Chapter 6 - DBCS "THE BRIDGE"
advertisement
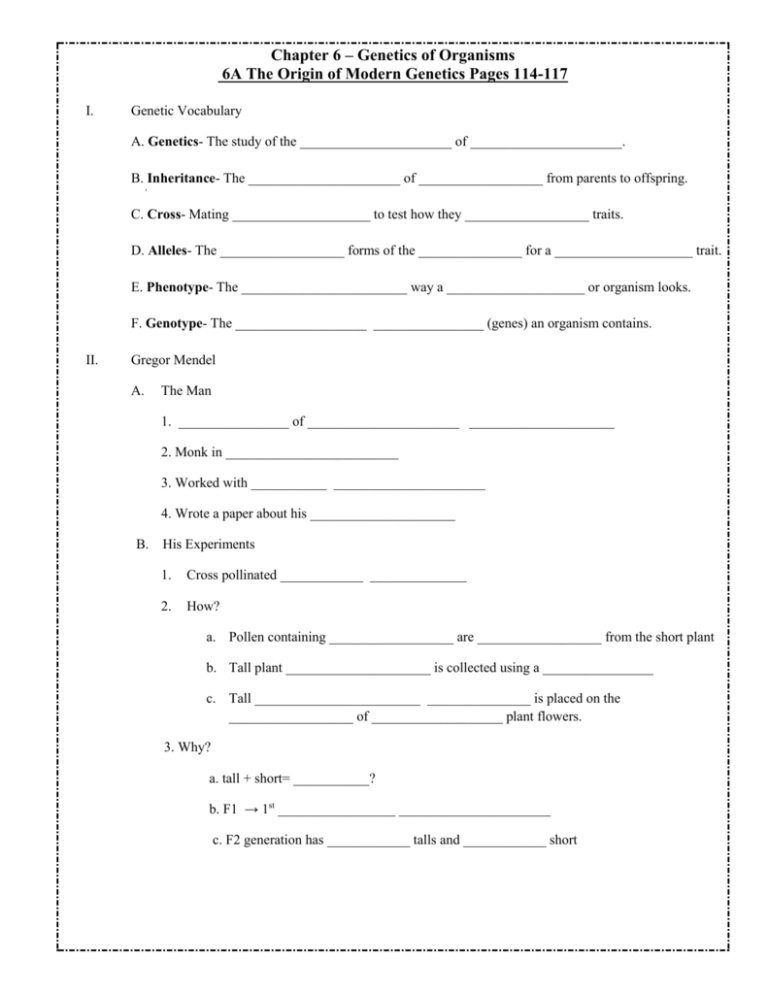
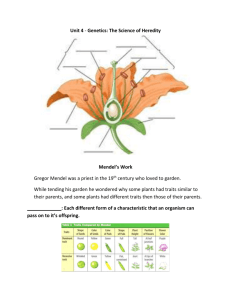
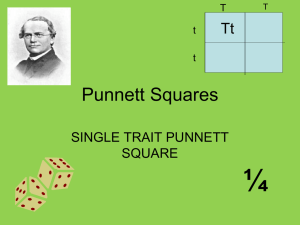
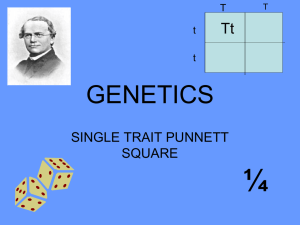
Chapter 6 – Genetics of Organisms 6A The Origin of Modern Genetics Pages 114-117 I. Genetic Vocabulary A. Genetics- The study of the ______________________ of ______________________. B. Inheritance- The ______________________ of __________________ from parents to offspring. C. Cross- Mating ____________________ to test how they __________________ traits. D. Alleles- The __________________ forms of the _______________ for a ____________________ trait. E. Phenotype- The ________________________ way a ____________________ or organism looks. F. Genotype- The ___________________ ________________ (genes) an organism contains. II. Gregor Mendel A. The Man 1. ________________ of ______________________ _____________________ 2. Monk in _________________________ 3. Worked with ___________ ______________________ 4. Wrote a paper about his _____________________ B. His Experiments 1. Cross pollinated ____________ ______________ 2. How? a. Pollen containing __________________ are __________________ from the short plant b. Tall plant _____________________ is collected using a ________________ c. Tall ________________________ _______________ is placed on the __________________ of ___________________ plant flowers. 3. Why? a. tall + short= ___________? b. F1 → 1st _________________ ______________________ c. F2 generation has ____________ talls and ____________ short C. His Theories 1. If the organism’s two _______________ (Mendel used the word __________) for the _____________ are the ____________, the organism is _________________ for that trait. 2. If the organism’s two ____________________ (factors) for a trait are ____________________, the ___________________ is _____________________ for that trait. 3. Each ___________________ (factor) in a set of two ________________ for a trait is either ______________________ or recessive. 4. When there is __________ of each the ___________________ trait is shown. Dominant- the _______________________ that is expressed even when a __________________ allele is present. Recessive- the characteristic that is expressed _____________ in the _________________ of a __________________ allele. 5. His Notations a. Dominant ______________are represented by __________________ ________________. b. ________________ alleles are represented with _________________ ________________. c. All ___________________ organisms have ___________ letters to represent their _______________________ for a particular trait, III. Post Mendel’s Experiments A. Mendel’s work went _______________________ for over ________years. B. In the mid __________ scientists described the ____________ molecule and realized that Mendel’s ________________ were actually _________________. ** Complete Section Review Page 118** 6B Heredity Pages 118-125 I. Using a Punnett Square A Punnett square is used to _____________________ genetic __________________ in order to __________________ the possible ___________________ for the ___________________. A. Using a Punnett Square 1. Suppose a purebred short pea plant is cross pollinated with a purebred tall pea plant. What possible heights would you expect to see in the offspring? 