Earth Systems Final Exam Review Answer Section
advertisement

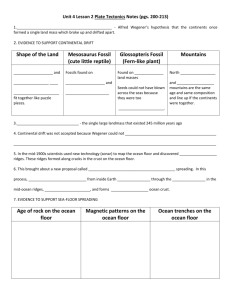
Earth Systems Final Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. The theory of plate tectonics helps scientists explain ____. a. how ocean currents move over Earth’s surface b. why hurricanes occur c. how earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur d. why Earth’s core is less dense than the mantle ____ 2. Which of the following is NOT an example of a renewable resource? a. cotton c. chicken b. lumber d. iron ____ 3. Which of the following is NOT one of the three types of rock? a. igneous c. sedimentary b. magma d. metamorphic ____ 4. A foliated metamorphic rock forms when crystals ____. a. combine and form visible bands b. combine but do not form visible bands c. become less compact d. align themselves parallel to the direction of the forces acting on them ____ 5. Which of the following is an example of a renewable resource? a. cotton c. natural gas b. copper d. coal ____ 6. Which of the following is an example of a nonrenewable resource? a. cotton c. cattle b. trees d. uranium ____ 7. The advantages of solar energy include the fact that it is ____. a. nonrenewable c. expensive b. non-polluting d. absent at night ____ 8. What is one of the drawbacks to the extensive use of solar energy? a. It is nonrenewable. b. Necessary equipment and installation are expensive. c. It is available only at night. d. It produces toxic pollution. ____ 9. What is the function of the atmosphere’s ozone layer? a. shields Earth from harmful solar radiation b. provides the oxygen needed by human life c. protects Earth from the sun’s heat d. removes pollution from the atmosphere ____ 10. What layer of Earth is labeled B in Figure 8-2? a. the continental crust c. the oceanic crust b. the lithosphere d. the mantle ____ 11. What layer of Earth is labeled E in Figure 8-2? a. the continental crust c. the oceanic crust b. the lithosphere d. the mantle ____ 12. Earth’s core is made of an alloy of ____. a. iron and nickel b. copper and iron c. zinc and magnesium d. iron and zinc ____ 13. In the plate tectonics theory, the lithosphere is divided into ____. a. 100 major plates b. 7 major plates and many smaller plates c. many small plates, but no large plates d. 50 major plates and many smaller plates ____ 14. The lithospheric plates move an average of ____. a. 5 inches per year c. 5 centimeters per year b. 50 inches per year d. 50 centimeters per year ____ 15. What type of plate boundary is illustrated in Figure 9-1? a. transform fault boundary b. divergent boundary c. convergent oceanic-oceanic boundary d. convergent oceanic-continental boundary ____ 16. What feature is labeled B in Figure 9-1? a. trench b. ocean ridge c. volcanic island arc d. continental volcanic arc ____ 17. What process is illustrated by the area labeled G in Figure 9-1? a. seafloor spreading c. rifting b. continental volcanism d. subduction ____ 18. The Hawaiian Islands were formed when the Pacific Plate moved over ____. a. a subduction zone c. the Aleutian Plate b. an ocean ridge d. a hot spot ____ 19. As the temperature of lava increases, ____. a. its viscosity decreases b. it begins to harden c. its viscosity increases d. it can flow a much shorter distance ____ 20. What feature is labeled A in Figure 10-1? a. pipe b. volcanic neck c. crater d. vent ____ 21. What type of volcano is illustrated in Figure 10-1? a. volcanic neck c. cinder cone b. shield volcano d. composite cone ____ 22. What feature is labeled D in Figure 10-1? a. pipe b. volcanic neck c. crater d. lava flow ____ 23. Most of the active volcanoes on Earth are located in a belt known as the ____. a. circum-Atlantic belt c. Ring of Lava b. Ring of Fire d. East African Rift Valley ____ 24. Which regions are thought to be the most level places on Earth? a. mid-ocean ridges c. deep-ocean trenches b. abyssal plains d. continental slopes ____ 25. The Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Mexico, and