V/m (D) 0.009 V/m (E) 0.00011 V/m 16. The capacitance of the parallel plates is (A) 9.0 x 109 F (B) 4.0 x 10-12 F (C) 6.3 x 10-6 F (D) 3.5 x 10-11 F (E) 7.0 x 1011 F 17. The charge on one of the plates is (A) 3.2 x 10-10C (B) 2.1 x 10-9 C (D) 5.2 x 10-6 C (E) 9.0 x 10-10 C (C) 4.4 x 10-7 C 18. If the distance between the plates is doubled and the area of each plate is doubled, which of the following is true? (A) Both the electric field and the capacitance are doubled (B) Both the electric field and the capacitance are quadrupled (C) The electric field is halved and the capacitance is unchanged (D) The electric field is halved and the capacitance is doubled (E) Neither the electric field nor the capacitance is changed. 19. The distance between two charged is halved. The force between the charges is (A) decreased by a factor of 4 (B) decreased by a factor of 2 (C) unaffected. (D) increased by a factor of 2 (E) increased by a factor of 4 20. There is a force F between two like charged spheres. The charge on one of spheres is doubled while the charge on the other is quadrupled. The spheres are moved apart until the distance between them is double the initial distance. The new force between them is (A) F/4 (B) F/2 (C) F (D) 2F (E) 4F 21. A +1000 C charge interacts with a –10 C charge. The force that the –10 C charge pulls on the +1000 C charge with is (A) much smaller than the force that the +1000 C charge pulls on the –10 C charge. (B) a little smaller than the force that the +1000 C charge pulls on the –10 C charge. (C) the same as the force that the +1000 C charge pulls on the –10 C charge. (D) a little bigger than the force that the +1000 C charge pulls on the –10 C charge. (E) much bigger than the force that the +1000 C charge pulls on the –10 C charge. 22. The mass of a proton is 1833 times larger than the mass of an electron. When a proton an electron interact with each other the oversized proton’s electric force on the electron is (A) many times larger than the electric force of the electron on the proton. (B) negligibly larger than the electric force of the electron on the proton. (C) exactly the same as the electric force of the electron on the proton. (D) negligibly smaller than the electric force of the electron on the proton. (E) many times smaller than the electric force of the electron on the proton. 23. The direction of the electric field at a point in space is the same as the direction that an imaginary (test) (A) mass moves. (B) positive charge moves. (C) negative charge moves. (D) neutral charge moves. (E) None of these is correct. 24. Field lines (A) extend from positive to negative. (B) never cross. (C) are in the direction of force on a positive charge. (D) leave and enter surfaces perpendicular to the surface. (E) All of these. 25. Charges +Q and −Q are located near a point P as shown. What is the direction of the electric field at point P? (A) +x (B) −x (C) +y (D) −y (E) zero 26. A positive and a negative charge are released near each other. As they move (A) F increases, a increases, and v increases. (B) F increases, a increases, and v decreases. (C) F decreases, a decreases, and v increases. (D) F decreases, a decreases, and v decreases. (E) F increases, a decreases, and v decreases. 27. Two like charges are released near each other. As they move (A) F increases, a increases, and v increases. (B) F increases, a increases, and v decreases. (C) F decreases, a decreases, and v increases. (D) F decreases, a decreases, and v decreases. (E) F increases, a decreases, and v decreases. 28. A proton and an electron are placed between the same charged plates. Assume the attraction to each other is insignificant compared to the attraction to the plates. Which of these is true? (A) The proton and electron move in the same direction, and the proton has a higher acceleration. (B) The proton and electron move in the same direction, and the electron has a higher acceleration. (C) The proton and electron move in the opposite directions, and the proton has a higher acceleration. (D) The proton and electron move in the opposite directions, and the electron has a higher acceleration. (E) The proton and electron move in the opposite directions, and have the same accelerations. 29. Two oppositely charged plates have a potential difference of 6 V. Which of the following is the best answer? (A) The negative plate is always designated as 0 V and this will mean that the positive plate must be 6 V. (B) The positive plate is always designated as 0 V and this will mean that the negative plate must be 6 V. (C) Zero volts must be in the middle, so the positive plate is +3 V and the negative plate is –3 V. (D) Both A and C are acceptable. Answer B is completely backwards. (E) Any numbering system is acceptable so long as the positive plate has a higher potential than the negative plate, and when the negative plates potential is subtracted from the positive plates potential a potential difference of 6 V is calculated. 30. Which of the following is true of the potential difference between plates? (A) The positive plate is always the high potential plate, and the negative plate is always the low potential plate. (B) The assignment of the high and low potential depends on whether a positive charge or negative charge is moving between the plates. A negative charge reverses the sign on everything in the problem. (C) Two points the same distance from the plates have the same potential. (D) Both A and B are correct. (E) Both A and C are correct. 31. Four equal charges are arranged in a square as shown above. Determine which is true regarding the electric field and electric potential at a point P at the center of the arrangement. (A) E ≠ 0 and V < 0 (B) E ≠ 0 and V = 0 (C) E ≠ 0 and V > 0 (D) E = 0 and V = 0 (E) E = 0 and V > 0 32. The potential difference between two points is 12 V. A +2 C charge is moved opposite the direction of the electric field. Which is true? (A) W = 24 J, ΔV = 12 (B) W = 24 J, ΔV = –12 (C) W = –24 J, ΔV = 12 (D) W = –24 J, ΔV = –12 (E) W = 0, ΔV = 0 33. 34.