1.NBT.3
advertisement

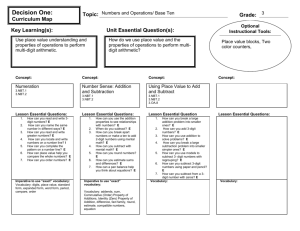
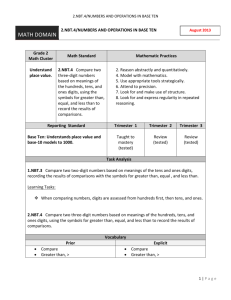
First Grade Unit 3 Purpose Of This Unit: Students develop strategies for adding and subtracting whole numbers based on their prior work with small numbers. This unit is designed to develop understanding of addition, subtraction, and strategies for addition and subtraction within 20. This unit will also help develop an understanding of whole number relationships and place value, including grouping in tens and ones. Unit Overview In this unit students will…. Represent a given number (0-19) on a ten-frame (double ten-frame) and relate the representation to the written numeral Given a number between 0 and 9, tell how many more are needed to make ten Given a number between 11-19, tell how many tens and ones (leftover) there are Given a number, tell/show numbers that are greater than, less than or equal Understand quantities to 99 Compare numbers up to 99 Use the >, < and = symbol appropriately Build numbers with place value mainpulatives Figure out which number is larger (or smaller or equals Read and write numbers using expanded form Use addition and subtraction to solve problems within 20 Determine the unknown whole number in addition and subtraction equations relating to three whole numbers (16 + ____ = 20) Justify the reasonableness of my answer and explain my strategies Add and subtract within 20 Unit 3: Understanding Place Value and Solving Addition and Subtraction problems CCSS Standards 1.NBT.1 1.NBT. 2 1.NBT.3 1.NBT.4 1.OA.1 1.OA.2 1.OA.6 Description Count to 120, starting at any number less than 120. In this range, read and write numerals and represent a number of objects with a written numeral. Understand that the two digits of a two-digit number represent amounts of tens and ones. Understand the following as special cases: Compare two two-digit numbers based on meanings of the tens and ones digits, recording the results of comparisons with the symbols >, =, and <. Add within 100, including adding a two-digit number and a one-digit number, and adding a two-digit number and a multiple of 10, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning used. Understand that in adding two-digit numbers, one adds tens and tens, ones and ones; and sometimes it is necessary to compose a ten. Use addition and subtraction within 20 to solve word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions, e.g., by using objects, drawings, and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem.1 Solve word problems that call for addition of three whole numbers whose sum is less than or equal to 20, e.g., by using objects, drawings, and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. Add and subtract within 20, demonstrating fluency for addition and subtraction within 10. Use strategies such as counting on; making ten (e.g., 8 + 6 = 8 + 2 + 4 = 10 + 4 = 14); decomposing a number leading to a ten (e.g., 13 – 4 = 13 – 3 – 1 = 10 – 1 = 9); using the relationship between addition and subtraction (e.g., knowing that 8 + 4 = 12, one knows 12 – 8 = 4); and creating equivalent but easier or known sums (e.g., adding 6 + 7 by creating the known equivalent 6 + 6 + 1 = 12 + 1 = 13). What Students Should Be Able to Do By the End of the Unit Count to 120. (1.NBT.1) Count to 120 starting at any number. (1.NBT.1) Read any number up to 120. (1.NBT.1) Write any number up to 120. (1.NBT.1) Label a set of objects up to 120 with the written numeral. (1.NBT.1) Represent 10 as ten ones. (1NBT.2) Represent numbers 11 to 19 as a ten and some ones. (1NBT.2) Represent multiple sets of ten using number names (2 tens is 20). (1NBT.2) Explain the value of each digit in a two-digit number (place value). (1NBT.2) Determine when a two-digit number is greater than, less than, or equal to another two-digit number. (1.NBT.3) Explain