File - Jenny Sattiewhite
advertisement

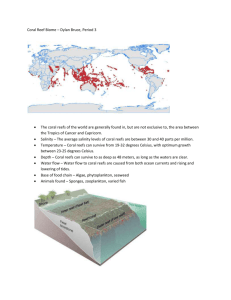
; Sunday Alok Jenny Sattiewhite Advanced Reading 0990-007 November 11th, 2014 Assignment: Signature assignment Biodiversity Biodiversity “Biodiversity is the variability among living organisms from all sources including, interlaid, terrestrial, and marine and other aquatic ecosystems and the ecological complexes of which they are a part of, this includes diversity within species and ecosystems. (What is Biodiversity pg. 3)” The meaning of their word biodiversity came from conservation biology (What is Biodiversity? pg. 1); the term was brought up in 1985 by Walter G. Rosen. For the national forum on biodiversity a conference that took place in Washington D.C in 1986. The word is a short phrase for biological diversity. It consists of four main diversity species diversity which is the diversity of species on earth ranging from animals and plants. Genetic diversity heredity quality that makes one single thing that’s from the same species unique in reason to one another and there’s ecosystem diversity many different ecosystem from mountain ecosystem, grassland ecosystems, desert ecosystem, fresh water ecosystems, forest ecosystems and marine ecosystem, than there is Ecological diversity (diversity of ecosystem) which is a variety of ways species interact with each other and their environment. The two largest ecosystems of them all are the tropical rainforest and the coral the two fall under the marine and forest ecosystems. Taxonomist (biologist who specialize in identifying and classifying life on the planet) have named approximately 1.7 million species and are looking at 13,000 more species to add to the list. Tropical rainforest is where there’s huge tall, thick evergreen woodland tress all over the place that structure the features of the vegetation in the forest. It has the most diversity of plants and animals, a whole lot more than the other ecosystems. You can find tropical rainforest in countries such as Africa, Asia and other parts of the world mostly developing countries, one of the largest well-known tropical rainforest is the amazon rain forest. The atmosphere is mostly wet and dry the season are really short and doesn’t really last for a long time. The reason why a rain forest is called a rain forest is because it rains a whole lot throughout the year. There is four layers to the forest one is the forest floor, second is the understory, third the canopy layer, and fourth the evergreen. It’s home to most of the earth’s plants and animals species like toucans, leopards, and jaguar are a few of the animals that live there and also it’s considered a home to different tribal groups that’s been living there for over thousands of years “Before 1500 A.D., there were approximately 6 million indigenous people living in the Brazilian Amazon. But as the forests disappeared, so too did the people. In the early 1900s, there were less than 250,000 indigenous people living in the Amazon” (Rainforests Facts | The Nature Conservancy pg. 4). This amazing and wonderful forest provides us with many types of food such as chocolate, sugar and medicine, it’s a really resourceful place and we get a lot from it. The rainforest as we may not know is the oldest biome on the earth! According to the nature conservancy it covers less than 2 percent of the Earth's total surface area and round the year of 2000 and 2012 2.3 million square kilometer of the tropical rainforest around the many parts of the world were cut down (Rain forests Facts | The Nature Conservancy pg.2).. According to live science Coral reefs are large underwater structures composed of the skeletons of coral, which are marine invertebrate animals. They’re made up of small animals called the polyps. Like the tropical rainforest the coral reef is one of the diverse ecosystems in the world. They grow better when they’re in warm clean low water. It takes time for a coral reef to grow it’s a really slow process, there is three types of coral reef fringing reefs, barrier reef, and coral atolls. Though they appear to be hard and strong, looks are deceiving coral reefs are really fragile. Beautiful colors it’s like an underwater city of colors, what makes the corals colorful is algae. Where you can find the largest amount of coral reef is in Australia the Great Barrier Reef is home to the largest groups of coral reef it provides homes to a number of organisms, fishes swim in to lay their eggs. The Great Barrier Reef is protected by The Great Barrier marine Park the