Earth Study Guide 22and23
advertisement

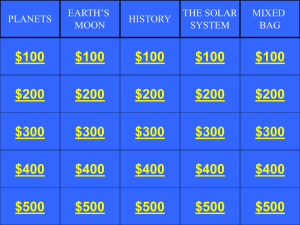
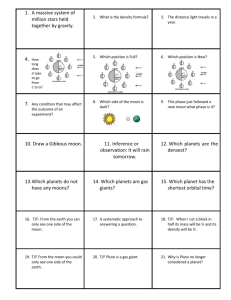
Name ______________________________ Study Guide (Answer Key) Earth Systems Ch. 22 & 23 1. Who developed a geocentric model of the universe describing the motions of the planets? Ptolemy 2. Which of our current planets were known to the ancient Greeks? Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter 3. How did Aristotle decide the Earth was round? It always casts a curved shadow during a lunar eclipse 4. Define retrograde motion. The apparent westward movement of a planet against a background of stars. 5. Define celestial sphere. A transparent, hollow sphere on which the stars traveled daily around Earth. 6. Define equatorial plane. An imaginary plane that cuts through the Earth perpendicular to the axis of rotation. 7. What did the geocentric model of the universe state? The Earth was the center of the universe. 8. What did the Ptolemaic model of the universe state? Earth was the center of the universe. 9. Which scientist proposed three laws of planetary motion using Tycho Brahe’s data? Kepler 10. Who was the first astronomer to propose a sun-centered solar system? Copernicus 11. Which scientist first discovered that Venus had phases, just like the moon? Galileo 12. Define mass. The measure of how much matter is in an object. 13. Define weight. The force that gravity exerts on an object. 14. What is the shape of a planet’s orbit? elliptical 15. What did Newton determine about planet’s orbits? He determined the nature of the forces that keep the planets in their orbits. 16. What scientist was the first to use a telescope in astronomy? Galileo 17. Who discovered the true shape of planetary orbits? Kepler 18. Which astronomer spent 20 years plotting the positions of the planets? Brahe 19. Make a list of Galileo’s astronomical discoveries. Sunspots, mountains on the moon, Jupiter’s four largest moons 20. What does the third law of planetary motion state? The period of revolution of a planet is related to the planet’s distance to the sun. 21. Define perihelion. The point at which Earth is closest to the sun. 22. Define aphelion. The point at which Earth is farthest from the sun. 23. Define precession. Earth’s axis slowly but continuously points in different directions. 24. What movement of Earth is responsible for day and night? rotation 25. Define rotation. The turning or spinning of a body on its axis. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. Define revolution. The motion of the Earth around the Sun. What causes the seasons on Earth? Earth’s tilted axis. Define perigee. The point at which the moon is closest to the Earth. Define apogee. The point at which the moon is farthest from the Earth. What is the moon’s period of revolution and its period of rotation? Revolution-27 1/3 days; Rotation-27 1/3 days (They are the same). What is the length of daylight on the moon? 2 weeks What occurs when the moon casts its shadow on Earth? Solar eclipse What are round depressions on the moon’s surface called? Craters What are the oldest features on the moon called? Highlands How old is the moon compared to Earth? About the same age as Earth List the planets known to have rings. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune List the Jovian planets. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune List the terrestrial planets. Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars What is the most obvious difference between the Jovian and terrestrial planets? Size Describe what occurred in nebular theory. Formation of the solar system from a huge cloud of dust and gases Which planets show evidence of water erosion? Earth and Mars Which planet has a crater surface similar to Earth’s moon? Mercury Which planet has the greatest temperature extremes? Mercury Which planet has a dense carbon dioxide atmosphere and high surface temperatures? Venus How many known satellites does Mars have? 2 What is the atmosphere of Venus composed mainly of? Carbon dioxide Which planet has a greater mass than all the remaining planets and moons combined? Jupiter Which planet could be described as a large, dirty ice ball? Pluto Which planet has the “Great Dark Spot”? Neptune Which planet’s axis of rotation is almost parallel with the plane of its orbit? Uranus Which planet was recently determined to have one satellite? Pluto Which way does a comet’s tail always point? Away from the sun Define a coma. The glowing head of a comet Define meteor. The small particles that produce a streak of light upon entering Earth’s atmosphere Define meteorite. The remains of extraterrestrial particles that are found on Earth’s surface.