Number System Unit Guide 2014
advertisement

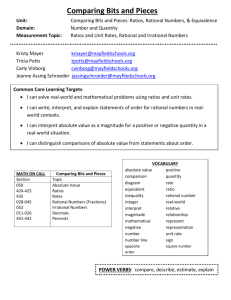
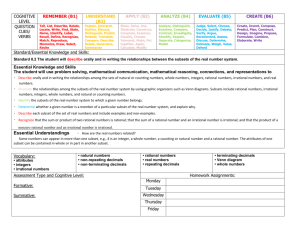
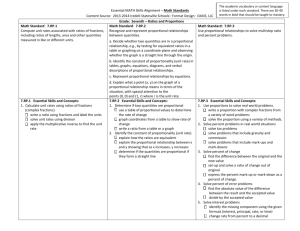
THE NUMBER SYSTEM Learning Targets Standard #s: Standards: Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract 7.NS.1 rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to 7.NS.2 multiply and divide rational numbers. Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational 7.NS.3 numbers. Computations with rational numbers extend the rules for manipulating fractions to complex fractions. Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal 8.NS.1 expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number. Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, 8.NS.2 locate them approximately on a number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions (e.g., π2). Unit Objectives: Students will be applying their prior knowledge of the number system to problems involving rational numbers. Students will be able to add, subtract, multiply and divide rational numbers. Students will transform rational numbers into decimals. Students will solve real world problems using rational numbers. Students will be able to find the squares and square roots of both rational and irrational numbers. Students will know the perfect squares. They will also be able to simplify perfect square radical expressions as well as non-perfect square radicands. Students will use the perfect squares to approximate square roots. VOCABULARY additive inverse property, rational numbers, opposite , integer , absolute value, properties of operations (associative, commutative, identity, distributive), terminating decimals, repeating decimals, complex fractions, order of operations, irrational numbers, real numbers, whole numbers, natural numbers, truncate, approximate, radicals, perfect square, perfect cubes, root, square root, radicand, estimate 1. Cooperation / Collaboration 3. Integrity / Attitude Listens and reflects Asks appropriate questions Takes leadership responsibilities Contributes as a group member Is adaptable Respects property, materials and classroom environment Demonstrates academic integrity Demonstrates ethical use of technology Demonstrates a positive attitude Respects self and others 2. Preparation / Organization Turns work in on time Prepares for tests/quizzes Brings required materials to class Keeps materials organized Is punctual 4. Active Learning / Effort Participates in class Reflects on learning to make improvements Uses class time effectively Explores possibilities and takes responsible risks Demonstrates persistence Works to best ability ------------------------------MY GOALS FOR THIS UNIT------------------------------Choose two goals for this unit of study. Use the Learning Behaviors listed above to help guide you in creating your two goals. Goal one: Goal two: Reporting Math Standards S1: Explains & applies concepts; interprets & carries out procedures Learning focuses on ● explaining and applying mathematical concepts; ● interpreting and carrying out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. S2: Uses knowledge & problem solving strategies to solve well-posed problems Learning focuses on: ● solving a range of complex well-posed problems; ● making productive use of knowledge and problem solving strategies. S3: Communicates & critiques reasoning Learning focuses on: ● clearly and precisely constructing viable arguments to support reasoning ● critiquing the reasoning of others S4: Models and analyzes data to interpret and solve real-world problems Learning focuses on: ● Analyzing complex, real-world scenarios; ● Constructing and using mathematical models to interpret and solve problems.