Accentuate the Negative
advertisement

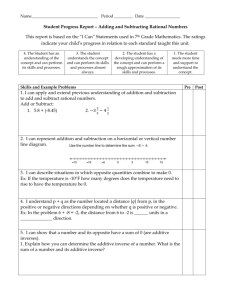
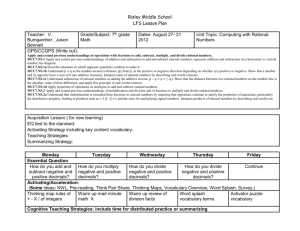
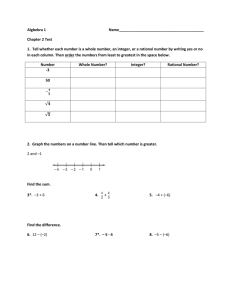
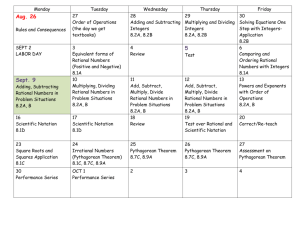
Accentuate the Negative The Learning will apply and extend previous understandings of operations with fractions to add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational numbers. Reasoning-DOK2 Created by Melissa Majeski – Warren Woods Middle School 7.NS.1 Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line. 7.NS.2 Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division of fractions to divide rational numbers. 7.NS.3 Solve real-world problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. **Skills needed in order to master learning target. Will not be tested individually on final assessment. Proficiency Level 3 R-DOK2 Rules for Adding: If the signs are the same, add and keep the sign. If the signs are different, subtract and keep the sign of the larger absolute value. Jessica made the addition model below of the expression (-5) + (-2) + 3 Jessica used the number line to conclude that the sum of the 3 numbers is -4. If she correct? Explain your thinking. Explain Thinking: Jessica solution, -4, is correct because since -5 and -2 have the same sign, you add them together and keep the sign, to get -7. Then you take -7 and add a positive 3. Since the signs are different, you subtract 3 from 7 to get 4. The final answer is a -4, because when you take the absolute value of -7 and 3, 7 is greater, so you take the sign of 7. AN5: I can show algorithms for adding rational numbers Created by Melissa Majeski – Warren Woods Middle School Proficiency Level 3 R-DOK2 Rational Numbers: Any number that can be written as a fraction. Examples: 3, -1, 0.04, -2.1, -½ , ¼ , 84% Non-Examples: 0.3333, √2, 𝜋 3 −1 Explain Thinking: Since 3, -1, 0.04, -2.1 and 84% can be written as 1 , 1 4 1 84 , 100 , −2 10 , 100, they are rational. Since 0.3333, √2, 𝜋 are repeating decimals or decimals that go on forever, they cannot be writing as a simple fraction. **AN1: I can explain and identify rational numbers Created by Melissa Majeski – Warren Woods Middle School Proficiency Level 3 R-DOK2 Compare the following numbers using, <, >, =, ≤, or ≥. 0.64 > 47% 7/10 = 0.7 -0.44 < 0.44 Order the following set of numbers from least to greatest. 5 -0.2, ½ , 0.3, -2, 8 Least to Greatest 5 -2, -0.2, 0.3, ½, 8 Explain Thinking: To order rational numbers, first I converted ½ to 0.5 and 5/8 to 0.625. Then, I used a number and located each number on the number. The larger the positive number, the further to the right of zero. The smaller the negative number, the further left of zero. **AN2: I can compare/order positive/negative rational numbers. Created by Melissa Majeski – Warren Woods Middle School Proficiency Level 3 K-DOK1 **AN3: I can locate rational numbers on a number line Created by Melissa Majeski – Warren Woods Middle School Proficiency Level 3 R-DOK2 Find the absolute value of each number. Then, order them from least to greatest. 1 | | , |−3|, |2| 2 Least to Greatest 1 , 2, 3 2 Explain Thinking: Since absolute value of a rational number is the distance from zero, and distance cannot be negative, ½ has the shortest distance from zero, and 3 has the largest distance from zero. **AN4: I can order the absolute value of rational numbers. Created by Melissa Majeski – Warren Woods Middle School Proficiency Level 3 R-DOK2 Rules for Subtracting: Add the additive inverse (opposite). Change the subtraction sign to an addition sign. Change the sign of the second number. Then follow the rules of addition. Explain what is meant by the following: p – q = p + (-q). Explain Thinking: Subtracting a number is the same as adding it’s opposite. For example: p = 4, q = 6 p – q = 4 – 6 = -2 is the same as p + (-q) = 4 + (-6) = -2 AN6: I can use algorithms to subtract rational numbers. Created by Melissa Majeski – Warren Woods Middle School Proficiency Level 3 R-DOK2 Rules for Multiplying: If the signs are the same, the product is positive. If the signs are different, the product is negative. Generate real-world situations that can be modeled by each of the following multiplication problems. Use the Integer Game as a resource. 4 x (– 7) = -28 If I lose 7 pounds per month for 4 months, my weight will change by -28 pounds total. AN7: I can use algorithms to multiply rational numbers Created by Melissa Majeski – Warren Woods Middle School Proficiency Level 3 R-DOK2 Rules for Dividing: If the signs are the same, the quotient is positive. If the signs are different, the quotient is negative. Are the answers to the three quotients below the same or different? Why or why not? a) −14 ÷ 7 = −2 b) 14 ÷ (−7) = −2 c) −(14 ÷ 7) = −2 The answers in the problems are the same: -2 because for (a) and (b) since the signs are different, the quotient is negative. For part (c) the negative in front of the parentheses changes the value inside the parentheses to its opposite. The value in the parentheses is 2, and its opposite is -2. AN8: I can use algorithms to divide rational numbers Created by Melissa Majeski – Warren Woods Middle School Proficiency Level 3 R-DOK2 Order of Operations: Parenthesis, Exponents, (Multiplication/Division from Left to Right), (Addition/Subtraction from Left to Right) 10 5 10 = 2(3 +16) -1 + 5 10 = 2(19) – 1 + 5 2(3+ 42) -1 + = 38 – 1 + 2 = 37+ 2 = 39 AN9: I can use order of operations to simplify expressions and solve problems. Created by Melissa Majeski – Warren Woods Middle School