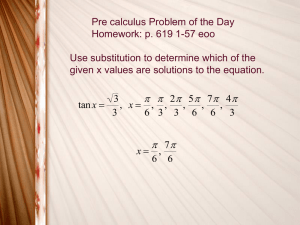
4. mathematics - Kendriya Vidyalaya, Gill Nagar, Chennai
advertisement
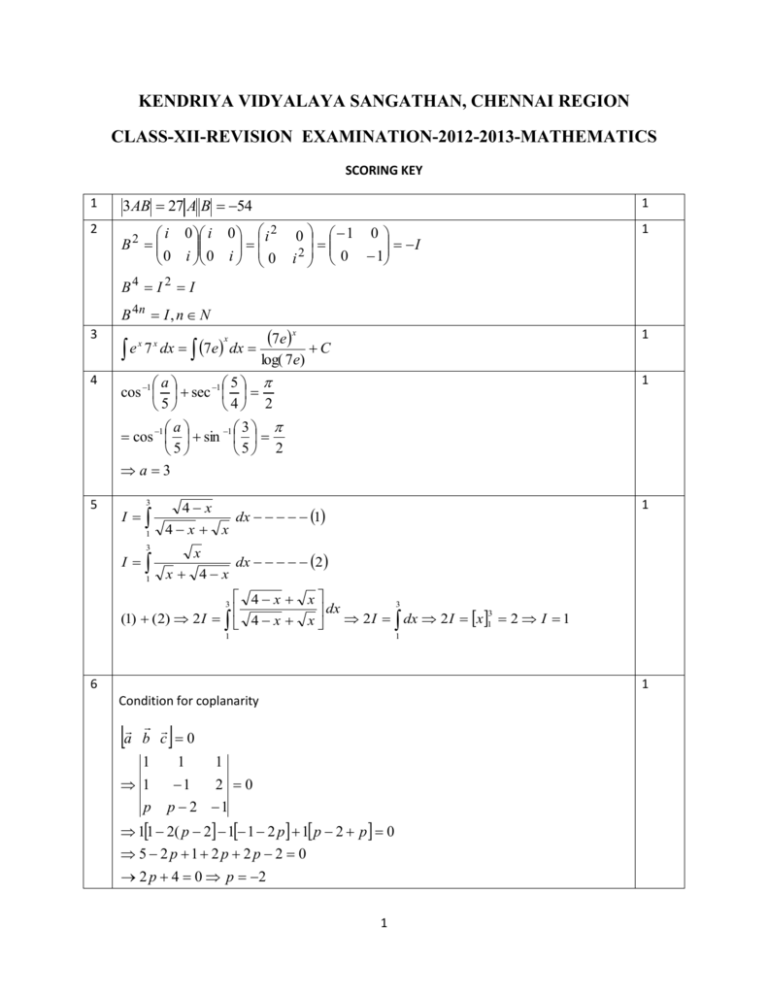
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, CHENNAI REGION CLASS-XII-REVISION EXAMINATION-2012-2013-MATHEMATICS SCORING KEY 1 3 AB 27 A B 54 2 i 0 i 0 i 2 B 2 0 i 0 i 0 1 0 1 0 I i 2 0 1 1 B4 I 2 I B 4n I , n N 3 e 7 dx 7e dx x x x 7ex log( 7e) 4 a 5 cos 1 sec 1 5 4 2 a 3 cos 1 sin 1 5 5 2 a3 5 I 4 x 3 1 4 x 3 I 1 x x x 4 x 1 C 1 1 dx 1 dx 2 4 x (1) (2) 2 I 4 x 3 1 x 3 dx 3 x 2 I dx 2 I x 1 2 I 1 1 6 1 Condition for coplanarity a b c 0 1 1 p 1 1 1 2 0 p 2 1 11 2( p 2 1 1 2 p 1 p 2 p 0 5 2 p 1 2 p 2 p 2 0 2 p 4 0 p 2 1 7 x 3y is a skew symmetric matrix then x= 0 ( diagonal elements of a skew x If 0 12 1 symmetric matrix is 0 ) and aij a ji a12 a 21 x 3 y 12 y 4 (or) AT A for a skew symmetric matrix 8 A(1,2,3), B(1,2,1) 1 AB (2,4,4) AB (2) 2 (4) 2 (4) 2 36 6 2 4 4 1 2 2 direction cosines of AB , , , , 6 6 6 3 3 3 9 a b , 60 a.b a b cos 8 1 2 1 a 8 2 2 a 16 a 4 b 10 11 R= (1,1), (2,2), (3,3), (1,2), (2,1), (1,3)(3,1) is the only relation which is reflexive , symmetric but not transitive . y log x x 2 a 2 dy 1 2x 1 2 2 2 2 dx x x a 2 x a dy 1 x 1 dx x x 2 a 2 x2 a2 x2 a2 x dy 1 dx x x 2 a 2 x 2 a 2 dy 1 dx x2 a2 1 1 2 dy x 2 a 2 1 dx 2 dy d 2 y dy x 2 a 2 2 . 2 2 x 0 dx dx dx x2 a2 d ½ 1 dy x 0 dx dx 2 1 y ½ 2 2 11 (OR) substitute ½ x cos 2 2 u tan 1 1 x2 1 x2 1 cos 2 2 sin 2 tan 1 tan 1 tan 2 1 cos 2 2 cos 1 1 cos 1 x 2 v where v cos 1 x 2 2 2 1 u v 2 du 1 dv 2 tan 1 12 1½ 1 1 From 0 to 9 the prime numbers are 2 , 3 , 5 , 7 X = 0 , 1,2 6 5 30 10 10 9 90 30 4 6 48 16 P(x=1)= 2 10 9 90 30 4 3 12 4 p(x=3)= 10 9 90 30 p( x = 0 ) = X p(x) 0 1 2 10 30 16 30 4 30 16 4 24 4 2 30 30 30 5 16 4 32 16 E ( x 2 ) x 2 P( x) 0 1 4 30 30 30 15 Mean = xp(x ) = 0 1 1 1 1 2 32 4 16 16 32 var( x) E ( x ) E ( x) 30 5 15 25 75 13 let the adjacent sides of the parallelogram be a 2iˆ 4 ˆj 5kˆ , b iˆ 2 ˆj 3kˆ area