the North Sea are all known for their reserves of what ocean resource? a. oil c. coal b. titanium d. diamonds ____ 26. In general, how do highland climates compare to nearby areas at lower elevations? a. They are warmer and drier. c. They are warmer and wetter. b. They are cooler and wetter. d. They are cooler and drier. ____ 27. What is the shape of a planet’s orbit? a. elliptical b. circular c. irregular d. parabolic ____ 28. Which scientist was the first to use the telescope in astronomy? a. Newton c. Copernicus b. Galileo d. Kepler ____ 29. Seasons are caused by ____. a. Earth’s rotation b. precession c. Earth’s tilted axis d. Earth’s distance from the sun ____ 30. One of the planets known to have rings is ____. a. Venus c. Uranus b. Mars d. Pluto ____ 31. Which of the following is NOT a terrestrial planet? a. Mercury c. Mars b. Earth d. Jupiter ____ 32. The most obvious difference between the terrestrial and the Jovian planets is ____. a. color c. orbital velocity b. size d. length of day ____ 33. Which of the following is NOT considered part of the solar system? a. terrestrial planets c. galaxies b. Jovian planets d. sun ____ 34. The planet with the greatest temperature extremes is ____. a. Earth c. Mars b. Venus d. Mercury ____ 35. Which planet has a dense carbon dioxide atmosphere and high surface temperatures? a. Venus c. Mars b. Earth d. Mercury ____ 36. How many known satellites does Mars have? a. 1 b. 2 c. 5 d. 0 ____ 37. Mons Olympus, a volcano the size of Ohio, is found on ____. a. Earth c. Mercury b. Mars d. Saturn ____ 38. What is the study of the atmosphere and the processes that produce weather and climate? a. oceanography c. meteorology b. geology d. astronomy ____ 39. The outer planets—Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune—are made up of ____. a. hydrogen, helium, and water b. iron, nickel, and carbon dioxide c. carbon, oxygen, and methane d. water, carbon dioxide, ammonia, and methane ____ 40. Which of Earth’s spheres includes the oceans, groundwater, lakes, and glaciers? a. the atmosphere c. the biosphere b. the hydrosphere d. the geosphere ____ 41. Which of the following is an environmental hazard created by humans? a. air pollution c. hurricane b. flood d. earthquake ____ 42. Which of the following is NOT caused by human interactions with the Earth system? a. air pollution c. mountain building b. water pollution d. deforestation ____ 43. Which of the following is an example of a renewable resource? a. iron c. energy from flowing water b. petroleum d. coal ____ 44. Resources that can be replenished over a relatively short time span are called ____. a. fossil fuels c. nonrenewable resources b. renewable resources d. mineral resources ____ 45. Which of the following is NOT an example of a nonrenewable resource? a. solar energy c. copper b. natural gas d. oil ____ 46. Which of the following is NOT considered to be a rock? a. coal c. pumice b. sandstone d. lava ____ 47. Fossils are only found in ____. a. intrusive igneous rocks b. foliated metamorphic rocks c. sedimentary rocks d. nonfoliated metamorphic rocks ____ 48. Renewable resources ____. a. can be replenished over months, years, or decades b. are all living resources c. have finite supplies that will one day be used up d. include iron, natural gas, and copper ____ 49. Harnessing the sun’s energy to produce heat or electricity is ____. a. non-polluting c. possible only in coastal areas b. inexpensive d. a major source of air pollution ____ 50. Wind power generates ____. a. noise pollution b. air pollution c. water pollution d. soil pollution ____ 51. Hydroelectric power is produced by ____. a. falling water that turns a turbine b. tides that pour through a dam barrier c. hot water that comes from deep underground d. electric current that flows across a dam ____ 52. According to Figure 4-2, what is the single largest source of air pollutants? a. solid waste disposal b. transportation