Readers Workshop Unit of Study 3
advertisement
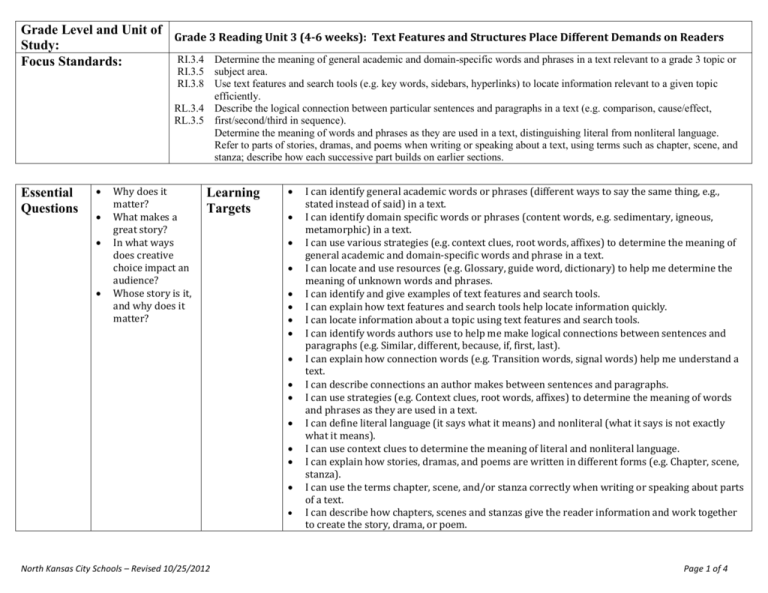
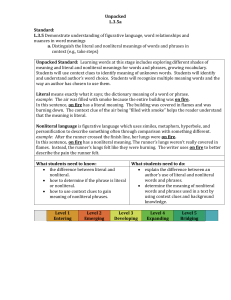
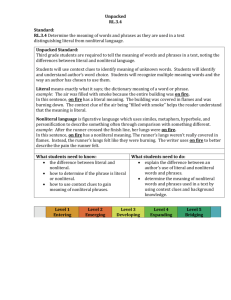
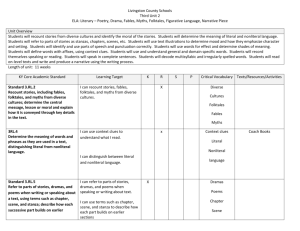
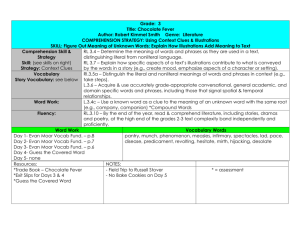
Grade Level and Unit of Grade 3 Reading Unit 3 (4-6 weeks): Text Features and Structures Place Different Demands on Readers Study: RI.3.4 Determine the meaning of general academic and domain-specific words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 3 topic or Focus Standards: RI.3.5 subject area. RI.3.8 Use text features and search tools (e.g. key words, sidebars, hyperlinks) to locate information relevant to a given topic efficiently. RL.3.4 Describe the logical connection between particular sentences and paragraphs in a text (e.g. comparison, cause/effect, RL.3.5 first/second/third in sequence). Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, distinguishing literal from nonliteral language. Refer to parts of stories, dramas, and poems when writing or speaking about a text, using terms such as chapter, scene, and stanza; describe how each successive part builds on earlier sections. Essential Questions Why does it matter? What makes a great story? In what ways does creative choice impact an audience? Whose story is it, and why does it matter? Learning Targets North Kansas City Schools – Revised 10/25/2012 I can identify general academic words or phrases (different ways to say the same thing, e.g., stated instead of said) in a text. I can identify domain specific words or phrases (content words, e.g. sedimentary, igneous, metamorphic) in a text. I can use various strategies (e.g. context clues, root words, affixes) to determine the meaning of general academic and domain-specific words and phrase in a text. I can locate and use resources (e.g. Glossary, guide word, dictionary) to help me determine the meaning of unknown words and phrases. I can identify and give examples of text features and search tools. I can explain how text features and search tools help locate information quickly. I can locate information about a topic using text features and search tools. I can identify words authors use to help me make logical connections between sentences and paragraphs (e.g. Similar, different, because, if, first, last). I can explain how connection words (e.g. Transition words, signal words) help me understand a text. I can describe connections an author makes between sentences and paragraphs. I can use strategies (e.g. Context clues, root words, affixes) to determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text. I can define literal language (it says what it means) and nonliteral (what it says is not exactly what it means). I can use context clues to determine the meaning of literal and nonliteral language. I can explain how stories, dramas, and poems are written in different forms (e.g. Chapter, scene, stanza). I can use the terms chapter, scene, and/or stanza correctly when writing or speaking about parts of a text. I can describe how chapters, scenes and stanzas give the reader information and work together to create the story, drama, or poem. Page 1 of 4 Suggested Resources Professional Resources: The Curricular Plan for Writing Workshop by Lucy Calkins and The Reading and Writing Project Non-Fiction Craft Lessons: Teaching Information Writing K-8 by Ralph Fletcher Wondrous Words by Katie Wood Ray Non-Fiction Matters by Stephanie Harvey Literature: Amelia Bedelia books (or any picture book that contains literal/nonliteral language) Owl Moon by Jane Yolen Amber was Brave Essie was Smart by Vera Williams Shel Silverstein and Jack Prelutsky poems Variety of informational texts (magazine articles, recipes, science experiment) ANY text that aligns to the specific teaching point Key Terminology Non-fiction, text features, glossary, table of contents, index, caption, informational, stanza, scene, chapter, transition words, idiom, simile, metaphor, personification, literal, nonliteral North Kansas City Schools – Revised 10/25/2012 Page 2 of 4 Culminating Activity Interdisciplinary Opportunities Science Social Studies North Kansas City Schools – Revised 10/25/2012 End Goals The student will: Identify general academic words or phrases (different ways to say the same thing, e.g., stated instead of said) in a text. Identify domain specific words or phrases (content words, e.g. sedimentary, igneous, metamorphic) in a text. Use various strategies (e.g. context clues, root words, affixes) to determine the meaning of general academic and domain-specific words and phrase in a text. Locate and use resources (e.g. Glossary, guide word, dictionary) to help me determine the meaning of unknown words and phrases. Identify and give examples of text features and search tools. Explain how text features and search tools help locate information quickly. Locate information about a topic using text features and search tools. Identify words authors use to help me make logical connections between sentences and paragraphs (e.g. Similar, different, because, if, first, last). Explain how connection words (e.g. Transition words, signal words) help me understand a text. Describe connections an author makes between sentences and paragraphs. Use strategies (e.g. Context clues, root words, affixes) to determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text. Define literal language (it says what it means) and nonliteral (what it says is not exactly what it means). Use context clues to determine the meaning of literal and nonliteral language. Explain how stories, dramas, and poems are written in different forms (e.g. Chapter, scene, stanza). Use the terms chapter, scene, and/or stanza correctly when writing