of parallelogram = a b 2 2 iˆ ˆj kˆ a b = 2 4 5 22iˆ 11 ˆj a b 11 5 1 2 3 vectors parallel to diagonals are a b and a b 3 1 2 Let a b = c c 3iˆ 6 ˆj 2kˆ , c 49 7 c 1 ˆ unit vector parallel to c 3i 6 ˆj 2kˆ c 7 Let a b d d iˆ 2 ˆj 8kˆ , d 69 d 1 ˆ unit vector parallel to d i 2 ˆj 8kˆ 69 d 1 1 14 x 2 ye dx y 2 xe y dy 0 x y x y y 2 xe dx x dy 2 ye y 1 x dx x dy y 2e y ½ 1 ½ substitute x= vy dx dv v y dy dy v y 2 dv 1 dv 1 dy v y 2vdv dy 2v dy 2v y v2 log y c v 2 log y c 2 x2 y2 x= 0 , y = 1 0 = log 1 + c c 0 log y c 1 ½ ½ x2 hence 2 log y y (OR) dy 3x 4 y dx dy e3 x4 y dx dy e 3 x .e 4 y dx log 1 ½ 4 dy e 3 x dx 4y e ½ e 4 y dy e 3 x dx e 4 y e 3x c 4 3 x=0,y=0 1 1 1 1 1 7 cc 4 3 4 3 12 ½ hence e 4 y e 3 x 7 4 3 12 15 ½ (a, b) * (c, d ) (a c, b d ) c a, d b (c, d ) * (a, b) 1 hence * is commutative (a, b) * (c, d )* (e, f ) (a c, b d ) * (e, f ) (a c e, b d f ) a (c e), b (d f ) (a, b) * (c e, d f ) (a, b) * (c, d ) * (e, f ) hence * is associative let ( c, d) be the identity element of ( a, b ) then ( a, b ) * ( c, d ) = ( a, b ) (a c, b d ) (a, b) a c a., b d b a 0, b 0 N 2 1 identity element for A on * does not exist (OR) 1 For any a A , a a 0 is even (a, a) R ,hence R is reflexive ( a, b) R a b is even b - a is even (b.a) R 1 hence R is symmetric ( a, b) R a b is even a – b is even ( b, c) R b c b-c is even a- b + b-c is even a-c is even (a, c) R hence R is transitive since R is reflexive , symmetric and transitive it is an equivalence relation 16 1½ ½ 5𝑥−2 ∫ 3𝑥²+2𝑥+1 dx d 5x-2 =A dx (1+2x+3x2 ) +B = A( 2+ 6x) + B 5 11 ,B= 6 3 5 2 6x 11 1 I 2 dx 2 dx 6 3x 2 x 1 3 3x 2 x 1 1 A= 5 1 I= 5 11 I1 I2 6 3 I 1 = log |3x² + 2x + 1| 1 dx 1 dx dx I 2 =∫ 3x²+2x+1 == 2 1 3 3 2 2 1 2 x x x 3 3 3 9 dx =1 2 3 1 x 3 1 x 3x+1 1 1 ) 1 3 1 tan−1 ( tan √2 2 2 3 2 2 2 3 3 3 I = 5/6 log |3x² + 2x + 1|- 11 3x+1 tan−1 +c 3√2 √2 (OR) dx x4 x( x 5 1) x 5 ( x 5 1) dx substitute x 5 t 17 ½ 4 ½ 1 dt I 5 t (t 1) 1 A B t (t 1) t t 1 1 A(t 1) Bt A 1, B 1 I 1 ½ 1 5 x dx dt x dx