article - Russian Urology Today
advertisement

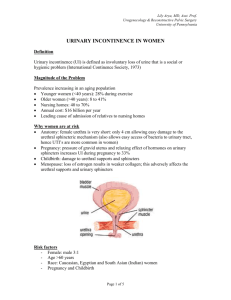
Abstract ID Number: AM15-3995 New Number: 383 Abstract Title: Magnetic resonance imaging in patients with stress urinary incontinence - new evaluation tools Authors: N. Tupikina 1, G.R. Kasyan 1, M.N. Barinova 2, B.N. Godunov 1, Y.A. Kupriyanov 1, D.Yu. Pushkar 1. (1) Moscow State University of Medicine and Dentistry, Dept. of Urology, Moscow, Russia, (2) Moscow State University of Medicine, Dept. of Radiology, Moscow, Russia Body: Introduction & Objectives The objective of this study was to clarify the role of MRI in evaluating anatomic abnormalities in patients with stress urinary incontinence (SUI). Material & Methods We performed MRI in 30 patients suffering from severe SUI. Static 2mm T2-weighted turbo spin-echo images were used in evaluating of structural derangements of the main supporting structures. Control group included 20 continent patients. For detailed assessment of urethral support disorders in women suffering from SUI, we draw on MRI image 2 lines through the bladder neck - along the axis of the proximal urethra and tangentially to the base of the bladder (the neck of the bladder during its dilation) with measuring posterior urethrovesical angle (β). The crossing of these lines with the longitudinal axis of the pubic formed a pubourethral triangle with vertex in the bladder neck. Then we dropped a perpendicular (pubourethral distance, h) from the bladder neck to the pubic side of triangle (a) and measured the area of this pubourethral triangle by formula S = ½ *a * h (Figure 1). Results The results showed statistically significant differences in the parameters of area pubourethral triangles in patients with SUI comparing with controls (152.09 ± 10.62 mm2 vs 242.71 ± 106.04 mm2 p = 0.0301), the length of the pubic side of the pubourethral triangle (a) (14.14 ± 5.04 mm vs 20.82 ± 7.69 mm, p = 0.0281) and value of posterior urethrovesical angle (152.09 ± 10.62⁰ vs 138.8 ± 12.59⁰, p = 0.0167, respectively). These data demonstrate the presence of defect of the front urethral support in women with SUI. Conclusions Position of urethrovesical segment plays an important role in the pathogenesis of stress urinary incontinence in women. Presented diagnostic system using pubourethral triangle assessment provides a new approach to the study the mechanisms of SUI development on the basis of anatomical and topographical features of the female urethra, which can serve as the beginning for the development of new methods of pathogenetic treatment of this nosology. The study was funded by the governmental grant, project МК-1921.2013.7