File - Ms. Mc Nelis Science Teaching Resources
advertisement

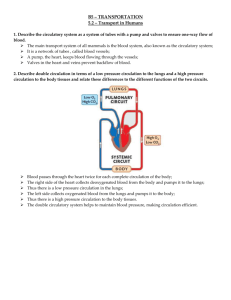
LEAVING CERT BIOLOGY Ms. Mc Nelis The Circulatory System The circulatory system in humans is a closed system: blood is contained within a continuous system of blood vessels Materials in the blood can leave the vessels (e.g. food, oxygen) and pass into the cells, but the blood itself cannot. Circulatory System consists of: Muscular heart Blood vessels: arteries, veins, capillaries, venules, arterioles Blood Heart Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Heart Portal vein: a portal vein is different from other veins because it has capillaries at both ends. E.g. hepatic portal vein (carries blood from intestine to liver) Artery Internal Structure of Blood Vessels Vein Capillary 1|Page LEAVING CERT BIOLOGY Artery Ms. Mc Nelis Vein Lumen Walls Valves Small lumen Large lumen Thick muscular walls Thin muscular walls Does not contain valves Contains valves to prevent backflow of blood Direction of Carries blood away Carries blood into blood flow from heart heart Pressure High blood pressure Low blood pressure Oxygen Usually carries blood Usually carries blood rich in oxygen, apart low in oxygen, apart from pulmonary artery from pulmonary vein Capillary Very tiny vessel Walls only one cell thick Does not contain valves Carries blood from arterioles to venules Medium pressure Oxygen passes out of capillary into body cells Double Circulatory System: In the pulmonary circuit : blood flows from the heart to the lungs and back In the systemic circuit : blood flows from the heart to the body (all other organs and cells) and back Structure of Heart 2|Page LEAVING CERT BIOLOGY Ms. Mc Nelis Structure of Human Circulatory System Heart • • • • Located in the thoracic (chest) cavity: area inside rib cage Contains strong double pump The cardiac muscle of the heart differs from other muscles in the body because it does not tire (involuntary muscle contraction) The coronary artery supplies the heart itself with blood – blood comes from aorta and back through coronary veins Cardiac Cycle The heart is relaxed and blood flows into atria from veins Bicuspid and tricuspid valves relax (open) and blood flows into ventricles Atria contract pushing more blood into ventricles The ventricles contract forcing blood into the arteries and at the same time the bicuspid and tricuspid valves slam shut (creating ‘lub’ sound) The ventricles relax and the semilunar valves slam shut to prevent backflow of blood (creating ‘dub’ sound) Diastole: the filling phase of the heart with blood. The heart is relaxed. Systole: the emptying phase when the heart muscles contract. 3|Page LEAVING CERT BIOLOGY Ms. Mc Nelis Pacemakers • • • • • Heartbeat can occur independently of the brain. Heartbeat is controlled by a small bundle of specialised tissue called a pacemaker (SA and AV nodes) located in the right atrium. Sinoatrial (SA) node sends out regular electrical impulses causing the atria to contract. It also stimulates the atrioventricular (AV) node. The AV node then stimulates the ventricles to contract. Location: • • • • • - SA node is in the wall of right atrium. - AV node is beside the tricuspid valve The pacemaker itself controls the heartbeat. Average rate = 75 beats per minute (bpm) But nerve signals from the brain and hormones can change the rate at which it operates. Factors such as exercise, change in temperature and shock can increase heart rate. Factors such as relaxation, sleep and alcohol can reduce heart rate. What causes a pulse? Pulse: expansion of artery due to pumping of heart Blood Pressure: the force exerted by blood on the wall of a blood vessel Effects of External Factors on Heart Rate Factor Smoking Diet Exercise Effect • Nicotine increases heart rate and raises blood pressure • Carbon monoxide reduces the amount of oxygen carried by the blood • Chemicals in smoke can cause clots in blood vessels leading to increased risk of heart attack and stroke • High salt diet – High blood pressure, greater risk of stroke • High fat diet – Blocked coronary arteries leading to heart attack • Heart can become stronger • Greater oxygen carrying capacity • Lower resting heart rate Ways to Maintain a healthy Heart Don’t smoke Eat less fat Eat less salt Exercise regularly Avoid excess stress 4|Page