dt 5 4 ½ ½ 1 x5 1 dt dt 1 1 log t 1 log t log( t 1 ) log C 5 t t 1 5 5 log( t 1) 5 ( x 5 1) x sin t dx dy dy sin t cos t , y cos t sin t tan t dt dt dx cos t 1½ 1 dy 1 at t dx 4 1 1 , y1 cos x1 sin 4 4 2 2 1 equation of tangent 1 y 1 1 x 2x 2 y 2 2 2 1 equation of normal 1 1 y 1 x 2x 2 y 0 2 2 1 6 18 x y z x2 1 x3 y2 1 y3 0 z2 1 z3 x y z x2 1 x y2 1 y z2 1 z x y z x2 1 1 x 2 y 1 xyz 1 y z2 1 1 z x2 y2 z2 ½ x3 y3 0 z3 x2 y2 0 z2 1 x2 y2 0 z2 1 x (1 xyz 1 y 1 z R1 R1 R2 , R2 R2 R3 0 x y (1 xyz) 0 y z 1 z x2 y2 0 1 xy 2 2 y z (1 xyz)(x - y)(y - z) 0 1 y z z2 1 z z2 1 (x - y)(y - z)(z - x)(1 xyz) 0 since x y z 1 xyz 0 xyz 1 19 ½ cos x tan 1 , x 2 2 1 sin x cos 2 x sin 2 x 2 2 tan 1 2 cos x sin x 2 2 cos x sin x cos x sin x 2 2 2 2 1 tan 2 x x cos sin 2 2 x cos sin 2 tan 1 x cos sin 2 20 1 lt x0 lt x0 lt f ( x) lt x0 f ( x) lt x0 16 x0 x x 1 tan 2 2 tan 1 tan tan x x tan 1 x x 2 4 2 4 1 tan 2 2 f ( x) f (0) x 16 x 4 x x 16 lt x x0 16 x 4 16 x 4 lt x0 x x 7 lt x0 1+1 4(½) 16 x 4 16 x 4 16 x 4 8 1½ 1 cos 4 x 2 sin 2 2 x 2 sin 2 2 x sin 2 x lt f ( x) lt lt lt 4 8 lt 8 2 2 2 x 0 x 0 x 0 x 0 2 x 0 x x 4x 2x f (0) a 8 2 Thoughts affecting the continuity while writing exam- ant two factors Lack of preparation, movement of students in the corridor, friend asking for answer, announcement of teacher regarding time, noise of the bell , any other distractions. The thoughts affecting continuity while writing exam are unavoidable at many occasions. We should learn and practice to avoid external disturbances and concentrate on our work to reach our goal. 21 Any point on the line x 1 y z 1 3 2 7 1 ½ 1 ½ Q(3 1,2 ,7 1) 1 P lies in the plane x + y – z = 8 1½ 3 1 2 7 1 8 3 , hence Q(-8,-6,-22) equation of line through P( 1 , 3 , 2), Q(-8,-6,-22) x x1 y y1 z z1 x 1 y 3 z 2 x 1 y 3 z 2 x x2 y y 2 z z 2 9 9 24 3 3 8 22 tan 1 1 y x dy 1 y 2 dx dx tan 1 y x dy 1 y2 dx tan 1 y x 2 dy 1 y 1 y2 ½ dx x tan 1 y dy 1 y 2 1 y 2 1 tan 1 y , Q 1 y2 1 y2 1 1 Pdy 1 y 2 dy tan y P e Pdy e