NEUROSCIENCE OPTION. Subtopic 4

NEUROSCIENCE OPTION. Subtopic 4- Neurotransmitters & Synapses
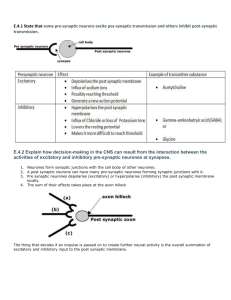
E.4.1 State that some pre-synaptic neurons excite post-synaptic transmission and others inhibit post-synaptic transmission.
This means that the neurotransmitter crossing the synaptic _________ to the next neurone can cause an action potential to be ___________, OR can ensure one is not ____________. This is decided by the type of
__________________ sent across the cleft.
E.4.2 Explain how decision-making in the CNS can result from the interaction between the activities of excitatory and inhibitory pre-synaptic neurones at synapses.
EXCITATORY NEUROTRANSMITTERS.
These neurotransmitters _____________ an action potential: they increase the permeability of the postsynaptic membrane to positive ions. This causes positive sodium ions (Na + ) which are in the synaptic cleft to ___________ into the postsynaptic neurone. The postsynaptic neurone is depolarized __________ (just in that area) by the influx of
____________ sodium ions.
During this depolarization, the inside of the neurone develops a net ___________ charge compared to the outside.
When the depolarisation is raised above _______________, an action potential begins.
INHIBITORY NEUROTRANSMITTERS
These cause ______________________ of the neurone, making the inside of the neurone more ____________, which makes it even more difficult for an action potential to be generated.
This is achieved in one of 2 ways:
the opening of ____________ channels, allowing negative chloride ions (Cl ) to enter the _____________ and making it hyperpolar.
K+ channels are opened, so ____________ potassium ions are moved _________ of the neurone, also resulting in hyperpolarization.
PUTTING IT TOGETHER
Each neurone can have synapses with hundreds of other neurons, receiving many excitatory and inhibitory ________.
The neurone sums up the signals, and will only __________ the action potential if the total sum is ____________. It is this interaction and summation of contradicting stimuli that is the way _______________ are made by the CNS.
E.4.3 Explain how psychoactive drugs affect the brain and personality by either increasing or decreasing post-synaptic transmission.
A drug can change post synaptic output by:
1.
___________ or ____________ the depolarising neurotransmitter
2.
Blocking or enhancing the ________________ neurotransmitter
This provides a complex of possible effects. The important issue however is to consider the type of
____________ in the post synaptic membrane and its associated ______________ effect on the mind.
The main neurotransmitters involved in psychoactive drugs are:
DOPAMINE
ACETYLCHOLINE
NORADRENALINE
GABA
1.
Psychoactive drugs are those that alter the state of mind by changing (stopping or enhancing ) the activity at the ______________________ neurone.
2.
Psychoactive drugs characteristically create either __________ or __________ moods.
NB: There are other ways to change transmission at the synaptic cleft but they involve the Presynaptic membrane and the enzymes that recycle neurotransmitter to the pre-synaptic membrane.
E.4.4 List three examples of excitatory and three examples of inhibitory psychoactive drugs.
E.4.5 Explain the effects of THC and cocaine in terms of their action at synapses in the brain.
Certain behaviours produce a pleasuable mood enhancing sensation. One of the causes of this natural 'high' mood is the secretion of the neurotransmitter ______________. Dopamine receptors are found in the post synaptic membrane which when activited ________________ the post synaptic neurone in regions of the brain associated with a feeling of _______________.
Cocaine
the drug attaches to the ___________ _________________ ___________
The recycling of dopamine is ____________ and it remains in the synaptic _______.
There is now a constant _____________ of the post-synaptic neurone (by the dopamine in the synaptic cleft)
Cocaine results in post synaptic excitement of cholinergic synapses which are associated will elevated levels of activity.
Cocaine is described as creating a mood of _____________.
Individuals show greater alertness / energetic behaviour/ very talkative
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC):
THC mimics the neuro-receptor _______________.
THC bonds to the post synaptic membrane for anandamide called the ____________ receptor.
The effect is to _________________ the post synaptic neurone.
THC is therefore a ______________ psychoactive drug
Cannabinol receptors are found at synapses in regions of the brain associated with short term memory, ____________ and ______________.
THC users report feeling ___________ and ________.
E.4.6 Discuss the causes of addiction, including genetic predisposition, social factors and dopamine secretion
Psychoactive drugs are often associated with ‘__________________. Addiction includes
____________ behaviour in which the drug taker:
__________ the use of the drug
Cannot exercise ______________in limiting the taking of the drug
Habituation means that increasing ______________ must be taken to achieve the same mental conditions.
Show side effects of talking the drug and _______________ behaviour if unable to satisfy the craving.
Other issues in addiction: