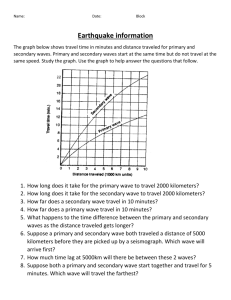
Earthquakes What is an earthquake? Earthquake= ground shaking
advertisement

Earthquakes What is an earthquake? What are the types of seismic wave? Earthquake= ground shaking as the result of plates sliding & colliding w/e@other Fault lines= cracks in the Earth’s surface where rocks slide against e@ other Release ++++ stored energy from rocks locked together @ a fault line Focus= the exact spot where rock breaks causing an EQ…underground Epicenter= spot on the surface above the focus (diagram) Seismic wave= energy wave of an EQ 3 types of seismic wave: 1) P wave= first wave of energy released (primary/pressure); fastest waves move like an accordion-in/out/in/outcompress/expand/compress/exp and 2) S wave= after P waves (secondary); side to side mvmt 3) Surface waves= P&S waves @ the epicenter out; roll like the ocean…Rayleigh waves move up and down & Love waves move side to side Which *from strongest to weakest* boundary has 1) convergent-subduction are deep the most and INTENSE!!! intense EQs? 2) convergent- mtn building are deep and intense!! 3) transform are shallow but can be intense-medium intensity 4) divergent are shallow and weak What are the 3 types of fault: different types 1) Normal fault= tension stress of faults? fault (pulling apart) Hanging wall goes down the footwall “Footwall plants it foot and stays put! Hanging wall moves!” 2) Reverse fault= compression stress fault (pushing together) Hanging wall moves up & over the footwall 3) Strike-slip fault= shearing stress fault (grating against e@ other…cheese grater) NO hanging or footwall b/c it doesn’t fall…it slides! (diagrams) How do seismologists measure and monitor EQ’s? EQs are unpredictable…can’t predict WHEN, but can predict WHERE SCALES to MEASURE: 1) Mercalli Scale= intensity @ a given place based on distance from the epicenter Seismic waves get weaker and weaker the farther away they go from the epicenter/focus Less damage farther away from the focus/epicenter 2) Richter Scale= magnitude of the seismic wave Good for small & close-by EQ Uses seismograph to measure wave magnitude…produces a seismogram=written record of the EQ (diagram) 3) Moment Magnitude Scale= rates the total energy released Combines data from seismographs, how much mvmt and strength of rocks that broke in the fault Rates ALL EQs ** regardless of the scale, the higher #’s mean more intense EQ!** ** each magnitude level is 10x energy/pwrful than the one before it TOOLS to MONITOR 1) Creep meter for horizontal mvmt 2) Tilt meter for up or down (vertical) mvmt 3) Laser-ranging device for horizontal mvmt 4) GPS for horizontal & vertical mvmt Find the epicenter by comparing the difference btwn p-wave & swave arrival at 3 seismographs. -the time difference = how far away the epicenter is from the seismograph -draw 3 circles & where they cross is the epicenter How do EQs cause death and destruction? (diagram) 1) Shaking ground will knock down buildings not built right Can fracture gas, water lines Knock down power poles which could start fires Could start a landslide/avalanche Soft/loose soil shakes more than solid rock so stuff built on soft/loose soil is damaged easier Buildings fall & people die 2) Liquefaction= water rising b/c of an earthquake’s shaking turning soft, loose soil into mud. Buildings sink into the mud, like quicksand ex: like swishing wet sand with your hand @ the beach 3) Tsunami= an ocean wave that gets bigger when it reaches shallow water Caused by an epicenter on the ocean floor @ a subduction zone Flick of the nonsubducting plate’s edge causes the tsunami Move as fast as a fighter jet…600ish mph Do not crest like a regular wave Are like a battering ram instead 4) Aftershock= a smaller EQ after a lrg EQ in the same place on the fault b/c of the fault settling back into its locked position can happen hours, days, months or even yrs after the lrg EQ can destroy weakened buildings **amt of death & destruction is determined where civilization is, magnitude of the EQ, building quality (well-built vs. poorly built), & distance from the epicenter b/c seismic waves lose energy the farther they go from the epicenter When and most intense/biggest magnitude: where was the 1960 in Chile-9.5 largest EQ? 1964 in Alaska-9.2 2004 in I. Ocean (Sumatra tsunami)-9.0 2011 in N. Japan (tsunami)-9.0 biggest death toll 2010 in Haiti (7.0)=222,570 2004 in I. Ocean (9.0)=227,898 2008 in China (7.9)=80, 587 2005 in Pakistan (7.6)=80,361 biggest EQ in CA: 1906 San Fransico (7.9)=3000