tan 1 ½ y 1 solution: xe Qe Pdy xetan 1 y Pdy ½ dy C tan 1 y tan 1 y e dy 1 y2 8 RHS tan 1 y tan 1 y 1 y 2 e dy substitute tan 1 y t 1 dy dt 1 y2 tan 1 y tan 1 y t 1 y 2 e dy te dt int egration by parts u t du dt , dv e t dt dv e t dt v e t udv uv vdu te e dt te xetan 1 y e tan 1 y tan t t 1 y 1 C t e t e t t 1 e tan 1 y tan 1 y 1 1 ½ 23 ½ s r 2 Surface area = rl r l r 1 V r 2 h 3 2 ½ 2 1 2 4 2 1 2 4 2 1 2 4 s r 2 2 r 2 T r h r l r r 9 9 9 r 2 2 2 4 2 4 1 1 2 4 s 2 2sr 2 2 r 4 2 2 4 s 2 sr r r r r 9 r 9 2r 2 2r 2 s 2 2sr 2 1 1 2 2 1 2 2 2 4 T 2r 4 T r s 2 sr T s r 2sr 2 2 9 r 9 9 dT 1 2 2 s r 8sr 3 0 2s 2 r 8sr 3 S 4r 2 dr 9 9 2 1 s r 2 4r 2 r 2 3r 2 3r r r r r r 1 sin sin 1 l 3r 3 2 d T 1 2 1 2 1 2 4s 2 2 2 2 2 s 24 s r 2 s 6 s 4 r 2 s 6 s 0 max 9 9 9 dr 2 9 l The volume of the cone is maximum when sin 1 1 1 1 3 (OR) let length = breadth = x . height = h volume = 1024cm 3 lbh 1024 x 2 h 1024 h 1024 x2 10240 1024 C 52lb 2.502hl b C 10 x 2 5 2 2 x C 10 x 2 x x dC 10240 1 20 x 10240 2 0 20 x x 3 512 x 8 2 dx x x d 2C 20480 2 20 10240 3 20 0 min imum 2 dx x3 x 10240 =640 + 1280 = 1920 Least cost =10(64) + 8 24 1 1 2 1 1 x sin x dx 1 sin x 0 I ( x) sin( x) ( x) sin x dx dx 1 sin( x) 1 sin x 0 0 I 2I 0 sin x 1 sin x 1 dx sin x 1 sin x sin x1 sin x dx 2 1 sin x 1 sin x 1 sin x 0 0 ½ sin x1 sin x dx 2 cos x 0 ½ 2I 2I sin x sin 2 x sin x sin 2 x dx 0 cos 2 x cos 2 x d x cos 2 x 0 10 1 2 tan x sec x tan x) d x tan x sec x (sec 2 x 1) d x 0 0 1 2 I sec x tan x x0 sec sec 0 tan tan 0 2 I 1 1 2 I 2 2 2 (OR) I 2 x sin x 1 cos x dx 0 I 2 x x cos 2 2 dx 2 x 2 cos 2 x 2 sin 0 I 2 0 x x 2 2 cos 2 dx 2 2 x x cos 2 2 dx 2 x 2 cos 2 2 sin 0 1 I 2 1 ½ 2 x 0 x sec 2 dx 2 2 x tan 2 dx 1 0 x tan 2 dx Integration by parts 0 x 1 x u tan du sec 2 dx , 2 2 2 1 dv dx v x udv uv vdu 2 x x 1 2 tan 2 dx x tan 2 2 x sec 0 0 2 1½ 2 x dx 2 2 1 x x 1 x x 2 I x sec 2 dx x tan x sec 2 dx x tan tan 20 2 2 20 2 20 2 4 2 11 1 25 Point of intersection of x = 4y- 2 and x 2 4 y