AP exam review guide
advertisement

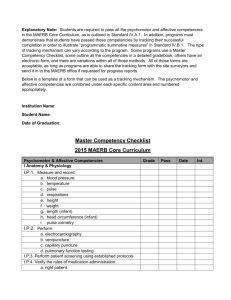
A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. 1. Earth Systems and Resources a. Chemistry i. What is an isotope? ii. What is an ionic compound, and what are some examples? iii. What is a covalent compound, and what are some examples? iv. What makes a chemical compound “organic”? v. What is an inorganic compound? Give examples. vi. What is a synthetic chemical? How many are there? How are they regulated? What do we know about the effects of these of humans? b. Earth Science Concepts: i. Geologic time scale ii. Plate tectonics iii. Earthquakes iv. Volcanism v. Seasons vi. Solar intensity vii. Latitude viii. Rock cycle (metamorphic, sedimentary, igneous rocks) ix. Crust x. Core xi. Mantle xii. Convergent boundary xiii. Divergent boundary xiv. Transform fault boundary xv. What is the composition of each of Earth’s layers? xvi. What is the practical significance today of the way Earth’s resources were distributed when the planet formed and cooled? xvii. What are some environmental consequences of the tectonic cycle? xviii. How and why do volcanoes and earthquakes occur? xix. What’s the difference between weathering and erosion? Why are both processes important? c. Atmosphere i. Atmospheric Composition iii. Climate ii. Weather iv. Coriolis effect A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. v. El-nino, La Nina, ENSO xii. Trade winds vi. Troposphere xiii. Westerly vii. Greenhouse effect xiv. Polar easterlies viii. Greenhouse gases xv. Doldrums ix. Convection Currents xvi. Jet Stream x. Precipitation xvii. Monsoon xi. Hadley Cell xviii. Rain shadow effect xix. How do winds and ocean currents transport nutrients and energy around the globe? xx. How do winds and ocean currents (gyres) transport pollution and waste? Where do they tend to concentrate? What does upwelling do for the oceans? xxi. Know the layers of the atmosphere and what occurs in each. temperature, ozone, d. Global Water, Surface Water, Resources and Use i. Freshwater xiii. Upwelling ii. Seawater xiv. Red tide iii. Watershed xv. Algal bloom iv. Estuary xvi. Groundwater v. Littoral zone xvii. Aquifer vi. Limnetic zone xviii. Ocean currents vii. Profundal zone xix. Water-stressed viii. Benthic zone xx. Water-scarce ix. Coastal zone xxi. Prior Appropriation x. Euphotic zone xxii. Coral reef xi. Bathyal zone xxiii. Epilimmion xii. Abyssal zone xxiv. Headwaters xxv. Discuss ways in which humans manage water distribution. xxvi. What are the major human uses of water? A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. xxvii. What factors will affect the future availability of water? xxviii. What are the natural sources of water on Earth? xxix. What are the primary repositories of fresh water on Earth? Which of these repositories is the largest? xxx. What’s the difference between a confined and an unconfined aquifer? How do their recharge rates differ? xxxi. How do human activities worsen the effects of droughts and floods? xxxii. How can desalination contribute to water supplies? What are the advantages and disadvantages? Where in the world is desalination widely used? xxxiii. Discuss the disadvantages of transporting large amounts of water (example: southern California) xxxiv. Absolutely be able to discuss 6-10 ways in which the average American can reduce their water consumption. xxxv. What are the advantages and disadvantages of large dams? xxxvi. How can corporate take over of water supplies affect the actual distribution? e. Soil and Soil Dynamics i. Silt vii. O,A,B,C horizons ii. Abiotic viii. Arable land iii. Biotic ix. Loamy soil iv. Clay x. Aggregates v. Sand xi. Monoculture vi. Physical, Chemical, Biological weathering xii. How do soils form? xiii. What are the roles of soils in the ecosystems? xiv. How do a soil’s physical and chemical properties influence its role as a medium for plant growth? xv. What role can alternating crops play in the quality of the soil? Specifically legumes. xvi. List some negative effects humans have had on the soils of the world. xvii. What factors caused the Dust Bowl of the 1930’s? A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. 2. The Living World a. Ecosystem Structure i. Habitat viii. Fundamental niche iii. Population ix. Symbiotic (parasitism, commensalism) iv. Community x. Predation ii. Niche v. Competition; interspecific intra and vi. Gause’s principal vii. Realized niche relationships mutualism, xi. Keystone species xii. Ecotones xiii. Biomes xiv. How do the terms “closed system/open system” apply to the cycling of matter and energy on Earth? xv. What are the different biomes around the world and what are the general characteristics of each? xvi. How does deforestation affect the ability of an ecosystem to function? b. Energy Flow i. Autotrophs x. Albedo ii. Heterotrophs xi. Decomposers iii. Producers xii. Trophic level iv. Chemotrophs xiii. Food chain v. Net primary productivity xiv. Energy pyramid vi. Gross primary productivity xv. Bioaccumulation vii. Primary consumers xvi. Biomagnification viii. Secondary consumers ix. Detritivores xvii. How does net primary productivity impact humans? Why is there a difference between GPP and NPP (where does that energy go)? xviii. Why is photosynthesis so important to us? A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. xix. How does the second law of thermodynamics apply to energy moving through an ecosystem? xx. Give an example of a toxin that biomagnifies. c. Ecosystem Diversity i. Biomes x. Macroevolution ii. Aquatic life zone xi. Bottleneck effect iii. Law of tolerance xii. Allopatric speciation iv. Law of the minimum xiii. Sympatric speciation v. Evolution xiv. Extinction vi. Phylogenetic tree xv. Provisions vii. Speciation xvi. Instrumental value viii. Species xvii. Intrinsic value ix. Microevolution xviii. Aesthetic value xix. What are the regulating services that nature provides? xx. What support systems does nature provide? xxi. What factors impact an ecosystems resilience? xxii. What is the theory of island biogeography? xxiii. Where are the greatest areas of biodiversity on Earth? d. Natural Ecosystem Change i. Ecological succession ii. Primary and succession iii. Climax community iv. Pioneer species v. Habitat fragmentation secondary vi. Edge effect vii. Endemic species viii. Indigenous species ix. Invasive species x. What were the effects of the 90’s fire at Yellowstone National Park? Why was this one incident such a great ecological study? xi. Be able to list at least 10 different invasive species and their impact on the environment? (Please include at least 5 Michigan specific examples) A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. e. Natural Biogeochemical Cycles i. Reservoir v. Precipitation ii. Exchange pool vi. Evaporation iii. Residency time vii. Transpiration iv. Conservation of matter viii. Carbon cycle 1. Respiration 2. Photosynthesis 3. Combustion 4. How are human actions impacting the carbon cycle? Specifically how does; a. combustion, b. deforestation, c. agriculture change carbon cycle? 5. Where are the largest carbon sinks on Earth? What’s happening to these specific areas? ix. Nitrogen cycle 1. Ammonia 2. Nitrates 3. Nitrification 4. Assimilation 5. Ammonification 6. How is nitrogen a limiting factor and what have humans done to change this? 7. What are the effects on the environment from artificial nitrogen fixation? 8. How can nutrient leaching effect the environment? x. Phosphorous cycle 1. Phosphate 2. Terrestrial cycle 3. Inorganic fertilizers A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. 4. What changes to the phosphorous cycle have human made? What are the affects of those changes? 5. How do excess nitrogen and phosphorous lead to cultural eutrophication? What are the issues with that? xi. Sulfur 1. Sulfur dioxide 2. Hydrogen sulfide 3. How does sulfur impact acid deposition around the world? f. Conservation i. What efforts are being done by individuals and governments to preserve biodiversity and ecosystems? 