Life cycles 2 Text Resource
advertisement

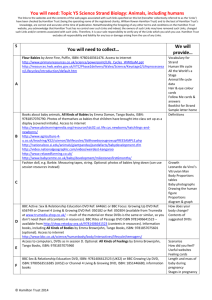
From William Shakespeare's As You Like It All the world's a stage, And all the men and women merely players: They have their exits and their entrances; And one man in his time plays many parts, His acts being seven ages. At first the infant, Mewling and puking in the nurse's arms. And then the whining school-boy, with his satchel And shining morning face, creeping like snail Unwillingly to school. And then the lover, Sighing like furnace, with a woeful ballad Made to his mistress' eyebrow. Then a soldier, Full of strange oaths and bearded like the pard, Jealous in honour, sudden and quick in quarrel, Seeking the bubble reputation Even in the cannon's mouth. And then the justice, In fair round belly with good capon lined, With eyes severe and beard of formal cut, Full of wise saws and modern instances; And so he plays his part. The sixth age shifts Into the lean and slipper'd pantaloon, With spectacles on nose and pouch on side, His youthful hose, well saved, a world too wide For his shrunk shank; and his big manly voice, Turning again toward childish treble, pipes And whistles in his sound. Last scene of all, That ends this strange eventful history, Is second childishness and mere oblivion, Sans teeth, sans eyes, sans taste, sans everything. © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 - Sc – Human Reproduction & Relationships - Session A2 We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites Animal Life Cycles Stages Animal Human Dog Cat Field mouse African elephant Tiger Fox Giraffe Wolf Chimpanzee Grey squirrel Horse Humpback whale Dolphin Sheep Pig Hamster Gestation period (days) 267 63 62 25 640 100 52 450 69 237 44 337 350 276 148 113 16 Average life span (years) 75 12 14 2 60 25 10 25 16 45 6 20 50 20 12 13 3 Useful websites: http://www.ypte.org.uk/animal-facts.php http://web.archive.org/web/20130816140543/http:/www.ngflcymru.org.uk/vtc/ngfl/science/10/Animal%20life%20cycles/Animal%20Lifecycles.pp tl PowerPoint presentation http://www.oum.ox.ac.uk/thezone/animals/life/produce.htm www.sharktrust.org/do_download.asp?did=27356 includes detail of shark life cycle © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 - Sc – Human Reproduction & Relationships - Session A2 We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites Follow Me Cards What is the name given when seeds produce tiny shoots and roots? To stop them becoming extinct Which three conditions are needed for seeds to start growing? Pollen and ovule Which part of the flower produces pollen? Extinct What pollinates a dandelion flower? Germination © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 - Sc – Human Reproduction & Relationships - Session A2 We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites Name the male part of a flower Petals Name the female part of a flower Air, water and warmth (not light) Which part of the flower attracts insects? Adolescent/ puberty How are the seeds Robin, alligator and of a strawberry turtle dispersed? © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 - Sc – Human Reproduction & Relationships - Session A2 We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites How are the seeds of a sycamore tree dispersed? Stamen/anther How is a coconut or water lily fruit dispersed? Fertilisation What do we call the spreading out of seeds from the parent plant? Stigma How are the seeds of goose grass or burdock dispersed? Ovary/carpel/ stigma © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 - Sc – Human Reproduction & Relationships - Session A2 We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites How are the seeds of lupins or gorse dispersed? Insect e.g. bee What do we call the joining of a pollen grain with an ovule? Metamorphosis What comes between a child and an adult in the human life cycle? By wind What do we call an animal that has died out altogether? Hooked onto animal fur © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 - Sc – Human Reproduction & Relationships - Session A2 We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites How long does a human baby take to develop before it is born? By water How long does a field mouse baby take to develop before it is born? By explosion What do we mean by the gestation period of an animal? Stamen/anther What is the scientific name for the place where a baby develops? 9 months/40 weeks © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 - Sc – Human Reproduction & Relationships - Session A2 We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites What do we call the sticky or hairy part of the flower where pollen lands? Pollination How long does an African elephant baby take to develop before it is born? Seed dispersal What do we call the transfer of pollen from one flower to another? 