x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 0 ( x 2)( x 1) 0 x 1,2 1 1 Area of the shaded region 1 x2 x2 dx 4 4 dx 1 1 2 2 1 2 1 x2 x3 2x 4 2 3 1 26 1 1 8 1 2 22 1 4 2 3 3 1 3 1 3 1 9 9 6 3 3 square units 4 2 4 2 4 2 8 2 1 2 3 x 4 2 y 2 2 3 3 3 4 z 11 AX B A 1(6) 2(14) 3(15) 6 28 45 67 1 6 adjA 14 15 2 13 8 9 1 6 17 13 adjA 1 1 A 5 8 14 A 67 9 1 15 17 13 4 6 1 X A 1 B 5 8 2 14 67 9 1 15 11 201 3 1 134 2 67 1 67 x 3, y 2, z 1 17 5 12 ½ 1 1 ½ 27 Let A denote the missing card as red, B missing card as black, C denote the first 13 cards ½ drawn are red P( A) P( B) P B C 25 26 C C 26 1 C ,P 51 13 , P C 51 13 A B 52 2 C13 C13 B PB P C A PB PC B P ( A) P C 1 1 26C13 26! 51 26 2 C13 C13 13 !13! 2 25 25 26 26 25! 26! 3 C C C13 C13 1 1 51 13 51 13 13! 12! 13 !13! 2 C13 2 C13 If the probability rate is high the player decides to go for it in the game of gambling.But the success rate will not be constant. By understanding the imbalance between success and failure rate one should not go for gambling game. 28 1½ 2 1 Let the no of kilograms of fertilizer of type I used be x kg and type II be y kg Minimize : z= 2x + 3y 1 subject to 10 5 x y 14 10 x 5 y 1400 2 x y 280 100 100 6 10 x y 14 6 x 10 y 1400 3 x 5 y 700 100 100 1 x, y 0 1½ 13 corner points Z=2x+3y in rupees (100,80) 440------ minimum (0,280) 840 (700/3, 0) 1400/3 Hence 100kg of type I and 80 kg of type Ii have to be used to minimize the cost. Natural fertilizers- any two bird seed bags, seaweed, fish emulsion,seaweed,animals and human waste,earthworms,ashes,vegetable waste 29 1 ½ 1 Equation of plane passing through the points A ( 2 , 1 , 1) , B ( 1 , 2, 1 ) and C ( 1 , 1 , 2). x x1 x 2 x1 x3 x1 x2 1 1 y y1 y 2 y1 y 3 y1 z z1 z 2 z1 0 z 3 z1 1 y 1 z 1 1 0 0 0 1 2 x y z40 Equation of line from P (1,1,1) x 1 y 1 z 1 1 1 1 Q ( 1, 1, 1) 1 Q lies in the plane x + y + z – 4 = 0 1 1 1 4 0 1 3 1 0 3 4 4 4 foot of perpendicu lar is Q , , 3 3 3 ½ ½ distance from P(1,1,1,) on the plane x + y + z – 4 =0 111 4 3 1 1 3 14