3. Population a. Population Biology Concepts i. Age-structure pyramids v. R-selected species ii. Carrying capacity vi. Competitive exclusion principle iii. Clumping dispersion vii. Predation iv. K-selected species viii. Parasites (pathogens) ix. How do populations and communities differ? x. Be able to discuss how size, density, and distribution all effect populations. xi. What’s the difference between density-independent and density-dependent factors? Give examples of both. xii. How can limiting factors affect a population? List some common limiting factors. xiii. What factors go into exponential growth? experiencing exponential growth? What eventually happens to all populations xiv. Be able to explain and give examples of predator-prey relationships. b. Human Population i. Birth rate iii. Ecological footprint ii. Death rate iv. Emigration A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. v. Immigration ix. Suburban vi. Founder effect x. Urban sprawl vii. Replacement birth rate xi. Urban blight viii. Total fertility rate xii. What is an age structure diagram? How do they differ for different populations (U.S. vs. India vs. China vs. African countries) xiii. What are the different survivorship curves and what factors of human society have influenced the changes experienced with survivorship? xiv. Be able to describe the governmental control efforts that have been made by China and India. What have been the effects of these efforts? xv. How does empower/educating women change the dynamics of population growth? xvi. What is “per capita”? When might this measurement be used? How does it apply to human population? xvii. What are the transitional stages of population growth with respect to developed countries? xviii. What is the rule of 70 and how do you use it? c. Sustainability i. What is meant by smart growth? Be able to give examples of things that make “smart growth”. ii. How does consumerism work against the idea of sustainability? Be able give examples of what multinational companies call “growth”. iii. How does microlending lead to sustainable growth? iv. Be able to explain inputs vs. outputs in a non-sustainable society vs. a sustainable society. v. What is stewardship? 4. Land and Water Use a. Agriculture i. Subsistence agriculture v. Plantation farming ii. Slash and burn agriculture vi. Overgrazing iii. Salinization vii. Green revolution iv. Monoculture viii. Contour plowing A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. ix. Intercropping x. What are the advantages and disadvantages of organic farming? xi. What are the advantages and disadvantages of local food production/consumption? xii. What’s the difference between malnourished, undernourished, over nourished? xiii. What are the advantages of polyculture? xiv. How does energy subsidies impact the global food chain? Specifically the U.S. and corn. xv. What are the different irrigation strategies? Which are the best? xvi. What is a “pesticide treadmill”? What does it result in? xvii. What is considered “conventional agriculture”? xviii. What is desertification? Why is it happening? xix. What are the goals of “alternative agriculture”? b. Forestry i. Old growth forest vii. Surface, ground, crown fires ii. Second growth forest viii. Conservation iii. Silviculture ix. Deforestation iv. Clear cutting x. Slash and burn v. Selective cutting xi. Tree farms vi. Agroforestry xii. How does the concept of maximum sustainable yield apply to forestry? xiii. What is the “resources conservation ethic”? xiv. What are the categories of public lands in the United States? xv. What does the term “multiple-use land” mean? xvi. What is ecologically sustainable forestry? xvii. What are the advantages and disadvantages of tree plantations? xviii. What is a prescribed burn? xix. What percent of old-growth forest is still present in the United States? A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. c. Rangelands i. What are CAFO’s? Why are they such a problem? ii. What are the effects of overgrazing? iii. What is the Taylor Grazing Act of 1934? d. Other Land use i. Terracing ii. Preservation e. Mining i. Renewable resource vii. Gangue ii. Nonrenewable resource viii. Tailings iii. Consumption ix. Underground mining iv. Production x. Overburden v. Ore xi. Strip mining vi. Metallic minerals and nonmetallic xii. What are the different types of mining and what are the impacts on the environment of each? xiii. What is a reserve, and how do we measure them? xiv. Why are economically valuable mineral resources distributed unevenly on the planet? xv. What are the consequences of surface mining versus subsurface mining, and how has mining legislation tried to reduce those impacts? xvi. Why is grass farming (grazing) better for the soil? xvii. What are some of the problems with abandoned mines? xviii. f. Fishing i. Fishery iv. Bottom trawling ii. Driftnets v. Aquaculture iii. Long lining vi. Coral bleaching A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. vii. By-catch viii. What is a “fishery collapse”? Give examples of where these have already happened. ix. What are some of the unintended side effects of aquaculture? g. Global Economics i. GDP iv. Incentive-based approach ii. GDI v. Green tax iii. Command-and-control approach vi. How does poverty and inequity impact the environment? 