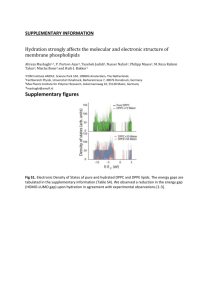
Ionic Liquid Matrix-Enhanced Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry
advertisement

Ionic Liquid Matrix-Enhanced Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry: The Role of Proton Transfer: Supporting Information Jennifer J. Dertinger, Amy V. Walker* Department of Materials Science and Engineering, RL 10, University of Texas at Dallas, 800 W. Campbell Rd, Richardson, TX 75080 * Address reprint requests to Amy V. Walker, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, RL10, University of Texas at Dallas, 800 W. Campbell Rd, Richardson, TX 75080; Ph: 972 883 5780; Fax: 972 883 5725; email: amy.walker@utdallas.edu O a) O N CH3 (CH2 )13CH 2 O O P DPPC O H O CH 3(CH 2) 13 CH2 O O O b) O N CD3 (CD2 )13CD 2 O O H O CD 3(CD 2) 13 CD2 P d62 DPPC O O O O c) D O CD 3 D N CD3 (CD2 )13CD 2 O O O CD 3(CD 2) 13 CD2 H P O O D D CD 3 CD 3 d75 DPPC O Figure 1. Structures of a) DPPC; b) d62 DPPC; and c) d75 DPPC. a) MI CHCA d) EI CHCA O N O N CN HO H D D b) dMI CHCA e) BI CHCA D O D N D O N D CN HO H f) trip CHCA c) MI2 CHCA O N N O N CN N O H H Figure 2. Structures of the ionic liquid matrices employed: a) MI CHCA; b) dMI CHCA; c) MI2 CHCA; d) EI CHCA; e) BI CHCA; and f) trip CHCA. normalized intensity (CHCA - H)- d75 DPPC d62 DPPC DPPC 187 188 189 190 191 m/z, negative ions Figure 3. SIMS spectra from m/z 187 to m/z 191 showing the (CHCA – H)- ion region for DPPC, d62 DPPC and d75 DPPC in a MI2CHCA matrix. The spectra are normalized to the intensity of (CHCA – H)- to make clear any changes in the (CHCA – H + 1)- and (CHCA – 2H + 2)- ion intensities. a) DPPC + intensity (a.u.) (C5H15NPO4) 183 184 185 186 187 m/z, positive ions d62 DPPC b) + (C5H15NPO4) intensity (a.u.) (C5H14DNPO4)+ 183 184 185 186 187 m/z, positive ions Figure 4. TOF SIMS spectra centered at m/z 185 of DPPC and d62 DPPC in a MI CHCA matrix. a) 16 DPPC d62 DPPC Enhancement 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 MI BI trip Matrix Cation 0.10 0.08 0.06 + I((cation + D) /I(cation + H) + b) EI 0.04 0.02 0.00 MI EI BI trip Matrix Cation Figure 5. a) Variation of secondary ion enhancements for the protonated molecular ion of DPPC and d62 DPPC with matrix cation. b) Variation of the ratio of I((cation + D)+ to I(cation + H)+ with matrix cation using the analyte d62 DPPC. Note: The molecular ion enhancements reported are lower for DPPC and d62 DPPC in these experiments because the experiments were performed using a slightly different spin coating conditions. In this case the concentration of DPPC and d62 DPPC were mixed with the ionic liquid for slightly longer than 5 mins before spin coating (due to problems with the spin coater). Reference Spectra for the Ionic Liquids Employed in this Study All ionic liquids were characterized using 1H NMR spectroscopy, IR spectroscopy and TOF SIMS. The spectra are shown below in the following order. For each ionic liquid the positive mass spectrum will be first, followed by the negative mass spectrum, and the IR spectrum. On the second page will be the 1H NMR spectra showing the proton shift. The ionic liquids are ordered alphabetically by acronym. BI CHCA Figure 6. Positive and negative ion mass spectra and IR spectrum of BI CHCA. Figure 7. 1H NMR spectrum of BI CHCA. dMI CHCA Figure 8. Positive and negative ion mass spectra and IR spectrum of dMI CHCA. Figure 9. 1H NMR spectrum of dMI CHCA. EI CHCA Figure 10. Positive and negative ion mass spectra and IR spectrum of dMI CHCA. Figure 11. 1H NMR spectrum of dMI CHCA. MI CHCA Figure 12. Positive and negative ion mass spectra and IR spectrum of MI CHCA. Figure 13. 1H NMR spectrum of MI CHCA. MI2CHCA Figure 14. Positive and negative ion mass spectra and IR spectrum of MI2CHCA. Figure 15. 1H NMR spectrum of MI2CHCA. Trip CHCA Figure 16. Positive and negative ion mass spectra and IR spectrum of trip CHCA. Figure 17. 1H NMR spectrum of trip CHCA.