Sum and Difference Identities Key
advertisement
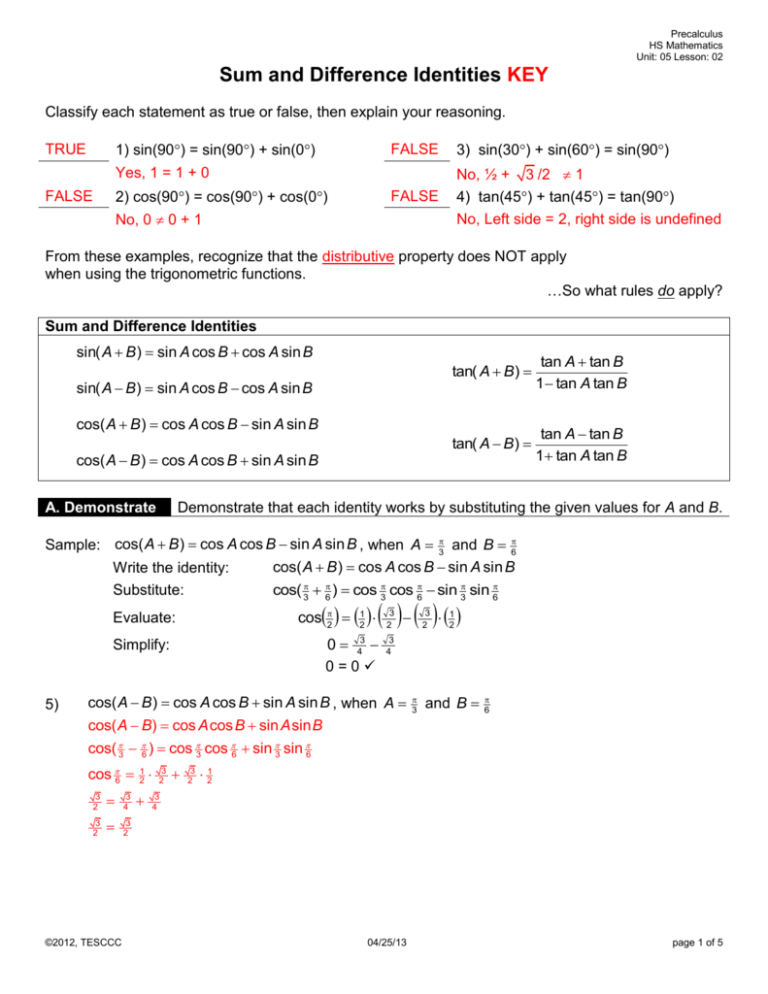
Precalculus HS Mathematics Unit: 05 Lesson: 02 Sum and Difference Identities KEY Classify each statement as true or false, then explain your reasoning. TRUE 1) sin(90) = sin(90) + sin(0) FALSE 3) sin(30) + sin(60) = sin(90) FALSE No, ½ + 3 /2 1 4) tan(45) + tan(45) = tan(90) No, Left side = 2, right side is undefined Yes, 1 = 1 + 0 FALSE 2) cos(90) = cos(90) + cos(0) No, 0 0 + 1 From these examples, recognize that the distributive property does NOT apply when using the trigonometric functions. …So what rules do apply? Sum and Difference Identities sin( A B ) sin A cos B cos A sin B sin( A B ) sin A cos B cos A sin B tan( A B) tan A tan B 1 tan A tan B tan( A B) tan A tan B 1 tan A tan B cos( A B ) cos A cos B sin A sin B cos( A B ) cos A cos B sin A sin B Demonstrate that each identity works by substituting the given values for A and B. A. Demonstrate Sample: cos( A B ) cos A cos B sin A sin B , when A 3 and B 6 cos( A B ) cos A cos B sin A sin B Write the identity: cos( 3 6 ) cos 3 cos 6 sin 3 sin 6 Substitute: cos2 21 Evaluate: 0 43 0=0 Simplify: 5) 3 2 3 2 3 4 3 2 3 2 ©2012, TESCCC 3 2 3 2 1 2 3 4 cos( A B ) cos A cos B sin A sin B , when A cos( A B) cos A cos B sin A sin B cos( 3 6 ) cos 3 cos 6 sin 3 sin 6 cos 6 21 3 2 3 and B 6 21 3 4 04/25/13 page 1 of 5 Precalculus HS Mathematics Unit: 05 Lesson: 02 Sum and Difference Identities KEY 6) sin( A B ) sin A cos B cos A sin B , when A sin( A B) sin A cos B cos A sin B sin( 3 6 ) sin 3 cos 6 cos 3 sin 6 sin 2 1 34 3 2 3 2 3 and B 6 3 and B 6 21 21 1 4 1 1 7) sin( A B ) sin A cos B cos A sin B , when A sin( A B) sin A cos B cos A sin B sin( 3 6 ) sin 3 cos 6 cos 3 sin 6 sin 6 8) 1 2 34 1 2 3 2 3 2 21 21 1 4 1 2 tan A tan B , when A 1 tan A tan B tan 3 tan 6 tan( 3 6 ) 1 tan 3 tan 6 tan( A B) tan( 6 ) 3 3 9) 3 3 3 1 3 3 3 3 and B 6 and B 6 33 2 33 2 3 1 1 2 6 3 3 3 3 3 tan A tan B , when A 1 tan A tan B tan 3 tan 6 tan( 3 6 ) 1 tan 3 tan 6 tan( A B) tan( 2 ) 3 3 3 3 33 4 3 3 1 1 0 3 3 3 1 3 33 (Both sides of the equation are undefined.) ©2012, TESCCC 04/25/13 page 2 of 5 Precalculus HS Mathematics Unit: 05 Lesson: 02 Sum and Difference Identities KEY B. Find Find the exact values for the trigonometric functions at 105 and 15 by writing the angles as a sum or difference of other special values (such as 60 and 45). Sample: cos(105) cos(60 45) cos 60 cos 45 sin 60 sin 45 21 10) 11) 3 2 6 4 3 2 6 4 2 2 2 6 4 2 2 21 2 2 6 2 4 2 4 tan( 105) tan( 60 45) tan60 tan 45 tan(60 45) 1 tan60 tan 45 3 1 1 3 ( 3 1) (1 3) (1 3) (1 3) 42 3 2 3 2 cos(15) cos(60 45) cos(60 45) cos 60 cos 45 sin60 sin45 21 13) sin(105) sin( 60 