5. Energy Resources and Consumption a. Energy Concepts i. Potential energy iv. Conduction ii. Kinetic energy v. Convection vi. First and second law of thermodynamics vii. You are about to invest in a 66-inch flat screen TV. These TV’s come in both energy star and non-energy star models. The cost of electricity is $0.15 per kWH, and you expect to watch TV an average of 4 hours per day. iii. Radiant energy 1. The non-energy star model uses 0.5kW. How much will it cost you per year for electricity to run this model? 2. If the energy star model uses only 40 percent of the amount of electricity used by the non-energy star model, how much money would you save on your electric bill over 5 years by buying the efficient model? viii. What is thermal inertia? How does is apply to heating and cooling buildings? b. Energy Consumption i. Barrels c. Fossil Fuel Resources and Use i. Seam iii. Proven reserve ii. Exploratory well iv. Crude oil A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. v. Shale oil ix. Bituminous coal vi. Tar sand x. Lignite vii. Petroleum xi. Fly-ash viii. Anthracite xii. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each of the non-renewable energy sources? xiii. What is the difference between Commercial Energy Source vs. Subsistence Energy Sources? xiv. Know the history pattern of energy consumption within the United States. xv. What are the major categories of energy consumption in the United States? xvi. What are the most efficient uses of energy in terms of transportation? xvii. Be able to explain the process in which a power plant produces electricity. xviii. What are some ways in which we can increase the efficiency of “the grid” and energy consumption? xix. Where are the major fossil fuel reserves located around the world? xx. What’s Hubbert’s Curve? What’s peak oil? What does it tell us? xxi. What are the major fossil fuels, and what are each used for? d. Nuclear Energy i. Fission iii. Half-life ii. Nuclear fusion iv. Curie v. What are the major advantages and disadvantages of nuclear energy? vi. What’s the difference of fusion and fission? vii. How is the waste contained and stored? How long does it need to be stored for? e. Hydroelectric Energy i. How does hydroelectricity work? ii. Where are the major dams located around the world? iii. What are the disadvantages/advantages to large dams? iv. What is the term siltation and how does it apply to dams? A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. f. Energy Conservation i. Give at least 10 examples of how we can use less energy. ii. What is a tiered rate system? What markets would this work for? iii. What are 5 building techniques that can be implemented to make more efficient buildings? g. Renewable Energy i. Gasohol viii. Nacelle ii. Biodiesel ix. Turbine iii. Hydroelectric power x. Wind farm iv. Fish ladder xi. Geothermal energy v. Passive collection xii. Hydrogen cell vi. Active collection xiii. CAFÉ standards vii. Photovoltaic cells xiv. How does tidal energy work? What’s the ultimate source of this energy? xv. What’s the difference between “potentially renewable” and “nondepletable” resources? xvi. How can biomass be used for fuel? xvii. What’s the difference between modern carbon and fossil carbon? xviii. What is ethanol and what it is used for? Are there any disadvantages? xix. What is the most available renewable energy source and what are the limitations to it? Meaning why aren’t we using more of it? xx. What are the advantages and disadvantages of geothermal energy? xxi. What are the advantages and disadvantages of wind energy? xxii. What is a fuel cell and how does it work? 6. Pollution a. Pollution Types i. Air 1. Primary and secondary pollutants 2. Moving sources A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. 