c. stationary source fuel combustion d. industrial processes ____ 53. According to Figure 4-2, what percentage of the major primary air pollutants is composed of nitrogen oxides? a. 13.6% c. 16.4% b. 49.1% d. 14.8% ____ 54. Cars with hybrid and electric motors ____. a. use more fuel than conventional cars b. create less air pollution than conventional cars c. use solar panels for power d. are no longer produced ____ 55. Earthquakes are usually associated with ____. a. violent weather c. large cities b. faults d. the east coast of North America ____ 56. During an earthquake, the ground surface ____. a. moves only in a horizontal direction b. moves only in a vertical direction c. can move in any direction d. does not move ____ 57. The adjustments of materials that follow a major earthquake often generate smaller earthquakes called ____. a. foreshocks c. aftershocks b. surface waves d. body waves ____ 58. The San Francisco earthquake of 1906 occurred along what fault? a. the San Francisco fault c. the California fault b. the Pacific fault d. the San Andreas fault ____ 59. An earthquake’s magnitude is a measure of the ____. a. size of seismic waves it produces b. amount of shaking it produces c. number of surface waves it produces d. damage it causes ____ 60. The scale most widely used by scientists for measuring earthquakes is the ____. a. seismic scale c. moment magnitude scale b. Richter scale d. epicenter magnitude scale ____ 61. What instrument records earthquake waves? a. seismogram b. seismograph c. Richter scale d. barometer ____ 62. Tsunamis are ____. a. often generated by movements of the ocean floor b. waves that are produced by tidal forces c. waves that cannot cause damage on land d. also known as tidal waves ____ 63. Why do earthquakes often cause damaging fires? a. Lightning strikes are common during earthquakes. b. Earthquake vibrations can break gas lines, water lines, and electrical lines. c. Tsunamis from earthquakes generate enough heat to start fires. d. Magma from deep underground escapes through faults. ____ 64. Earth’s thin, rocky outer layer is its ____. a. core b. mantle c. outer core d. crust ____ 65. Earth’s inner core is solid because of ____. a. the composition of its rock b. its great diameter c. extreme temperatures d. immense pressure ____ 66. The supercontinent in the continental drift hypothesis was called ____. a. Panthalassa c. Mesosaurus b. Pangaea d. Africa ____ 67. New ocean crust is formed at ____. a. divergent boundaries b. convergent boundaries c. continental volcanic arcs d. transform fault boundaries ____ 68. Deep ocean trenches are associated with ____. a. ocean ridge systems c. transform fault boundaries b. subduction zones d. rift zones ____ 69. A lava flow with a surface of rough, jagged blocks and sharp, angular projections is called a(n) ____. a. pyroclastic flow c. pahoehoe flow b. aa flow d. ash flow ____ 70. Structures that form from the cooling and hardening of magma beneath Earth’s surface are ____. a. vents c. plutons b. calderas d. lahars ____ 71. Approximately how much of Earth’s surface is covered by land? a. 30 percent c. 60 percent b. 50 percent d. 70 percent ____ 72. Approximately how much of Earth’s surface is covered by water? a. 50 percent c. 70 percent b. 30 percent d. 40 percent ____ 73. Approximately when did the ocean become an important area of study? a. 200 years ago c. 1000 years ago b. 500 years ago d. 2000 years ago ____ 74. Which ocean has the greatest average depth? a. Atlantic b. Pacific c. Indian d. Arctic ____ 75. The largest of Earth’s oceans is the ____. a. Pacific b. Atlantic c. Indian d. Arctic ____ 76. Which of the following is NOT considered one of the four major oceans? a. Atlantic c. Indian b. Pacific d. Antarctic ____ 77. According to Figure 14-1, which of the following statements about the distribution of land and water is true? a. The percentage of land and water is roughly equal in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. b. The