only threats to this reef are climate changes, crown-of-thorns outbreaks, overfishing and spills and ballast discharge. The climate change is the biggest threat as of now. It’s a great tourist attraction specially the Great Barrier Reef thousands of people go to Australia just to see it every year. Indonesia is home to one third of the world’s coral reef which covers 33,000 miles and accounts for one quarter of the fish species. Due to destructive fishing, tourism, and bleaching only 7% is in great condition with 69% of poor to fair condition with a prediction of 70% will be loss by 2050. Coral reef has been on earth for millions of years, it’s like the oceans rainforest (nfw.org. n.p.) . Even though it’s a resourceful place that we all benefit from it’s starting to disappear before our eyes. There are many things causing damage to these beautiful coral reefs such as dynamite fishing which is where they take sticks of dynamite, grenades, or homemade explosives are throwing in to the water and detonate which kills fish within and around the blast area, it kills the corals in the area which than destroys the habitat for the remaining fish and other sea animals important to the reef health. There is mudroom which is where they cover coral reefs with nets and drop large stones or rocks onto the reef destroying it and causing fish and animals to flee. You have to think about how the fishing equipment is destroying the coral reefs like gill nets, fish traps, anchors that break branching corals than there is the way that the equipment is dropped around or on the reef causing damage to the structure of the reef. There are plastic debris and nets kill several reef species they are often called ghost nets, they are nets or plastic pieces that have been abandoned in the ocean and end up catching sea animals and killing them because they are not able to escape. Coral reef can repair itself from small damage but the large destruction can complicate the progress. Pesticides can interfere with the coral reproduction and growth; there is Aspergillosis which is a fungal infection that kills the soft corals such as sea fans, causes an increase in yellow band disease which is a bacterial infection that kills the reef which causes issues with building hard corals by % 50. In Taiwan the corals are being destroyed by untreated sewage and influx of tourist taking coral as souvenirs.(Wikipedia.com.n.p) Though the tropical rainforest and coral reef are both the most diverse places on the planet 50-90% of Earths plants and animal species are found in the tropical regions they’re different it many ways. Coral reefs are found in low level water anywhere in the ocean. We benefit from so much from tropical rain forest and coral reefs from food supplies and approximately half of all synthetic drugs have a natural origin, including 10 of the 25 highest selling drugs in the U.S. (nfw.org.n.p.) Volcanos have caused major problems to both our tropical rain forests and coral reef. Volcanos have destroyed wide areas with the lava flows, pyroclastic flows, atmospheric effects, gases and tsunami, forest fires and earth quakes. Pyroclastic flows are a fast moving current of gases and rock. Atmospheric effects are reduction in the power of the solar radiation due to absorption, scattering and reflection in the atmosphere. Aquatic life is affected with the increase in acidity, increase in turbidity change in the temp which affects the food supply. Eruptions can also cause a problem with bird migration, roosting and feedings. The good news volcanic soil is very rich, and when everything cools off, plants can make a big come comeback, like places where it rains a lot life will start to grow faster, within ten years there could have a low forest but areas where it’s very dry will take much longer to regrow Mount St Helen volcano eruption killed an estimate 24,115 animals from the pyroclastic flow in the 1980 eruption. The Santa Maria ( Guatemala) volcano in 1902 killed around 1500 people as well as thousands of birds, and soon after life was growing again and then there were so many insects, ones carrying diseases too which eventually 3000-6000 people died from malaria (volcanoes of the world, by Tom Siskin and Lee Seibert) What is Biodiversity? It’s a variation of species of life from sea life, to human life, to planets and animals there is many ecosystems in biodiversity genetic which consists of variation of genes, than you have Ecological diversity is the way species interact with each other and their environment than there is