3. Stationary sources 8. Photochemical smog 4. Point source 9. Acid precipitation 5. Non-point source 10. Catalytic converter 6. Ozone 11. Volatile compounds 7. Industrial smog organic 12. Sick building syndrome 13. Know the major air pollutants and their effects on the environment. 14. Explain the difference between primary and secondary pollutants. 15. What is particulate matter and what are some of the possible effects? 16. What are the major sources of anthropogenic emissions? 17. What is a thermal inversion and how can this impact smog in a given area? 18. What are the major effects of acid deposition? 19. What are some of the ways air pollution can be reduced? 20. What are CFC’s, what is their impact on the environment, and what has been done to combat this problem? 21. Be able to list the major sources of indoor air pollution and the possible side effects of each. 22. What type of ultraviolet radiation is most strongly absorbed by ozone in the stratosphere? ii. Water 1. Dead zone 7. Wastewater 2. Hypoxic 8. Physical treatment 3. Eutrophication 9. Sludge processor 4. pH 10. Gray water 5. Dissolved oxygen 11. Primary, secondary, tertiary treatment 6. Turbidity 12. Identify major substances that pose hazards to humans and the environment. 13. What is wastewater and why is it an environmental hazard? A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. 14. What are the major steps and process involved in wastewater treatment? 15. How does oxygen-demanding waste impact the quality of the water? 16. Identify major pathogens that are of concern with water quality. 17. Be able to describe the parts and how a septic tank can be used to treat wastewater. 18. What is sludge and what typically happens to it? 19. What are manure lagoons and how can they lead to contamination? 20. What role does bacteria play in the process of water treatment? 21. How does acid rain impact the environment, and what are the sources for acid deposition? 22. Lead, mercury, arsenic are all water pollutants; what are the sources of these and what are the possible side effects? 23. What is a “green” wastewater treatment plant? What are the advantages of this type of system? 24. What organisms are extremely susceptible to water pollution? Why so? 25. What is BOD? 26. iii. Solid 1. Open-loop recycling 5. Leachate 2. Closed-loop recycling 6. Waste-to-energy programs 3. Composting 4. NIMBY 7. Heat island 8. What are some of techniques used to get rid of waste? 9. What are the advantages and disadvantages to landfills? Describe the basic design features taken into account when building a new landfill. 10. What is meant by the term “cradle-to-grave”? 11. How can “reduce, recycle, reuse” provide a major reduction is solid waste production? 12. What is the current trend of solid waste production in the United States? 13. What is e-waste? Why is it such a problem? What can be done to reduce the problem? A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. 14. What is composting? What are the advantages to it? Who can compost? 15. What are the possible harmful effects of leachate? 16. What is incineration? What are the advantages and disadvantages of incineration? 17. How much leachate might be collected? a. Annual precipitation at a landfill in the town of Fremont is 100mm per year, and 50 percent of this water runs off the landfill without infiltrating the surface. The landfill has a surface area of 5000m2. Underneath the landfill, the town installed a leachate collection system that is 80 percent effective. Any leachate not collected by the system enters the surrounding soil and groundwater. This leachate contains cadmium and other toxic metals. Calculate the volume of water in cubic meters (m3) that infiltrates the landfill per year. 18. What is a waste-to-energy program? What are some advantages of it? 19. What are brownfields? 20. What is a life-cycle analysis? 21. What is an Integrated Waste Management program? iv. Hazardous 1. Surface impoundment 2. Deep well injections 3. Transuranic waste 4. What is the “Love canal”? What is it an example of? Why did the corporation get away with contaminating the environment? 