45) sin(60 45) sin60 cos 45 cos 60 sin 45 12) 2 4 2 2 2 2 2 4 3 2 6 4 2 2 2 6 4 sin(15) sin( 60 45) sin(60 45) sin60 cos 45 cos 60 sin 45 ©2012, TESCCC 3 2 6 4 2 2 21 2 2 6 2 4 2 4 04/25/13 page 3 of 5 Precalculus HS Mathematics Unit: 05 Lesson: 02 Sum and Difference Identities KEY 14) tan( 15) tan( 60 45) tan60 tan45 tan(60 45) 1 tan60 tan45 C. Find 3 1 1 3 ( 3 1) (1 3) (1 3) (1 3) 4 2 3 2 3 2 Use the sum and difference identities to evaluate functions of other rotation angles. R 257 , 24 25 R+S S 35 , 54 R and S are rotation angles (between 0 and 90) whose terminal sides ) and ( 35 , 54 ) , respectively. intersect the unit circle at ( 257 , 24 25 15) RS (1, 0) 16) 17) sin R = 24/25 cos R = 7/25 tan R = 24/7 sin S = 4/5 cos S = 3/5 tan S = 4/3 With a calculator in degree mode, solve for the measures of R and S. Then use these values to estimate R+S and RS. R = 73.74 R+S = 126.87 S = 53.13 RS = 20.61 Use the sum and difference identities to find the exact values for the trigonometric functions for R+S and RS. sin( R S ) sinR cosS cosR sinS sin( R S ) sinR cosS + cosR sinS 24 3 7 4 24 3 7 4 25 5 25 5 25 5 25 5 72 125 cos(R S ) 28 125 72 125 44 125 cos(R S ) cosR cosS + sinR sinS 3 7 24 4 25 5 25 5 21 125 18) Write down the sine, cosine and tangent values for each angle. 96 125 117 125 28 125 100 125 4 5 cosR cosS sinR sinS 3 7 24 4 25 5 25 5 21 125 96 75 125 125 53 How can the answers to #16 be used to check the answers to #17 (using a calculator)? sin(126.87) 0.8 = 4/5. cos(126.87) -0.6 = -3/5. sin(20.61) 0.352 = 44/125. cos(20.61) 0.936 = 117/125. More exact values could be found using the store key for angles R and S, i.e. sin -1(24/25) ENTER 73.73979529 STO ALPHA R and do the same for S, then use sin(R + S). ©2012, TESCCC 04/25/13 page 4 of 5 Precalculus HS Mathematics Unit: 05 Lesson: 02 Sum and Difference Identities KEY D. Prove Use the sum and difference identities to verify (or prove) other identities. Sample: Verify that sin( 2 x ) cos x (Sum/Difference Identity) sin( 2 x ) sin 2 cos x cos 2 sin x (1) cos x (0) sin x cos x 19) (Evaluate/Substitute) (Simplify) Prove cos( 2 x ) sin x cos( 2 x ) cos 2 cos x sin 2 sin x (0)cos x (1)sin x sin x 20) Prove sec( 2 x ) csc x 1 sec( 2 x ) cos( 2 x ) 1 1 1 csc x cos 2 cos x sin 2 sin x (0)cos x (1)sin x sin x 21) Prove cos( x ) cos x cos( x ) cos(0 x ) cos0cos x sin0sin x (1)cos x (0)sin x cos x Hint: Rewrite x as “0 – x” 22) Prove sin( x ) sin x sin( x ) sin(0 x ) sin0cos x cos0sin x (0)cos x (1)sin x sin x Hint: Rewrite x as “0 – x” 23) Prove tan( x ) tan x tan( x ) tan(0 x ) Hint: Rewrite x as “0 – x” ©2012, TESCCC tan0 tan x 0 tan x tan x tan x 1 tan0 tan x 1 (0) tan x 1 04/25/13 page 5 of 5