2. It does NOT matter which side of the Punnett Square Purebred Tall Parent each parent goes on. T T Pure Bred Short Parent 3. Suppose two hybrid tall pea plants are cross pollinated. What possible heights would you expect to see in the offspring? Hybrid Tall Parent T 4. Each box represents a _____________________________ Hybrid T for the offspring. Tall t Parent t B. Your turn to make a Punnett Square. 1. In humans, the allele for dimples is dominant over the allele for no dimples. 2. A woman who is purebred for dimples marries a man who is hybrid for dimples. What are the possibilities for their children as far dimples are concerned? What percentage of their children will be…… A) purebred dimples ____________ B) hybrid? _____________ C) purebred for no dimples ____________ D) What is the phenotype for hybrid children? _________ C. Variations on Mendel’s Theories (You will NOT be responsible for Punnett Squares for these ) 1. Incomplete Dominance- two different alleles result in blending Ex: Snapdragons: red + white= pink 2. Condominance – Both alleles for a trait are dominant and both forms of the trait are seen Ex: Roan cattle: red + white= roan 3. Polygenic Inheritance- two or more genes are responsible for producing a single trait. Ex: human hair color 4. Multiple Alleles- more than two alleles for a particular gene Ex: human blood type D. Sex chromosomes and Inheritance 1. Sex chromosomes a) The 23rd pair of chromosomes in ____________________. b) Females have two ______ chromosomes c) Males have only one ______ and one ___________. 2. It is the X or Y _________________ of the father’s sperm that determine the sex of the child (boy/girl) Mother X X X Girl Y Boy Father Sex- linked traits- Inherited traits _____________________ by genes located on the sex _______________________. 3. Most sex-linked traits are ___________________, with ________________ on the X chromosome. Ex: red/green color blindness Carriers- People who have the ________________ for a trait but do not _______________ it themselves. See the Barnett Family p. 124-125 ** Complete Section Review page 125 ** 6C Genetic Disorders Pages 125-127 I. Genetic Disorders - a condition caused by a ________________ _______________ in an ____________________. II. What Does the Bible Say? A. God makes people _________________ the way __________ wants them to be. B. God ____________________ a baby’s development. Psalm 139:13-16 C. God’s original __________________ was very good. Genesis 1:31 D. Human _______________ is the cause of ________________ and ________________ in this world. Genesis 3 E. God can use ____________________ to give _________________ and _________________. F. God can use ____________________ to _____________________ His will. ** Complete Section Review page 127 ** END OF CHAPTER 6