Southern Hemisphere is covered by much more water than the Northern Hemisphere. c. The Northern Hemisphere is covered by much more water than the Southern Hemisphere. d. Earth is covered by more land than water. ____ 78. Which ocean in Figure 14-1 is represented by Point A? a. Pacific c. Indian b. Atlantic d. Arctic ____ 79. Isolated volcanic peaks on the ocean floor are called ____. a. seamounts c. nodules b. ridges d. plateaus ____ 80. What technology do scientists use to measure ocean depth? a. sonar c. rope b. laser d. submersible ____ 81. Important mineral deposits, including large reservoirs of oil and natural gas, are associated with ____. a. rift zones b. ocean trenches ____ 82. Which part of the ocean is deepest? a. ridges b. rifts c. mid-ocean ridges d. continental shelves c. trenches d. seamounts ____ 83. Which of the following is NOT an energy resource obtained from the ocean? a. oil c. coal b. natural gas d. gas hydrates ____ 84. How much of the world’s oil production currently comes from offshore regions? a. 10 percent c. 50 percent b. 30 percent d. 75 percent ____ 85. Which ocean resources are second in economic value to oil? a. sand and gravel c. evaporative salts b. manganese nodules d. iron and natural gas ____ 86. Rain, snow, sleet, and hail are all examples of ____. a. evaporation c. precipitation b. condensation d. deposition ____ 87. The change of state from a gas to a liquid is called ____. a. evaporation c. condensation b. sublimation d. deposition ____ 88. The process of converting a liquid to a gas is known as ____. a. evaporation c. condensation b. sublimation d. deposition ____ 89. Air that has reached its water-vapor capacity is said to be ____. a. dry c. stable b. unstable d. saturated ____ 90. Which cloud type is best described as sheets or layers that cover much or all of the sky? a. cumulus c. stratus b. cirrus d. alto ____ 91. Which cloud type consists of globular cloud masses with a cauliflower structure? a. cumulus c. stratus b. cirrus d. alto ____ 92. Which clouds are often associated with thunder and lightning? a. cirrostratus c. cumulonimbus b. altostratus d. nimbostratus ____ 93. In the Ptolemaic model of the universe, ____. a. Earth was flat b. Earth was the center of the universe c. the sun was the center of the solar system d. Earth was much larger than the sun ____ 94. The first early astronomer to propose a sun-centered solar system was ____. a. Galileo b. Newton c. Copernicus d. Brahe ____ 95. Which of the following is NOT a Jovian planet? a. Earth c. Neptune b. Saturn d. Uranus ____ 96. Which of the following is NOT characteristic of the Jovian planets? a. large size c. thin atmospheres b. composed mainly of gases and ices d. located beyond the orbit of Mars ____ 97. The Jovian planets contain a large percentage of the gases ____. a. nitrogen and argon c. oxygen and nitrogen b. hydrogen and helium d. hydrogen and oxygen ____ 98. The atmosphere of Venus is composed primarily of ____. a. water vapor c. hydrogen b. oxygen d. carbon dioxide ____ 99. Which of the following planets does NOT have rings? a. Mars c. Neptune b. Uranus d. Saturn ____ 100. Which planet, when viewed through a telescope, appears as a reddish ball interrupted by some permanent dark regions that change intensity? a. Mercury c. Mars b. Earth d. Saturn ____ 101. Which planet has a greater mass than the combined mass of all the remaining planets and their moons? a. Venus c. Jupiter b. Saturn d. Pluto Earth Systems Final Exam Review Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. C 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. D B A A D B B A C D A B C D A D D A A D C B B A B A B C C D B C D A B B C D B 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. A C C B A D C A A A A B D B B C C D A C B A B D D B A B B C A C A B A D B B A A 81. D 82. C 83. C 84. B 85. A 86. C 87. C 88. A 89. D 90. C 91. A 92. C 93. B 94. C 95. A 96. C 97. B 98. D 99. A 100. C 101. C