How is Soil Made
advertisement

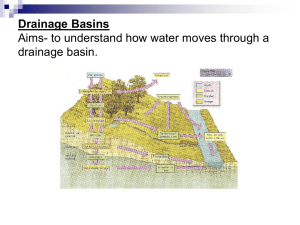
Soil Note Guide #2 – How is Soil Made? I. II. Soil is made from weathered rock fragments a. Parent rock – the source of mineral fragments which make soil (what gets broken down to make soil) i. Chemical weathering: During this process, the mineral composition of the rock is changed due to the influence of water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. 1. Example: Feldspar changes to clay 2. Example: Acid rain dissolves calcite in limestone a. Leading causes are emissions from factories, coal fire power plants and automobiles ii. Mechanical weathering: The breakdown of rock into smaller pieces by physical means. 1. Example: River breaks down rock 2. Example: Tree roots widen cracks in rock b. Bed rock – layer of rock beneath the soil i. Residual soils - stay on top of the parent rock (in this case, the parent rock IS the bedrock) ii. Transported soils – Blown or moved away from parent rock (in this case, the parent rock and the bed rock are DIFFERENT) 1. Can be moved by a. Wind b. Water c. Glaciers All Soils are Not the Same – Soil Properties a. Soils created by different parent rock have different minerals b. Texture – the AMOUNT of sand, silt, or clay particles i. Impacts infiltration 1. Definition: The process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil 2. Clay has low infiltration 3. Sand has high infiltration c. Structure – the ARRANGEMENT of sand, silt, or clay particles i. Impacts infiltration 1. Blocks or plates of soil make it more difficult for water to penetrate the soil’s surface! 2. Granular soil high higher infiltration d. Fertility i. Definition: Soil with the ability to hold nutrients and pass them on to a plant. ii. Soil nutrients come from 1. Parent rock 2. Humus – Dark, organic material formed in soil from the decayed remains of plants and animals a. Humus is broken down by decomposers i. Fungi ii. Bacteria e. Horizons i. Definition: A layer in a soil profile 1. MATCH THE LAYERS TO THE PICTURE (*hint* they are NOT in alphabetical order!) O – leaf litter and animal scat, _A – Topsoil contains nutrients for plants E – Lots of leaching (removal of nutrients due to passing water) B – Collects the dissolved substances from upper horizons C – Partially weathered bedrock R – Bedrock with little to weathering E – Lots of leaching (removal of nutrients due to passing of water) R – Made of bed rock that has little or no weathering B – Collects the dissolved substances from upper horizons O- Present in forests; made of leaf litter and dead plants C- Partially weathered bed rock A – Topsoil (contains the nutrients for plant growth)