Subjects, verbs and sentences
advertisement

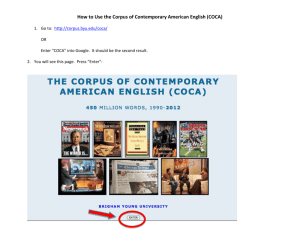
University of Guyana ENG1105 (2014-2015) Week one Subject of a sentence 1. What is the ‘subject’ of a sentence in English? The subject of a sentence is the ‘what’/’who’ the sentence is about. Identify the subjects of the sentences below. i. She had cut her hand. ii. One important benefit of this course is that it will help you write well for your other course assignments. iii. The man in the blue coat is my father. iv. It had been a very long day. v. The telephone rang all morning. vi. Children go to school early in the morning vii. Swimming is a good form of exercise viii. In Guyana, there are many automobiles. ix. Where did you put my coat? x. You need a pdf reader. xi. Come to class often. xii. You can come to class early. xiii. Mary and John walk a mile each day. xiv. Stop talking at once! xv. Studying can be very rewarding xvi. I left early because I needed to be there on time. Notice that there are different kinds of subjects (compound subjects, simple subjects, implied subjects). 2. What part of speech can the subject be? _______________________________ ENG1105 Information and notes. Prepared exclusively for students of Carolyn Cummings 2014/08/09 1 3. What is a verb? The verb of a sentence expresses action, state or possibility. Identify the verbs of the sentences above. Say whether they express action, state or possibility. 4. What is a sentence? A sentence must have a subject and a verb. It must also make sense. Identify the sentences below i. She had cut her hand. ii. One important benefit of this course. iii. The man in the blue coat. iv. A very long day. v. The telephone rang all morning. vi. They play. vii. The countries with the largest capital cities in Europe and Africa. viii. The woman with the bag in the elevator in the city mall. ix. Damon’s monument over the river in Essequibo Region two which is Anna Regina. x. I love fish. The number of words you may write do not determine whether or not you have written a sentence. A sentence must have a subject and verb. In English, sentences begin with capital letters and end with periods (‘fullstops’). A sentence may be: Declarative (statement) Interrogative (question) Imperative (command) Exclamatory Simple, Compound and Complex sentences A. Simple sentences ENG1105 Information and notes. Prepared exclusively for students of Carolyn Cummings 2014/08/09 2 A simple sentence consists of a single clause. A clause is a group of words that contains a subject and verb (just like a sentence). A clause may form part of a sentence or it may be a complete sentence in itself. E.g. it is raining B. Compound sentences Consists of two or more main clauses linked by a coordinating conjunction: E.g i. It is raining but I am still going out. i. I was born in Trinidad but I live in Guyana. ii. Would you prefer this one or do you prefer that? iii. Stop the talking and do your work. iv. Mary is young however she looks very old. Complex Sentences C. A complex sentence consists of a main clause and one or more subordinate clauses. Identify the main clauses/sentences i. I took the shoes back to the store because they were big ii. If the sun shines we will go to the party. iii. While you wait read a book. iv. We visited the factory where our mother works. v. While they sat in the car, the children ate mangoes which they got from their aunt. vi. Jenny phoned her parents as soon as she arrived vii. This is the house where my mother lived as a child. viii. These apples are cheaper than the ones I bought last week. ix. If you smell smoke, you must call the fire engine immediately. x. The address to which they were sent did not exist. Select the subordinate clauses and rewrite them Write 5 of each kind of sentence. ENG1105 Information and notes. Prepared exclusively for students of Carolyn Cummings 2014/08/09 3