why a two-digit number is greater than, less than, or equal to another two-digit number. (1.NBT.3) Record the comparison using the symbols >, <, and =. (1.NBT.3) Use concrete models or drawings to show a strategy based on place value (collecting tens, collecting ones, and if necessary, composing ten ones to make a ten) and other strategies (such as applying the operations properties) to add the following: a two-digit number and a none-digit number, a two-digit number and a multiple of ten, and a two-digit number and a two-digit number. (1.NBT.4) Write down and explain the steps that I followed as I used the concrete models or drawings to show how I added. (1.NBT.4) Model addition and subtraction word problems using objects, drawings, and equations with unknown numbers in different positions. (1.OA.1) Solve addition and subtraction word problems using objects, drawings, and equations. (1.OA.1) Solve word problems with unknown numbers in different positions (e.g., 6 + = 8, + 2 = 8, 6 + 2 = __). (1.OA.1) Model addition and subtraction word problems using objects, drawings, and equations with unknown numbers in different positions. (1.OA.2) Add three whole numbers whose sum is less than or equal to 20. (1.OA.2) Solve word problems with three whole numbers using objects, drawings, and equations. (1.OA.2) Add and subtract within 10 easily. (1.OA.6) Add and subtract by counting on or counting back (e.g. 1 + 5 = 6, 7 - 5 = 2) (1.OA.6) Add and subtract by making 10. (e.g. 7 + 3 = 10, 10 - 6 = 4) (1.OA.6) Add and subtract by using doubles (or halves). (e.g. 4 + 4 = 8, 6 - 3 = 3) (1.OA.6) Add and subtract by adding 10. (e.g. 5 + 10 = 15, 17 - 10 = 7) (1.OA.6) Vocabulary Words add addition bundle compare compose decompose greater Than difference digit equation sum how many making ten numerals tens ones unknowns put together word problem less than more fewer symbol count counting on fluency place value put together relationship subtract subtraction take apart take from Lesson Planning Lessons for Learning Place Value and Solving Addition and Subtraction Word Problems (Part I) The following lessons below will cover the following standards: 1.NBT.1 1.NBT.2 1.NBT.3 1.OA.1 1OA.2 1.OA.6 Following this link will take you to the Lessons for Learning for the CCSS in Mathematics http://maccss.ncdpi.wikispaces.net/file/view/CCSSMathTasks-Grade1.pdf/464833108/CCSSMathTasks-Grade1.pdf pg.17 (1.NBT.2), (1.NBT.1) pg.22 (1.NBT.3), (1.NBT.1) pg.27 (1.NBT.2), (1.NBT.3) pg.31 (1.NBT.2), (1.NBT.3) pg.41 (1.NBT.2), (1.NBT.3) pg.44 (1.NBT.3), (1.NBT.2) pg.51 (1.OA.1), (1.OA.6) pg.54 (1.OA.1), (1.OA.6) pg.59 (1.OA.1), (1.OA.2) pg.62 (1.OA.1) pg.65 (1.OA.6) Lessons for Exploring Two-Digit Numbers (Part II) The following lessons will cover the following standards: 1.NBT.1 1.NBT.2 1.NBT.3 Following this link will take you to the First Grade Exploring Two-Digit Numbers Unit http://maccss.ncdpi.wikispaces.net/file/view/1stGradeUnit.pdf/298210818/1stGradeUnit.pdf Lesson 1.1 Lesson 1.2 Lesson 2.1 Lesson 2.2 Lesson 2.4 Lesson 2.5 (1.NBT.1, 1.NBT.2) (1.NBT.1, 1.NBT.3) (1.NBT.1, 1.NBT.3) (1.NBT.1, 1.NBT.2, 1.NBT.3) (1.NBT.1, 1.NBT.2, 1.NBT.3 (1.NBT.1, 1.NBT.3) Everyday Mathematics (Part III) The following lessons in the EDM Teacher’s Edition will cover the following standards: 1.OA.2, 1.OA.6 2.13 3.10 8.4 4.11 (1.OA.1) (1.OA.1) (1.OA.1) (1.OA.6) 4.12 5.7 5.9 5.11 (1.OA.6) (1.OA.6) (1.OA.6) (1.OA.6) Problem Solving Resource The Following Link Below will take you to the Problem Solving Table and Problem Solving Structures. Make sure to scroll down the page to access all resources. https://grade1commoncoremath.wikispaces.hcpss.org/Problem+Solving Strategies for Addition Resource The Following Link Below will take you to Strategies for Computation (Addition) https://grade1commoncoremath.wikispaces.hcpss.org/Strategies+for+Computation+%28Addition%29