25 days © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 - Sc – Human Reproduction & Relationships - Session A2 We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites Why are lots of flowers brightly coloured? Frogspawn (eggs), tadpole, tadpole with legs, frog What does the The time taken for ovary of a flower a baby to develop contain? in the uterus What do we call the process of To attract insects transformation for pollination from a tadpole to a frog? © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 - Sc – Human Reproduction & Relationships - Session A2 We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites Name the two things which join to make a seed? Uterus/womb Which needs caring for the longest: calf, puppy or human baby? Egg, caterpillar, pupa, butterfly Name the four stages of a butterfly life cycle Ovules © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 - Sc – Human Reproduction & Relationships - Session A2 We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites Give three examples of young animals that are laid as eggs Human baby Why is it important for organisms to reproduce? By birds or animals (in their poo) Name the four stages of the life cycle of a frog 640 days © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 - Sc – Human Reproduction & Relationships - Session A2 We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites Follow Me Answers What is the name given when seeds produce tiny shoots and roots? Which three conditions are needed for seeds to start growing? Which part of the flower produces pollen? Germination Air, water and warmth (not light) Stamen/anther What pollinates a dandelion flower? Insect e.g. bee Name the male part of a flower Stamen/anther Name the female part of a flower Ovary/carpel/ stigma Which part of the flower attracts insects? How are the seeds of a strawberry or dispersed? How are the seeds of a sycamore tree dispersed? How is a coconut or water lily fruit dispersed? What do we call the spreading out of seeds from the parent plant? How are the seeds of goose grass or burdock dispersed? How are the seeds of lupins or gorse dispersed? What do we call the joining of a pollen grain with an ovule? What comes between a child and an adult in the human life cycle? What do we call an animal that has died out altogether? How long does a human baby take to develop before it is born? How long does a field mouse baby take to develop before it is born? What do we mean by the gestation period of an animal? Petals By birds or animals (in their poo) By wind By water Seed dispersal Hooked onto animal fur By explosion Fertilisation Adolescence/puberty Extinct 9 months/40 weeks 25 days The time taken for a baby to develop in the uterus © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 - Sc – Human Reproduction & Relationships - Session A2 We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites What is the scientific name for the place where a baby develops? What do we call the sticky or hairy part of the flower where pollen lands? How long does an African elephant baby take to develop before it is born? What do we call the transfer of pollen from one flower to another? Why are lots of flowers brightly coloured? What does the ovary of a flower contain? What do we call the process of transformation from a tadpole to a frog? Name the two things which join to make a seed? Which needs caring for the longest: calf, puppy or human baby? Name the four stages of a butterfly life cycle Give three examples of young animals that are laid as eggs Why is it important for organisms to reproduce? Name the four stages of the life cycle of a frog Uterus/womb Stigma 640 days Pollination To attract insects for pollination Ovules Metamorphosis Pollen and ovule Human baby Egg, caterpillar, pupa, butterfly Robin, alligator and turtle To stop them becoming extinct Frogspawn (eggs), tadpole, tadpole with legs, frog © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 - Sc – Human Reproduction & Relationships - Session A2 We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites Some Mammal Babies Kangaroos A kangaroo is born very tiny – the size of a jellybean! It then crawls up its mother’s belly, clinging to her fur and down inside her pouch. This pouch is like a furry bag on the outside of the mother kangaroo’s belly. The joey (this is what baby kangaroos are called) immediately finds, then attaches its mouth to the mother’s teat for food. It stays inside the pouch for 7 – 10 months. The mother lets the joey fall out. It only stays out for a few minutes, though, before jumping back in! For the next few months it spends more time inside the pouch than out. When it is out of the pouch it stays very close to the mother and, if scared, jumps back into the pouch headfirst! The mother carries the joey around with her and the joey continues to suckle until it becomes too heavy for the mother. Dolphins Dolphins are born tail-first so that they don’t drown. Often the mother is helped by another dolphin, which pulls the baby out of the mother by its tail and takes it straight up to the surface of the water so that it can breathe. The dolphin calf nurses from its mother for about one and a half years. It drinks her milk about four times an hour, though only quickly each time. In one year the dolphin calf grows 7 times its birth weight because the dolphin mother’s milk is rich in fat. The young dolphin stays with its mother for 3 – 6 years. Bats Bats