3.PSY 304 - MentalHealth
advertisement
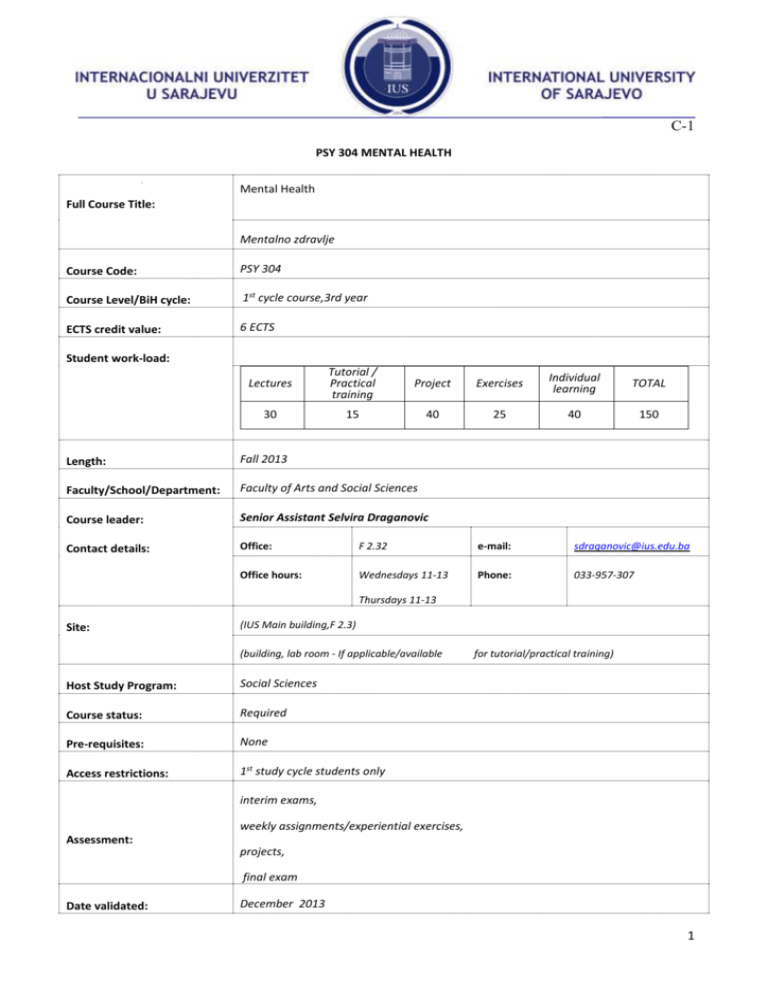
C-1 PSY 304 MENTAL HEALTH Mental Health Full Course Title: Mentalno zdravlje Course Code: PSY 304 Course Level/BiH cycle: 1st cycle course,3rd year ECTS credit value: 6 ECTS Student work-load: Lectures Tutorial / Practical training Project Exercises Individual learning TOTAL 30 15 40 25 40 150 Length: Fall 2013 Faculty/School/Department: Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences Course leader: Senior Assistant Selvira Draganovic Contact details: Office: F 2.32 e-mail: sdraganovic@ius.edu.ba Office hours: Wednesdays 11-13 Phone: 033-957-307 Thursdays 11-13 Site: (IUS Main building,F 2.3) (building, lab room - If applicable/available Host Study Program: Social Sciences Course status: Required Pre-requisites: None Access restrictions: 1st study cycle students only for tutorial/practical training) interim exams, weekly assignments/experiential exercises, Assessment: projects, final exam Date validated: December 2013 1 C-1 Course aims: Learning outcomes: Indicative syllabus content: The course is dedicated to the study of mental health, mental illness, mental distress and the manifestation of behaviours and experiences that may be indicative of mental health/ mental illness or psychological impairment. Multiple causality/ positive and negative factors are emphasized including various forms of mental health/illness. Understanding developmental perspective in MH, attachment, attitude and major forms of events and distress, including daily hassles, optimism/pessimism orientation, understanding emotions, communication patters, stress, grief and psychological disorders anxiety, mood disorders, eating disorders ‘On successful completion of this course the student will be able to explore basic differences between mental health and mental illness explore main causes of mental health problems describe basic symptoms of ill and positive mental health describe basic symptoms of various mental disorders describe an appropriate method for the scientific study of mental health. The course is dedicated to the study of mental health, mental illness, mental distress and the manifestation of behaviours and experiences that may be indicative of mental health/ mental illness or psychological impairment. Multiple causality/positive and negative factors are emphasized including various forms of mental health/illness. Understanding developmental perspective in MH, attachment, attitude and major forms of events and distress, including daily hassles, optimism/pessimism orientation, understanding emotions, communication patters, stress, grief and psychological disorders anxiety, mood disorders, eating disorders contributing to mental health/mental illness will be discussed. The format of the course will be didactic, experiential, and interactive. Assigned readings will be given weekly.) Learning delivery: lectures, exercises, case studies, projects, weekly assignment Assessment Rationale: (Briefly explain the reasons for the methods used. Precise assessment criteria need to be issued below for each assessment component/task set) Interim I 20%, Interim II 20%, weekly assignments/experiential exercises 10 %, Assessment Weighting: project 10%, class participation and in class activities 10%, Essential Reading: Recommended readings: final exam 30%) 1. Current Concepts of Positive Mental Health, 2. Promoting the emotional Well-being of Children and Adolescence Multidisciplinary Handbook of Child and Adolescent Mental health for front line professionals, 3. Clinical manual of prevention in mental health, Why Zebras don’t get ulcers, An updated guide to stress, stress related diseases and coping, Warning: Psychiatry can be hazardous to your Mental health ) Intranet web reference: N/A Important notes Course policy: (lateness in assignments /SS project submission and improper outlook will result in point deduction. What is meant by improper outlook: paper submitted without proper academic cover page, content, introduction, body, conclusion and 2 C-1 reference: where applicable. Workshops and in class activities will also be closely monitored- you can get 10% of your final mark for this activity. There will be no additional make up exams, works, assignments (except in cases where valid excuse applies: serious illness certified by a doctor). Students are expected to show academic integrity, professionalism, collaboration in assignments, attendance. Mission Statement: Let’s achieve positive mental health Quality assurance: (Ways of monitoring quality and complaints system) IUS quality management office, students evaluations, in class discuassions, e-mail, formal feedback from students, assistants and colleagues at the end of semester. Course schedule: 3 C-1 Week Lesson / Date Topics to be covered 1 01.10/13 Course introduction 2 08.10.13 Mental health /hygiene defined Mental health conceptualization Class activities Lab activities Course syllabus