Semester-1-review-answer-key
advertisement

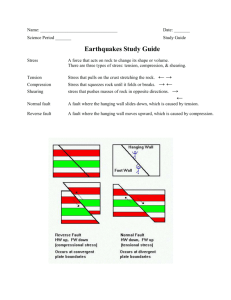
SEMESTER 1 EXAM REVIEW 7th grade Integrated Science 1. What is tension? Thins in the middle and pulls apart. 2. What is an aftershock? A smaller earthquake that occurs after the larger earthquake. 3. What is a footwall/hanging wall? Footwall lies under the fault, hanging wall sits over the fault. 4. How do rocks move in a slip-strike fault? Move past each other, shearing 5. What force produces a normal fault? Tension A reverse fault? Compression 6. Describe anticlines and synclines. Anticline bend upward into an arch while a syncline bends downward to form a v-shape. 7. What is a plateau? Large area of flat land elevated high above sea level 8. What/where is the focus? And the epicenter? The focus is an area beneath the Earth’s surface where rock that was under stress begins to break and move. The epicenter is the point on the surface directly above the focus. 9. Describe P waves, S waves and surface waves? What order do they arrive? 1.P waves compress like an accordion. 2.S waves move side to side. 3.Surface waves move up and down. P waves arrive first 10. Which seismic waves produce the most severe ground movement? Surface waves 11. What is the moment magnitude scale? Rates the total energy the earthquake releases. 12. What kind of fault does shearing create? Strike-slip fault 13. How does a seismograph record the earth’s vibrations? The pen stays stationary while the paper records the vibrations of the drum. 14. What is compression? Squeezes together 15. Are earthquakes predictable? No – Even with devices and geologists, they still can’t predict when an earthquake will happen. SEMESTER 1 EXAM REVIEW 7th grade Integrated Science 16. What patterns do seismograph data reveal? Reveals the vibrations of Pwaves, Swaves, Surface Waves __________ 17. Metric system measurements are based on a multiple of 10. True 18. What is observation? Based on five senses 19. What is a hypothesis? Possible explanation for a set of observations and must be testable. 20. Why are line graphs useful? They show how data are related. 21. What is a scientific theory? Well tested explanation for a wide range of observations or experimental results. 22. What is feedback? Output that changes the system in some way. 23. What is a system? A group of parts that work together. 24. What are Earth’s layers? Crust, mantle, outer core, inner core 25. What does it mean to be extinct? Term used to refer to a group of related organisms that has died out and has no living members. 26. Why is the fossil record important? How different groups of organisms change over time. 27. What does Wegner’s hypothesis say? All continents were once joined together in a single land mass and have since drifted apart. 28. Explain sea-floor spreading Continually adds new materials to the ocean floor at the mid-ocean ridge. 29. What is a caldera? Huge hole left by the collapse of a volcanic mountain. 30. How do the dissolved gasses in magma affect the volcano? Provides the force that causes magma to erupt to the surface. SEMESTER 1 EXAM REVIEW 7th grade Integrated Science Scientific law – A statement that describes what scientists expect to happen everytime under a particular set of conditions. Rock cycle – A series of processes on Earth’s surface and in the crust and mantle that slowly changes focks from one kind to another. Which location would you most likely find volcanoes? P. 197 2nd par. – Along mid-ocean ridges and where plates subduct. Uniformitarianism - glossary A principle that states that the geologic processes that change Earth today also changed Earth in the past? Fossils – review sheet in notebook on p. 50. Preserved remains or traces of once living organisms. Plate tectonics p. 183 Earth’s plates are in slow constant motion driven by convection currents.