5. What is the “superfund” program? Who pays for it? b. Impacts on the Environment and Human Health i. Toxicity vi. Acute effect ii. Dose-response analysis vii. Chronic effect iii. LD50 viii. Disease iv. ED50 ix. Pathogen v. Poison x. Risk assessment A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. xi. Risk management xii. What is an “inert ingredient” and what can they cause? Be able to give an example. xiii. What are synthetic organic compounds and what are some possible side effects? Be able to list several of these. Specifically know about; a. perchlorates, b. PCB’s, c. PBDE’s, d. DDT. xiv. What are some possible problems associated with crude oil and the environment? Be able to list some possible ways to clean up an oil spill. xv. What are some of the impacts of thermal pollution? Where does this normally occur? xvi. What are some of the impacts of noise pollution? Where does this normally occur? c. Economic Impacts i. Cost-benefit analysis ii. Marginal costs and benefits iii. Externalities d. Recycling, Reducing, Reusing i. Natural services (biological services) ii. Be able to discuss many ecological services provided by nature and how they’re being impacted. 7. Global Change a. Stratospheric Ozone i. What’s the importance of the ozone layer? b. Global Warming i. IPCC iv. Carbon sequestration ii. Anthropogenic v. Kyoto accord iii. Greenhouse gases vi. Heat island vii. What are the possible implications of global climate change on drought, floods, famines? viii. What are the effects of unequal heating of the Earth? ix. What is adiabatic cooling and adiabatic heating? x. What is latent heat release and how does it impact the atmosphere? xi. What are the major greenhouse gases? What are the major anthropogenic sources of each? A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. xii. What are some natural sources of greenhouse gases? xiii. Be able to explain the connection between global increase in temperature and the increase in CO2. xiv. How can ice-core samples be used to measure CO2 levels? xv. What are some of the possible effects on the; a. polar ice caps, b. glaciers, c. permafrost, d. sea levels, e. precipitation patterns, f. storm intensity, g. ocean currents. xvi. What is the Kyoto protocol? xvii. What is carbon sequestration? xviii. What is “cap and trade”? c. Loss of Biodiversity i. What are the major causes for global loss of biodiversity? ii. Know and explain HIPPO. iii. Be able to list and describe the effects of at least 5 invasive species. iv. What is a biosphere reserve? How do they help with diversity? 8. Lab Concepts that need to be understood a. Soil i. Chemical properties (pH, Nitrogen, Phosphorous, Potash, type, water-hold capacity, permeability, friability, percent humus, buffering capacity) b. Water i. (pH, DO, turbidity, phosphate, BOD, chlorine, nitrates, dissolved solids, fecal coliform) c. Air i. (particulates, ozone, CO2, lichen, scrubbers) d. Biodiversity sampling i. (macroinvertebrates, trees, plants, birds, etc.) e. Mining i. Cost-benefit analysis of mining f. Tragedy of the commons A.P. Environmental Science Exam Vocabulary Review You should know these words extremely well, that means be able to use them in sentences and explain the meaning of each. This is the first step to being successful on the A.P. exam. Then you should answer all of these questions and be able to explain your answers to someone else. i. Over use of “commons”, know why this occurs and how to prevent it g. LD50 h. Gross and Net Primary Productivity i. Population Growth i. Bacteria bottle j. Variables, Graphs, Units 9. Real-world examples of Environmental Concepts a. Chernobyl d. Synfuels b. Tidal wave power being used in Portugal e. Dust bowl c. OTEC plant in Hawaii 10. Laws a. 1977 Soil and Water Conservation Act b. 1985 Food Security Act c. 1964 Wilderness Act d. 1968 Wild and Scenic Rivers Act e. 1976 Resource Conservation and Recovery Act f. 1982 Nuclear Waste Policy Act g. 1976 Toxic Substances Control Act h. 1970 National Environmental Policy Act i. 1990 Pollution Prevention Act j. 1990 Environmental Education Act k. 1978 Montreal Accord l. 1997 Kyoto Protocol f. United States peak-oil production g. Cancer alley