Notes
advertisement
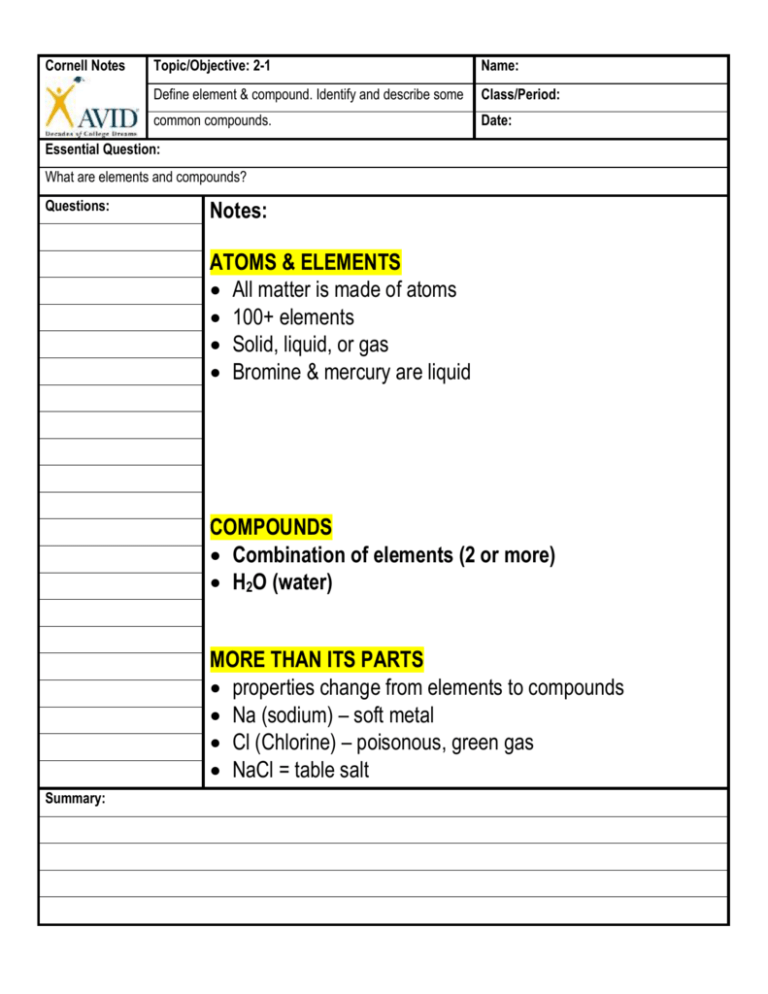
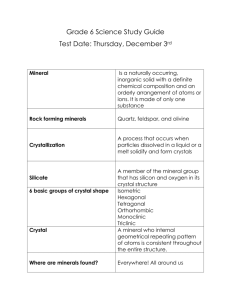
Cornell Notes Topic/Objective: 2-1 Name: Define element & compound. Identify and describe some Class/Period: common compounds. Date: Essential Question: What are elements and compounds? Questions: Notes: ATOMS & ELEMENTS All matter is made of atoms 100+ elements Solid, liquid, or gas Bromine & mercury are liquid COMPOUNDS Combination of elements (2 or more) H2O (water) MORE THAN ITS PARTS properties change from elements to compounds Na (sodium) – soft metal Cl (Chlorine) – poisonous, green gas NaCl = table salt Summary: Cornell Notes Topic/Objective: 2-2 Name: Interpret chemical symbols. Recognize common chemical formulas of some familiar compounds. Class/Period: Date: Essential Question: What are chemical formulas? Questions: Notes: CHEMICAL SYMBOLS Each element has a symbol Capital (H) or capital & lowercase (He) Not all from English names CHEMICAL FORMULAS Compounds have formulas Tells what’s in the compound NaCl (salt) H2O (water) SUBSCRIPTS Below the line (sub) After the symbol No subscript = ONE atom H = one hydrogen H2O = 2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen Summary: Cornell Notes Topic/Objective: 2-3 Name: Define mineral. Identify and describe some minerals Class/Period: Found in Earth’s crust. Date: Essential Question: What are minerals? Questions: Notes: EARTH’S CRUST Made of elements & compounds 75% silica (oxygen + silicon) Sand is silica in the form of quartz NATURAL SOLIDS Minerals are: Naturally occurring Solids Elements (gold, silver) or Compounds (quartz) NOT from living things (inorganic) Definite chemical make-up ROCK-FORMING MINERALS 2000+ minerals on Earth Only 20 common in Earth’s crust METAL MINERALS Resources – recovered for use Aluminum, copper, silver Useful - can be flattened, hammered, & stretched Summary: Cornell Notes Topic/Objective: 2-4 Name: Describe the properties that can be used to identify Class/Period: minerals. Date: Essential Question: How do we identify minerals? Questions: Notes: PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Used to ID minerals Color, streak, luster, hardness COLOR AND STREAK Color is NOT always the same (quartz – clear, purple, etc) Malachite – green (color), Azurite – blue (color) Streak – across a white plate Streak is always the same; Color can be different LUSTER 1. Metallic (shiny) 2. Nonmetallic (dull) 3. Waxy 4. Vitreous (clear, glassy) HARDNESS Resistance to being scratched Mohs’ Scale #1 Talc – softest #10 diamond – hardest Summary: Cornell Notes Topic/Objective: 2-5 Name: Explain how density, magnetism, and an acid test can be Class/Period: Used to identify minerals> Date: Essential Question: What are some other ways to identify minerals? Questions: 1. How can density be Used to identify minerals? 