TLM52 Cultures of English Language Teaching Title Cultures of
advertisement
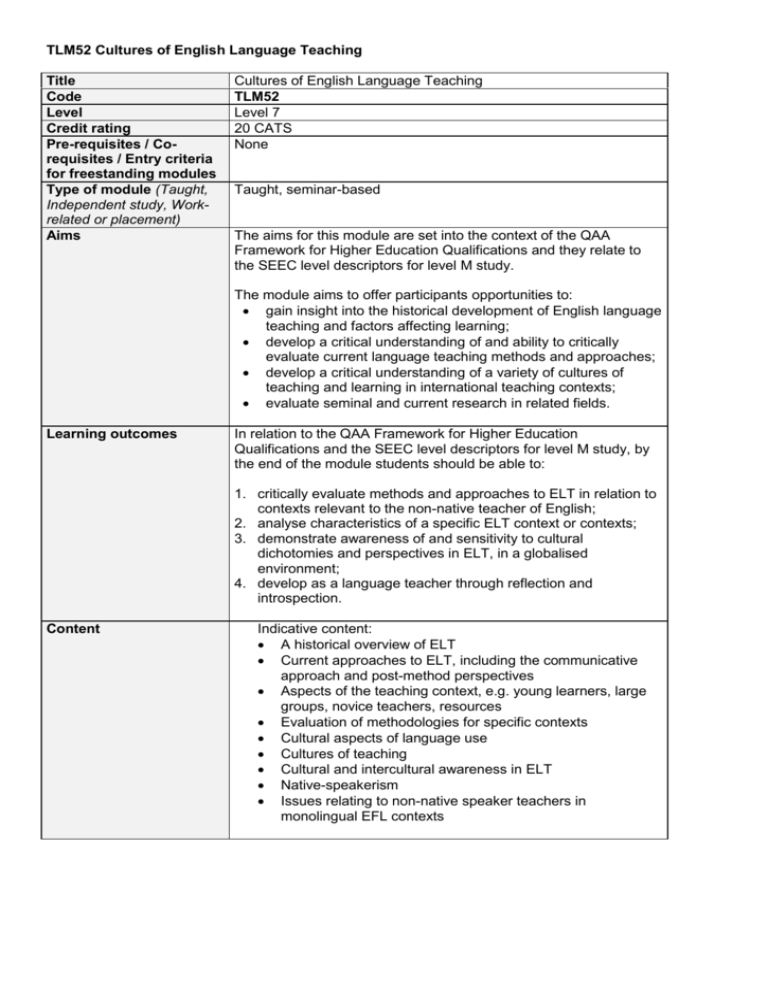
TLM52 Cultures of English Language Teaching Title Code Level Credit rating Pre-requisites / Corequisites / Entry criteria for freestanding modules Type of module (Taught, Independent study, Workrelated or placement) Aims Cultures of English Language Teaching TLM52 Level 7 20 CATS None Taught, seminar-based The aims for this module are set into the context of the QAA Framework for Higher Education Qualifications and they relate to the SEEC level descriptors for level M study. The module aims to offer participants opportunities to: gain insight into the historical development of English language teaching and factors affecting learning; develop a critical understanding of and ability to critically evaluate current language teaching methods and approaches; develop a critical understanding of a variety of cultures of teaching and learning in international teaching contexts; evaluate seminal and current research in related fields. Learning outcomes In relation to the QAA Framework for Higher Education Qualifications and the SEEC level descriptors for level M study, by the end of the module students should be able to: 1. critically evaluate methods and approaches to ELT in relation to contexts relevant to the non-native teacher of English; 2. analyse characteristics of a specific ELT context or contexts; 3. demonstrate awareness of and sensitivity to cultural dichotomies and perspectives in ELT, in a globalised environment; 4. develop as a language teacher through reflection and introspection. Content Indicative content: A historical overview of ELT Current approaches to ELT, including the communicative approach and post-method perspectives Aspects of the teaching context, e.g. young learners, large groups, novice teachers, resources Evaluation of methodologies for specific contexts Cultural aspects of language use Cultures of teaching Cultural and intercultural awareness in ELT Native-speakerism Issues relating to non-native speaker teachers in monolingual EFL contexts Learning and teaching strategies A series of seminar and workshop sessions, for which students are given pre-tasks and/or reading. In addition, follow-up reading is indicated. Student Central is used to deliver course materials and promote discussion before and after seminars, and to facilitate peer feedback. To help prepare assignments students are given individual and/or small-group tutorials. Students are encouraged to use library resources, including on-line resources, to read around the topics covered in the taught sessions. Peer support is encouraged, including the reading of drafts of writing. Learning support (ensure that all resources, including electronic sources, are fully referenced) Books: Bateman, B., Lago, B. (2011) Methods of Language Teaching DVD. London: Routledge. Breen, M. & Littlejohn, A. (Ed.) (2000) Classroom Decision-Making: Negotiation and Process Syllabuses in Practice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Burns, A., Richards, J.C. (2009) Cambridge Guide to Second Language Teacher Education. New York: Cambridge University Press. Ellis, R. (2003) Task-based language learning and teaching. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Hall, G. (2011) Exploring English Language Teaching. Abingdon: Routledge. Holliday, A. (2005) The struggle to teach English as an international language. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Kramsch, C. (1993) Content and culture in language teaching. Oxford: Oxford University Press. McDonough, J. & Shaw, C. (2002) Materials and Methods in ELT: A Teacher's Guide (2nd edition). Oxford: Blackwell. Richards, J.C. (2001) Curriculum Development in Language Teaching. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Richards, J.C., Renandya, W.A. (Eds.) (2002) Methodology in Language Teaching. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Richards, J.C., Rodgers, T.S. (2001) Approaches and Methods in Language Teaching (2nd edition). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Senior, R. (2006) The experience of language teaching, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Thornbury, S. (2006) An A-Z of ELT: A dictionary of terms and concepts used in English Language Teaching. Oxford: MacMillan e-journals available from online library: TESOL Quarterly The ELT Journal Language Learning Journal System Other journals: English Teaching Professional Teacher Training IATEFL Matters A variety of useful web-sites e.g. The British Council http://www.britishcouncil.org/new/ http://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/ Cambridge ELT http://peo.cambridge.org/ IATEFL http://www.iatefl.org/ Assessment task Assessment will be in the context of the University of Brighton Assessment Policy and the Faculty Code of Practice in Assessment, and students will be required to complete the following tasks: A portfolio (100%) 1. Critical reflection on own English language learning context (1,000 words) (LO2). 2. An essay (3,000 words) which critically examines an ELT ‘problem’ relevant to pedagogic decision-making in a specific international teaching context (LO1, LO3). The module pass mark is 50%. Referral task: Reworking of original task(s). Assessment criteria General criteria for assessment are framed by the SEEC descriptors (link to Learning Outcomes) for level M. Against specific criteria, credit will be awarded for: For the reflection: 1. in-depth understanding of the nature of a specific English language learning context; 2. critical appreciation of key influences on the learning experience; 3. awareness of the complexity of practical and cultural influences which have helped shape pedagogic choices. 4. in-depth and insightful reflection on own learning experiences. For the essay: 1. a critical understanding of a specific ‘problem’ relevant to a personal English language teaching context; 2. in-depth understanding of the nature of this English language teaching context; 3. critical appreciation of ELT methods and approaches and the principles underpinning them; 4. awareness of the complexity of cultural influences in global ELT. All learning outcomes must be achieved in order to pass the module at the threshold level. Brief description of module content and/or aims for publicity Area examination board Module co-ordinator Site where delivered Date of first approval Date of last revision This module is designed for aspiring English language teachers, who are non-native speakers of English, and who are interested in deepening their understanding of the historical development of ELT and of the cultures of teaching associated with it. There are opportunities throughout the module to reflect on personal learning histories and to engage with key issues of particular relevance to international ELT contexts and the experience of the non-native English language teacher. English Language and Linguistics Postgraduate Board Dr Angela Pickering and Barbara Chamberlin Falmer June 2002 Sep. 2010 Date of approval of this version Version number Replacement for previous module Route for which module is acceptable and status in Route (Mandatory, Compulsory or Optional) Course(s) for which module is acceptable and status in course (Mandatory, Compulsory or Optional) School home External examiner(s) April 2012 6 MA ELT (compulsory) MA TESOL (optional) MA TESOL with ICT (name change from MALT May 2014) (optional) MA ELT (compulsory) MA TESOL (optional) MA TESOL with ICT (name change from MALT May 2014) (optional) Humanities Dr Nick Andon (01/12/2013 to 31/12/2017)