Common Core Number Common Core Standard Date Introduced
advertisement

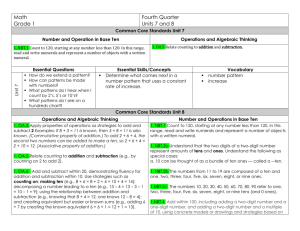
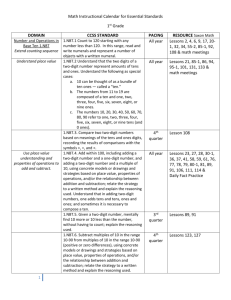
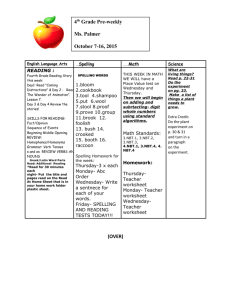
Common Common Date Core Core Introduced Number Standard Reading - Literature CC.1.RL.1 We can ask and answer questions about key details in a text. CC.1.RL.2 We can retell stories, including key details, and demonstrate understanding of their central message or lesson. CC.1.RL.3 We can describe characters, settings, and major events. CC.1.RL.4 We can identify words or phrases in stories or poems that suggest feelings or appeal to the senses. CC.1.RL.5 We can explain major differences between books that tell stories and books that give information. CC.1.RL.6 We can identify who is telling the story at various points in a text. CC.1.RL.7 We can use illustrations and details in a story to describe its characters, setting, or events. CC.1.RL.9 We can compare and contrast the adventures and experiences of characters in stories. CC.1.RL.10 With prompting and support, we can read prose and poetry of appropriate complexity for grade 1. Reading - Informational CC.1.RI.1 We can ask and answer questions about key details in a text. CC.1.RI.2 We can identify the main topic and retell key details in a text. CC.1.RI.3 We can describe the connection between two individuals, events, ideas, or pieces of information in a text. CC.1.RI.4 We can ask and answer questions to help determine or clarify the meaning of words and phrases in a text. CC.1.RI.5 We know and use various text features to locate key facts or information in a text. CC.1.RI.6 We can distinguish between information provided by pictures or illustrations and information provided by the words in a text. CC.1.RI.7 We can use illustrations and details in a text to describe the key ideas. CC.1.RI.8 We can identify the reason the author gives to support points in a text. CC.1.RI.9 We can identify basic similarities and differences between two texts on the same topic. CC.1.RI.10 With prompting and support, we can read informational texts appropriately complex for grade 1. Reading –Foundational CC.1.RF.1 We can recognize the distinguishing features of a sentence. CC.1.RF.2a We can distinguish long from short vowel sounds in spoken single-syllable words. CC.1.RF.2b We can orally produce single-syllable words by blending sounds including consonant blends. CC.1.RF.2C We can isolate and pronounce the beginning, middle and ending sounds in spoken single syllable words. CC.1.RF.2d We can segment spoken single-syllable words into their complete sequence of individual sounds. CC.1.RF.3a We know the spelling-sound correspondences for common consonant digraphs. CC.1.RF.3b We can decode regularly spelled one-syllable words. CC.1.RF.3c We know the final e and common vowel team conventions for representing long vowel sounds. CC.1.RF.3d We use knowledge that every syllable must have a vowel sound to determine the number of syllables in a printed word. CC.1.RF.3e We can decode two-syllable words following basic patterns by breaking the words into syllables. CC.1.RF.3f We can read words with inflectional endings. CC.1.RF.3g We can recognize and read grade-appropriate irregularly spelled words. CC.1.RF.4a,b We can read grade-level text with purpose, understanding and with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression CC.1.RF.4c We can use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary. Writing CC.1.W.1 We can write an opinion piece which tells the reader the topic or name of the book we are writing about and state an opinion, a reason for the opinion and provide a sense of closure. CC.1.W.2 We can write informative/explanatory texts in which we name a topic supply some facts about the topic, and provide some sense of closure. CC.1.W.3 We can write narratives in which we tell about two or more sequenced events, include details about what happened, use words to signal event order, and provide some sense of closure. CC.1.W.5 We can focus on a topic, respond to questions and suggestions from peers, and add details to strengthen writing as needed. CC.1.W.6 We can explore a variety of digital tools and collaborate with friends to produce and publish writing. CC.1.W.7 We can participate in shared research and writing projects. CC.1.W.8 We can recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question. Language Arts – Speaking and Listening CC.1.SL.1 We can participate in conversations about first grade topics and texts with peers and adults in small and larger groups. CC.1.SL.1a We can follow rules for speaking and listening during conversations. CC.1.SL.1b We can continue a conversation with multiple exchanges. CC.1.SL.2&3 We can ask and answer questions to help us gain an understanding of information. CC.1.SL.4 We can describe