Biology: Fermentation, Cell Division, Mitosis, Meiosis Study Guide
advertisement
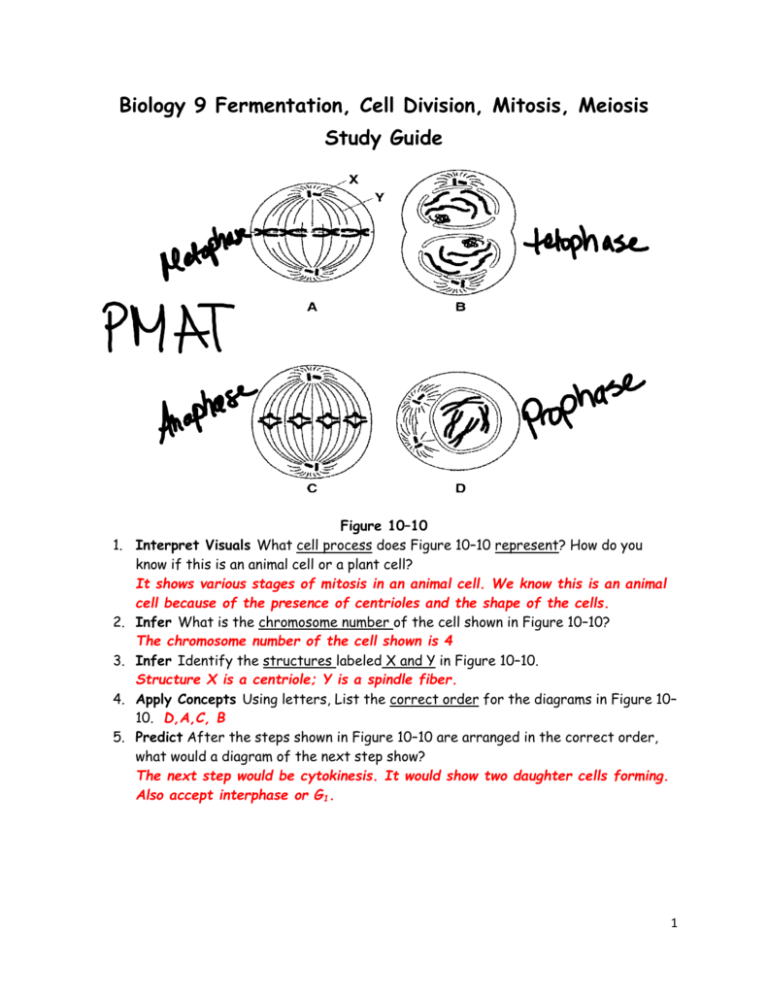
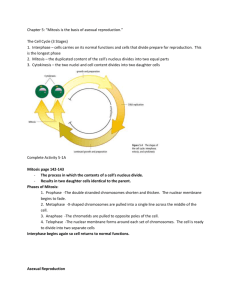
Biology 9 Fermentation, Cell Division, Mitosis, Meiosis Study Guide 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Figure 10–10 Interpret Visuals What cell process does Figure 10–10 represent? How do you know if this is an animal cell or a plant cell? It shows various stages of mitosis in an animal cell. We know this is an animal cell because of the presence of centrioles and the shape of the cells. Infer What is the chromosome number of the cell shown in Figure 10–10? The chromosome number of the cell shown is 4 Infer Identify the structures labeled X and Y in Figure 10–10. Structure X is a centriole; Y is a spindle fiber. Apply Concepts Using letters, List the correct order for the diagrams in Figure 10– 10. D,A,C, B Predict After the steps shown in Figure 10–10 are arranged in the correct order, what would a diagram of the next step show? The next step would be cytokinesis. It would show two daughter cells forming. Also accept interphase or G1. 1 Figure 10–8 6. Identify the structure labeled A: Structure A is the Cell Plate Figure 10–7 7. Identify the phase of mitosis in each step. A interphase, B prophase, C metaphase, D Anaphase, E Telophase, F cytokinesis 8. Prokaryotes reproduce by an asexual process known as binary fission. 9. Distinguish between sexual in asexual reproduction in terms of the type of offspring produced. During sexual reproduction, cells can produce genetically different offspring, whereas during asexual reproduction, cells produce genetically identical offspring. 10. How do the number of chromosomes found in gametes compare to the number of chromosomes found in body cells? An organism’s gametes have half the number of chromosomes found in the organism’s body cells. 2 Figure 9–4 11. Identify each of the pathways in figure 9-4. Pathway A – Lactic Acid Fermentation, B – Alcoholic Fermentation, C – Cellular Respiration 12. Name 3 problems that growth causes cells. 1) Difficulty taking nutrients in, difficulty removing wastes, & too much demand on cell DNA 13. Name the phases of mitosis in correct sequence Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase 14. What are the 2 main types of fermentation? The 2 main types of fermentation are alcoholic and lactic acid 15. Where does lactic acid fermentation occur? Lactic acid fermentation occurs in body’s muscles 16. What process causes bread dough to rise, and gives bread a spongy texture? Alcoholic fermentation is responsible for bread dough rising 17. How does the body continue producing ATP beyond 90 seconds of activity? The body continues to generate ATP through cell respiration 18. As a cell grows larger – what happens to the cells volume compared to its surface area? As a cell grows larger, its volume increases faster than its surface area 3 19. Asexual and Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Advantage: Genetic diversity Fast reproduction; more numerous offspring Disadvantage: Longer process Lacks genetic diversity – may limit ability to adapt to changing environment Similarities Both produce offspring and pass genetic information from parent to offspring Differences 2 parents; genetically different offspring Single parent; genetically identical offspring 20. Cell Cycle Cell grows – Letter A G1 DNA is copied – Letter B S G2 Cell continues to grow; prepares for mitosis – Letter C M P- prophase M- metaphase Letter D A- anaphase T- Telophase Cytoplasm splits – Letter D Cytokinesis Figure 10–3 21. What process produces gametes? Gametes are produced through a process called meiosis Figure 11–4 22. What process is occurring in figure 11-4 Crossing-over occurs during prophase I 4 23. Through what process and during which phase do chromosomes form tetrads? During Meiosis I, prophase I – homologous chromosome pairs form tetrads 24. What is formed at the end of meiosis? Meiosis results in the formation of 4 haploid cells. Mitosis Meiosis Form of reproduction Number of daughter cells Change in chromosome number Number of cell divisions Difference in alleles between parent cell and daughter cells 5