are unusual as they are the only mammals that can fly. When the mother is ready she hangs head up, rather than upside down, and as the baby bat emerges she catches it with her tail! She licks it to free its wings and legs, which are stuck to its body. Its eyes are closed for the first day, and it is quite naked for the first several days. Within a week the baby bat is carried on the nightly hunts by its mother; it grasps her fur and feeds at one of her two nipples. After two or three weeks the adults share their food with the baby, and after five weeks the young bat will be able to hunt on their own. They are fully-grown after ten weeks and could live to be between ten and twenty years old. © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 - Sc – Human Reproduction & Relationships - Session A2 We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites Booklist for Strand It’s so Amazing (ages 7 & up) by Robie H Harris, Walker Books ISBN 0763613215 Let’s Talk about where Babies come from by Robie H Harris, Walker Books ISBN 9781844281732 (same as above) It’s Perfectly Normal (same series ages 10 & up) by Robie H Harris, Walker Books ISBN 0763624330 Let’s Talk about Sex by Robie H Harris, Walker Books ISBN9781844281749 (same as above) How Did I begin? by Mick Manning & Brita Granström, Franklin Watts ISBN 9780749656614 Osborne Facts Of Life: Growing Up by Susan Meredith, ISBN 9780746031421 Puberty and Your Body by Alison Cooper, Wayland ISBN 9780750250887 What’s Happening to Me? by Peter Mayle, Lyle Stuart ISBN 0818403128 Where Did I Come From? by Peter Mayle, Macmillan ISBN 0230015492 Where Willy Went… by Nicholas Allan Red Fox, ISBN 9780099456483 Usborne Facts of Life: Growing Up by Susan Meredith, Usborne ISBN 9780746031421 Hair in Funny Places by Babette Cole, Red Fox ISBN 9780099266266 Mummy Laid an Egg by Babette Cole, Red Fox ISBN 978-0099299110 Flour Babies by Anne Fine, Puffin ISBN 978-0140361476 Drama Flour Babies by Anne fine with resources by Rachel O’Neill, Collins ISBN 0003303128 (activities aimed at slightly older chn but could be read as a play in class) The World is Full of Babies! by Mick Manning & Brita Granström, Franklin Watts Ltd ISBN 0749627522 In the News: HIV & Aids by Andrew Campbell, Franklin Watts Ltd ISBN 0749657863 Ceremonies and Celebrations: Weddings by Linda Sonntag ISBN 0739832727 Rites of Passage: Weddings by Paul Mason ISBN 043117721X Wedding Days: Celebrations of Marriage by Anita Ganeri ISBN 0237528436 Rites of Passage: Coming of Age by Mandy Ross ISBN 9780431177182 Ceremonies and Celebrations: Growing Up by Susan Behar ISBN 0750233079 or Special Ceremonies: Growing Up by Polly Goodman ISBN 9780750249737 We are Britain by Benjamin Zaphaniah and Prodeepta Das, Frances Lincoln ISBN 978-0711219021 © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 - Sc – Human Reproduction & Relationships - Session A2 We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites An example letter home to parents/carers Dear Parent/Carer, Sessions on Human Reproduction & Relationships As part of the school’s Science and PSHE programme your child is soon to receive lessons on human reproduction, sexual health, relationships and puberty, which will include videos from the BBC Sex & Relationships Education DVD/ BBC Growing Up DVD/ Channel 4 Living and Growing series * and input from the class teacher. Nowadays there is a vast amount of, sometimes confusing, information about relationships and sex on the internet, on TV, in magazines, etc which young people may have access to, and this can sometimes make an already confusing time seem even more complicated! If young people can start their transition into adulthood with good information and the confidence and knowledge to understand what is happening to them, they will hopefully grow into confident and healthy adults able to make positive choices. This can start with learning the basics about growing up and the sessions in school may reinforce what you are already doing at home. Human reproduction, sexual health, relationships and puberty education are important issues which concern us all. The sessions will include work about (fill in information about the topics you will be addressing). As with all areas of the Curriculum teachers aim to answer children’s questions in a frank and honest manner and are best placed to decide at what level any discussion should be aimed for the class as a whole, small groups or the individual children. We would welcome your support in the successful delivery of this programme. Please feel free to contact the class teacher (insert name here instead) if you have any concerns or queries. If you wish to withdraw your child from some of the Sex Education Sessions, please contact the Headteacher so that appropriate arrangements can be made. Yours faithfully * delete as appropriate You may wish to include a slip for parents/carers to sign to show they have read this letter. © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users Y6 - Sc – Human Reproduction & Relationships - Session A2 We refer you to our warning, at the top of the You Will Need document, about links to other websites