species diversity which is the variation of species. There are many different aspects to each diversity it changes in different areas of the world due to their climates, the countries they are located in, if they are on land or sea life. Each of these diversities is being effected everyday due to climate changes, pollution and mankind destroying it. Much of our rainforest and coral reefs are being damaged daily and we are losing such precious life in these regions of the world we need to take precautions and be serious of the effects that we have on other diversities and come together to help fix the problem because the future for ecosystems is not looking bright, we need to help protect these ecosystems because we often benefit from much of what they have to offer and if we lose them completely mankind will be in serious trouble, this is a serious manner for all diversities. WE MUST TAKE ACTION NOW to prevent further damages and find ways to help better all of our ecosystems. Work Cites Books Groombridge, Brian, and Martin Jenkins. World Atlas of Biodiversity: Earth's Living Resources in the 21st Century. Berkeley, CA: U of California, 2002. Print. Lovejoy, Thomas E., and Lee Jay. Hannah. Climate Change and Biodiversity. New Haven: Yale UP, 2005. Print. Lévêque, C., and Jean-Claude Mounolou. Biodiversity. Chichester, England: John Wiley & Sons, 2003. Print. Maclaurin, James, and Kim Sterelny. What Is Biodiversity? Chicago: U of Chicago, 2008. Print. Primack, Richard B., and Richard Corlett. Tropical Rain Forests: An Ecological and Biogeographical Comparison. Malden, MA: Blackwell Pub., 2005. Print. Websites "Coral Reef Biome Facts." Coral Reef Biome Facts. Softschools.com, 2005-2014. Web. 20 Oct. 2014. <http://www.softschools.com/facts/biomes/coral_reef_biome_facts/168/>. "Exploring the Tropical Rainforest." Exploring the Tropical Rainforest. Missouri Botanical Garden/ MBGnet, 2002. Web. 20 Oct. 2014. <http://www.mbgnet.net/sets/rforest/explore/valley.htm>. Hills, Abby. "Are Coral Reefs Really the Rainforest of the Sea? A Comparison between Coral Reefs and Rainforest (Final)." Are Coral Reefs Really the Rainforest of the Sea? A Comparison between Coral Reefs and Rainforest (Final). N.p., 7 May 2014. Web. 20 Oct. 2014. <http://jrscience.wcp.miamioh.edu/fieldcourses07/PapersMarineEcologyArticles/AreCoralReefsr eallytheRai.html>. Knowlton, Nancy, and Smithsonian NMNH. "Corals and Coral Reefs." Smithsonian Ocean Portal. The Ocean Portal Team, 2013. Web. 9 Nov. 2014. <http://ocean.si.edu/corals-and-coralreefs>. NOAA Coral Reef Conservation Program National Oceanic, and Atmospheric Administration U.S. Department of Commerce. "Why Is Biodiversity Important? Who Cares?" - Global Issues. Ed. Webmaster. Department of Commerce National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, July 2001. Web. 1 Nov. 2014. <http://www.globalissues.org/article/170/why-is-biodiversity-important-who-cares>. "Oceans' Bounty." Oceans' Bounty. Earth Day Canada, n.d. Web. 12 Oct. 2014. <http://www.ecokids.ca/pub/eco_info/topics/oceans/oceans_bounty.cfm>. "Rainforests Facts | The Nature Conservancy." Rainforests Facts | The Nature Conservancy. The Nature Conservancy, n.d. Web. 8 Nov. 2014. <http://www.nature.org/ourinitiatives/urgentissues/rainforests/rainforests-facts.xml>. "Tropical Rainforest." Tropical Rainforest. Internetgeography, 2009. Web. 12 Oct. 2014. <http://www.geography.learnontheinternet.co.uk/topics/rainforest.html>. "What Is a Rainforest?" What Is a Rainforest? N.p., n.d. Web. 4 Oct. 2014. <http://www.srl.caltech.edu/personnel/krubal/rainforest/Edit560s6/www/what.html>. "What Is Biodiversity? - National Wildlife Federation." What Is Biodiversity? - National Wildlife Federation. National Wildlife Federation, 1996-2014. Web. 30 Oct. 2014. <http://www.nwf.org/Wildlife/Wildlife-Conservation/Biodiversity.aspx>. "Biodiversity, Tropical Rain Forest." Biodiversity, Tropical Rain Forest. N.p., 1999 Web. 13 Nov. 2014. Blong, R.J., 1984, Volcanic hazards: A source book on the effects of eruptions: Academic Press, Orlando, Florida, 424 p. Del Moral, R., 1981, Life returns to Mount St. Helens, Natural History, v. 90, no. 5, p. 36-46. World of Biology. McGrath, Kimberley A., ed. The Gale Group, Farmington Hills, MI: 1999. Precious Heritage: The Status of Biodiversity in the United States. Stein, Bruce A., Lynn S. Kutner and Jonathan S. Adams. Oxford University Press, New York: 2000. "Environmental Issues with Coral Reefs." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 11 Sept. 2014. Web. 13 Nov. 2014