2. How could you use a Magnet to determine if an Unknown mineral is Magnetite? 3. What is the acid test? Summary: Notes: DENSITY Mass ÷ volume g/cm3 Always the same for a mineral MAGNETISM Iron, nickel, cobalt, or steel Ex: magnetite contains iron and is magnetic THE ACID TEST Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) will fizz Calcite & dolomite Cornell Notes Topic/Objective: 2-6 Name: Define crystals & show how they are related to minerals. Class/Period: Distinguish between fracture and cleavage in minerals. Date: Essential Question: What are crystals, cleavage, and fracture? Questions: Notes: 1. What is a crystal? CRYSTAL SHAPES All minerals are made of crystals 6 basic crystal systems 2. What is cleavage in Minerals? 3. How are fracture and Cleavage different? Summary: CLEAVAGE Smooth, flat planes Mica – thin, flat sheets Galena – cubes Feldspar – step-like cleavage FRACTURE Uneven surfaces Copper – hackly Obsidian – concoidal Asbestos – splinters Cornell Notes Topic/Objective: 2-7 Name: Describe the main ways minerals are formed. Class/Period: Date: Essential Question: How are minerals formed? Questions: 1. How are minerals and Rocks related? 2. How do crystals that Cool very slowly differ from Crystals that cool rapidly? Notes: MINERALS IN THE CRUST Earth’s crust is made of rocks and minerals MAGMA COOLING Magma is molten (melted) rock Slow cooling = large crystals Fast cooling = small crystals EVAPORATION Water evaporates and crystals remain Crystals grow together to form rock 3. How do crystals form Evaporated water? 4. What are chimneys? Summary: PRECIPITATION Warm solutions hold more As it cools, elements & minerals leave the solution They crystalize out as solids Cornell Notes Topic/Objective: 2-8 Name: State some common uses of minerals. Class/Period: Date: Essential Question: How are minerals used? Questions: 1. What are 2 minerals Used by the human body? 2. What is an ore? Notes: MINERAL USES Used in products o Talc – powder o Graphite – pencils Human Body o Calcium & phosphorous – bones & teeth o Iron – makes new red blood cells ORES Hematite – iron Bauxite – aluminum Halite - salt 3. What are three Precious stones? Summary: GEMSTONES AND GEMS Gemstones – beautiful and long-lasting Gems - cut and polished gemstones Precious stones – rare o Diamonds, rubies, sapphires, emeralds Semi-precious – more common o Opal, amethyst, topaz, garnet, aquamarine