Key from 1/22
advertisement
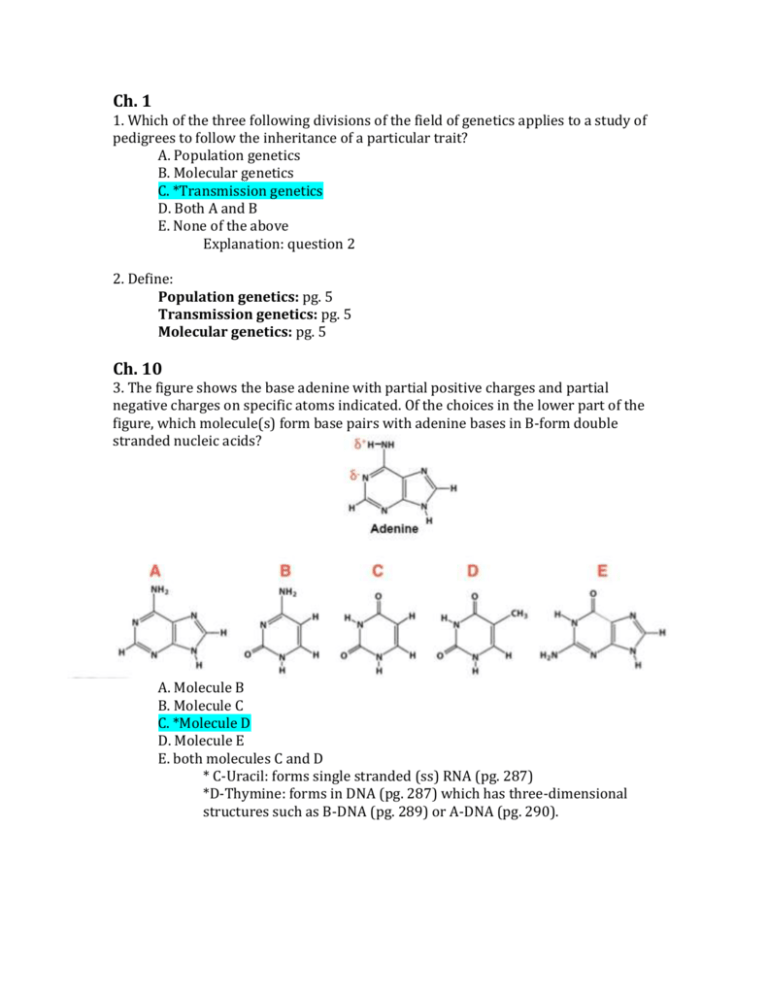
Ch. 1 1. Which of the three following divisions of the field of genetics applies to a study of pedigrees to follow the inheritance of a particular trait? A. Population genetics B. Molecular genetics C. *Transmission genetics D. Both A and B E. None of the above Explanation: question 2 2. Define: Population genetics: pg. 5 Transmission genetics: pg. 5 Molecular genetics: pg. 5 Ch. 10 3. The figure shows the base adenine with partial positive charges and partial negative charges on specific atoms indicated. Of the choices in the lower part of the figure, which molecule(s) form base pairs with adenine bases in B-form double stranded nucleic acids? A. Molecule B B. Molecule C C. *Molecule D D. Molecule E E. both molecules C and D * C-Uracil: forms single stranded (ss) RNA (pg. 287) *D-Thymine: forms in DNA (pg. 287) which has three-dimensional structures such as B-DNA (pg. 289) or A-DNA (pg. 290). 4. Answer the following for Purines and Pyrimidines: What is the ring structure? Purines: 6-member ring attached to a 5-member ring. Pyrimidines: 6-member ring What are the bases? Purines: Adenine and Guanine Pyrimidine: Cysteine, Thiamine, Uracil *pg. 286-287 5. Which of the following single-stranded RNA molecules could form a hairpin loop structure? A. *5’ – GGGGUUUUCCCC – 3’ B. 5’ – AAAAAAAAAAAA – 3’ C. 5’ – AGAGAGAGAGAG – 3’ D. 5’ – GGGGUUUUGGGG – 3’ E. all of the above, any single stranded RNA sequence can form a hairpin loop *pg.291; fig. 10.17








