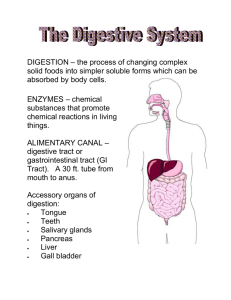
digestive system

EXPLORING THE BODY SYSTEM BY SYSTEM: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM:
(page 94, 127-130) Name: __________________________ 8___
LEARNING OUTCOME #3: INTERPRET THE HEALTHY FUNCTION OF HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS, AND ILLUSTRATE WAYS THE BODY
REACTS TO INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL STIMULI
3a) describe, in general terms, body systems for respiration, circulation, digestion, excretion and sensory awareness
3b) describe in general terms, the role of individual organs and tissues in supporting the healthy functioning of the human body
3c) describe ways in which various types of cells contribute to the healthy functioning of the human body
3d) describe changes in body functions in response to changing conditions
FUNCTION: break down food pieces into much ____________ particles so they can be
____________ and _____________________throughout the body. _______________ tissue lines all the inner organs.
1. You receive your energy from _____________ (sugars and starches), ____________ (fats and oils) and ________________.
2. There are two types of digestion: a) ____________________ digestion involves the physical breakdown of food. b) ___________________ digestion involves the use of ___________________ (saliva,
__________ enzymes and ____________).
Work through the stations to complete the following stages and types of digestion.
Fill in all the blanks and label the diagrams.
MOUTH: 2 TYPES OF DIGESTION
3. ________________ digestion begins in your mouth with your ____________by chewing food.
4. ________________ digestion also starts in your mouth but uses ___________________ to chemically break food down. ____________ is produced in 3 glands around your mouth. a.
Salivary enzyme digests large ____________ molecules into smaller ______________ molecules.
ESOPHAGUS: SWALLOWING
5. Food moves from the mouth to the stomach through the
_______________________.
6. The esophagus is made up of ___________ muscular tissue covered by _______________ tissue.
7. The esophagus moves food in wave-like movements called
____________________ caused by the contraction of the muscle tissue.
STOMACH:
Chyme is the partially digested food that is found in the stomach
8. ____________________ digestion continues with the muscular walls of the stomach churn food.
9. _______________ juices are secreted into the stomach from the ______________ _________.
GASTRIC juices composed of ____________, ______________ _________, _________ and the enzymes chemically digest the ________________ into smaller pieces.
10. The mucus prevents the gastric juices from _________________ the ____________.
SMALL INTESTINE
11. Only _____________________ digestion continues and the absorption of the tiny food molecules takes place.
12. _________________ produces and sends digestive enzymes into the small intestine.
The enzymes produced in the walls of the small intestine and the pancreatic juices
(enzymes) complete the breakdown of _____________________ and ___________________ .
The pancreas also produces insulin, which is responsible for regulating carbohydrate and fat metabolism (blood sugar) in the body.
13. The liver produces _____________ that is stored in the _______ _________. The bile is sent to the small intestine to breakdown large globules of _______________ (fats and oils) into smaller droplets.
14. The surface area of the small intestine is increased by small, finger-like projections called __________________. This helps in the absorption of nutrients into the
__________________ tissue and then into the _________________.
15. VILLI: and MICROVILLI are covered with _________________ tissue.
Color the blood red. Show how nutrients diffuse into the blood stream.
LARGE INTESTINE
16. Digestion is ___________________________.
17. Absorption of __________________ along with some ____________ and _____________.
18. Undigested food is formed into ___________ and collected in the _______________.
19. Stomach problems? An ulcer can affect the digestive system. What is an ulcer?
What is the cause of ulcers?
20. Other disease or problems with the digestive system:
What is celiac disease?
Celiac disease is a digestive disease that damages the small intestine and interferes with absorption of nutrients from food. People who have celiac disease cannot tolerate gluten, a protein in wheat, rye, and barley. Gluten is found mainly in foods but may also be found in everyday products such as medicines, vitamins, and lip balms.
When people with celiac disease eat foods or use products containing gluten, their immune system responds by damaging or destroying villi Without healthy villi, a person becomes malnourished, no matter how much food one eats.
What is chronic diarrhea?
Diarrhea is loose, watery stools. Chronic, or long lasting, diarrhea typically lasts for more than 4 weeks. Children with chronic diarrhea may have loose, watery stools continually, or diarrhea may come and go. Chronic diarrhea may go away without treatment, or it may be a symptom of a chronic disease or disorder. Treating the disease or disorder can relieve chronic diarrhea.
What is Crohn's disease?
Crohn's disease is a chronic, or long lasting, disease that causes inflammation —irritation or swelling—in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Most commonly, Crohn's affects the small intestine and the beginning of the large intestine. However, the disease can affect any part of the GI tract, from the mouth to the anus.
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory disease of the GI tract, called inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
What are foodborne illnesses?
Foodborne illnesses are infections or irritations of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract caused by food or beverages that contain harmful bacteria, parasites, viruses, or chemicals. The GI tract is a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus. Common symptoms of foodborne illnesses include vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, and chills.
Most foodborne illnesses are acute, meaning they happen suddenly and last a short time, and most people recover on their own without treatment. Rarely, foodborne illnesses may lead to more serious complications.
What is GER?
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) occurs when stomach contents flow back up into the esophagus —the muscular tube that carries food and liquids from the mouth to the stomach.