and content will be introduced to the students along with assessment components No lab activities Problems/ Readings Assignment s (Homework ) Current concepts of Mental Health by Jahoda Pp 3-20 Learning objectives (After this lesson student will be able to:) -define/Mental hygiene Positive mental health!? Differentiate between suitable and unsuitable conceptualizations of MH Mental health criteria Positive mental health_ 3 15.10.13 Psychological meaning of various concepts of mental health: 6 approaches to MH Multiple criteria for MH Mental health: Developmental perspective Current concepts of Mental Health by Jahoda Pp 20 -59 - name and define Psychological meaning of various criteria t: Attitude toward the Self, Growth, Development, Self actualization, Integration Autonomy, Perception of reality, Environmental mastery -name multiple criterion approach to MH and MD -name developmental perspective in MH 4 C-1 Attachment theory and mental health Formation of Attachment Interaction Internal working models and attachment Disorders of attachment – adolescence 4 22.10.13 5 29.10.13 6 05.11.13 1st Interim exam 7 Emotion regulation and mental health Physiology/feelings/expression Emotional differentiation and acknowledgement Self regulation, tolerance and management of emotions Desomatization and expression Utilisation and responding Enhancing emotional regulation Attention and mental health12.11.13 ADHD . Addiction as a mark of adulthood Autonomy / Youth movements Adolescent rebellion Attention through provocation The right to be Identify Promoting the emotional positive role Well-being of Children model in and Adolescence by Kedar your life Nath Dwivedi and Peter Brinley Harper, editors (2004), pp49-69 Identify 10 of your strengths and 10 weaknesses Promoting the emotional Well-being of Children and Adolescence by Kedar Nath Dwivedi and Peter Brinley Harper, editors (2004)pp 69-85 Why is empathy important? Promoting the emotional Well-being of Children and Adolescence by Kedar Nath Dwivedi and Peter Brinley Harper, editors (2004) pp 85 -101 -define Attachment -explain the role of different attachment styles in Mental health -explain disorders of attachment understand the difference between physiology, feelings and expression explain and differentiate various emotions -explain between regulation, tolerance and management of emotions Understand between emotional utilisation and responding -attention process and types understand developmental process of attention role of attention in MH Adolescence and attentional problems 5 C-1 misunderstood/mutual challenge 8 19.11.13 Parenting The Importance of Parenting in promoting posMH Quality in relationship??? “Good enough” Developmental needs in parents and children Enlist 3 unhealthy responses to difficult emotions like guilt and anger Promoting the emotional Well-being of Children and Adolescence by Kedar Nath Dwivedi and Peter Brinley Harper, editors (2004) pp113-132 What factors had infuelnced development of your personality the most? Promoting the emotional Well-being of Children and Adolescence by Kedar Nath Dwivedi and Peter Brinley Harper, editors (2004)pp 132-149 How do you react to constructive criticism or positive feedback? Promoting the emotional Well-being of Children and Adolescence by Kedar Nath Dwivedi and Peter Brinley Harper, editors (2004)pp149- 198 understand: The role of parents and parenting styles in MH Define quality relationship Developmental needs of parents and children and their role in MH Transition to parenthood 9 26.11.13 10 03.12.13 11 10.12.13 Life skills education through schools Critical thinking Creative thinking Problem solving Effective communication Interpersonal relationships Self awareness/ empathy/coping with emotions Anxiety, depression, eating disorders, conduct disorders/prevention and coping Emotional, cognitive, behavioural level Primary, secondary tertiary prevention Understand the role of education in development of life skills and their role in MH Understand major types of psychological disorders in adolescence -identify primary, secondary and tertiary MH prevention strategies 2nd INTERIM EXAM 6 C-1 12 17.12.13 13 24.12.13 14 22.01.14 15 Stress defined Why is stress so stressful Types of stress GAS stages of stress Coping with stress Promotion of pro-social development Protective and adverse factors relating to MH Temperament Character Personality What are your stress coping strategies? Lecturer’s Handouts What are risk and protective factors in your psychologic al well being? Multidisciplinary Handbook of Child and Adolescent Mental health for front line professionals pp- 21-79 Understand stress, its biological and psychological processes and their relation to mental and physical health -identify types and stages of stress Identify different coping strategies Understand the role of temperament, personality and character in mental health Enlist protective and risk factors in mental health FINAL EXAM 7