people, places, things, and events with relevant details, expressing ideas and feelings clearly. CC.1.SL.5 We can add drawings or other visual displays to descriptions when appropriate to clarify ideas thoughts, and feelings. CC.1.SL.6 We can produce complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation. Language Arts CC.1.L.1,a We can speak and write using correct grammar and conventions. We can print upper and lowercase letters correctly. CC.1.L.1b We can use common, proper, and possessive nouns. CC.1.L.1c We can use singular and plural nouns with matching verbs in a sentence. CC.1.L.1d We can use personal and possessive pronouns. CC.1.L.1e We can use verbs to convey past, present and future. CC.1.L.1f We can use adjectives correctly. CC.1.L.1g We can use conjunctions correctly. CC.1.L.1h We can use determiners. CC.1.L.1i We can use frequently occurring prepositions CC.1.L.1j We can produce and expand simple and compound sentences. CC.1.L.2 We can write sentences which include capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing CC.1.L.2a We can capitalize dates and names of people. CC.1.L.2b We can use end punctuation for sentences. CC.1.L.2c We can use commas in dates and to separate single words in a series CC.1.L.2d We can use conventional spelling for words with common spelling patterns and for frequently occurring irregular words. CC.1.L.2d,e We can use conventional spelling for words with common spelling patterns and for frequently occurring irregular words, as well as spell untaught words phonetically, drawing on phonemic awareness. CC.1.L.4a We can use sentence-level context as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. CC.1.L.4b We can use the most frequently occurring inflections and affixes as a clue to the meaning of an unknown word. CC.1.L.4c We can identify frequently occurring root words and their inflectional forms. CC.1.L.5a,b,c We can sort common objects into categories by one or more attributes and understand why they belong in the category and identify the real-life connection. CC.1.L.5d CC.1.L.6 We can distinguish meanings among verbs differing in manner and adjectives differing in intensity defining and acting out meanings. We can use words and phrases learned from conversations and reading. Common Common Date Core Core Introduced Number Standard Math - Operations and Algebraic Thinking CC.1.OA.1 We can solve addition and subtraction word problems to 20 with unknowns in all positions. CC.1.OA.2 We can solve word problems that call for addition of three whole numbers whose sum is less than or equal to 20. CC.1.OA.3 We can apply properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract. CC.1.OA.4 We understand subtraction as an unknown-addend problem. CC.1.OA.5 We can relate counting to addition and subtraction. CC.1.OA.6 We can use a variety of strategies add and subtract within 20, demonstrating fluency for addition and subtraction within 10. CC.1.OA.7 We understand the meaning of the equal sign, and determine if equations involving addition and subtraction are true or false. CC.1.OA.8 We can determine the unknown whole number in an addition or subtraction equation relating three whole numbers. Math – Numbers and Operations in Base Ten CC.1.NBT.1 We can count to 120, starting at any number less than 120 and read and write numerals and represent a number of objects with a written numeral. CC.1.NBT.2 We understand that each digit in a two-digit number represents amounts of tens and ones. CC.1.NBT.3 We can compare two two-digit numbers and record the results of comparisons with the symbols >,=,<. CC.1.NBT.4 We can find the sum of problems with both one and two digit addends. CC.1.NBT.5 When given a two-digit number, we can mentally find 10 more or 10 less than the number, without having to count; and explain the reasoning used. CC.1.NBT.6 We can use concrete models or drawings and strategies we have learned to subtract multiples of 10 and explain our reasoning. Math – Measurement and Data CC.1.MD.1 We can order three objects by length and compare the lengths of two objects indirectly by using a third object. CC.1.MD.2 We can use multiple copies of a shorter object to measure a longer one. CC.1.MD.3 We can tell and write time in hours and half-hours using analog and digital clocks. CC.1.MD.4 We can organize, represent, and interpret data with up to three categories. Math – Geometry CC.1.G.1 We can distinguish between defining attributes and non-defining attributes and build and draw shapes that possess these attributes. CC.1.G.2 We can compose two-dimensional or three-dimensional shapes to create a composite shape and compose new shapes from the composite shapes. CC.1.G.3 We can partition circles and rectangles into two and four equal shares and describe the shares using the words halves, fourths, and quarters.