or speaking about parts of a text. Describe how chapters, scenes and stanzas give the reader information and work together to create the story, drama, or poem. Math Encore Page 3 of 4 Lesson 1 (3-5 Days) RI 5 Teaching Point: Lesson 2 (5-7 Days) RI8 Teaching Point: Lesson 3 (5-7 Days) RL 4 RI 4 Teaching Point: Lesson 4 (3-5 Days) RL 5 Teaching Point: Readers use text features and search tools (e.g. key words, sidebars, hyperlinks) to locate information relevant to a given topic Readers describe the logical connection between particular sentences and paragraphs in a text Readers use strategies to determine meaning of words and phrases in informational texts and literature Readers refer to parts of stories, dramas, and poems when writing or speaking about literature Instructional Ideas: Instructional Ideas: Instructional Ideas: Immerse students in a variety of informational texts (Science, social studies books, magazines, trade books) o Identify and give examples of text features and search tools (key words, sidebars, hyperlinks) found in text o Create an anchor chart listing text features/search tools and their purpose Explain how text features and search tools help locate information quickly o Model locating information about a topic using text features o Model how readers use search tools (key words, sidebars, hyperlinks) to locate information relevant to a given topic Student Experiences: Look through bins of informational text books to find examples of different text features and search tools – chart features/tools and their purpose to add to anchor chart Using informational text of choice, explain how the text features in that particular text can help them locate information quickly When given a topic, locate information on that topic using text features and search tools Using technology, find information relevant to a given topic using search tools (key words, side bars and hyperlinks) Using a variety of informational text, identify words authors use to help the reader make logical connections between sentences and paragraphs (e.g., similar, different, because, if, first, last) o Highlight these words on a paper copy of text, and ask students to do the same o Model finding connection words in a variety of informational text (ex. Magazine article, set of directions, science experiment). Chart words authors use to help readers make connections Think aloud how connection words (ex. Transition words, signal words) help you understand a text o Model how transition words/signal words help direct the reader to make comparisons, identify cause/effect, identify sequence – first, second, third Think aloud to describe connections an author makes between sentences and paragraphs o Model how the transition/signal words connect sentences and paragraphs Student Experiences: In informational text of choice, identify connection words that the author uses to help make logical connections between sentences and paragraphs (could highlight words or mark with post-its); share and add to anchor chart Explain how connection words (transition words, signal words) helped students to understand their informational text Describe connections an author makes between sentences and paragraphs North Kansas City Schools – Revised 10/25/2012 Using informational text: Model how to identify general academic (different ways to say the same thing) words or phrases and domain specific (content) words or phrases Model how proficient readers use a variety of strategies to determine the meaning of general academic and domain-specific words and phrases o Context Clues o Affixes o Root Word Model how to locate and use resources to determine the meaning of unknown words in (glossary, guide word, dictionary). Chart the resources. Using literature pieces of choice: Model how proficient readers use a variety of strategies to determine the meaning of words and phrases o Context Clues o Affixes o Root Word Define literal language (it says what it means) and nonliteral (what it says is not exactly what it means) o Using Amelia Bedelia (or text of choice), model how to identify literal and nonliteral language o Model how to use context clues to determine the meaning of literal and nonliteral language. Create a 3-column chart with “phrase/ meaning/words from text that helped me” Student Experiences: In literature of their choice: o Use various strategies (context clues, root words, affixes) to determine the meaning of words and phrases o Identify literal and nonliteral language o Use context clues to determine the meaning of literal and nonliteral language – create 3-column chart In informational text of choice: o Identify domain-specific and general academic words or phrases o Use various strategies (context clues, root words, affixes) to determine meaning of general academic and domain-specific words and phrases o Locate and use resources to determine the meaning of unknown words and phrases Instructional Ideas: Explain how stories, dramas, and poems are written in different forms (specifically chapter, scene and stanza) o Show examples of each Model using the terms chapter, scene and stanza when writing or speaking about parts of the text o In reader’s notebook, model how to write about parts of the text using the above terms o In conversation, model how to speak about parts of the text using the above terms Think aloud how chapters, scenes, and stanzas give the reader information and work together to create the story, drama, or poem o Using a short poem, think aloud how the stanzas give the reader information and work together to create the poem o Using familiar chapter book, discuss how the chapters give the reader information and work together to create the story o Using a play, think aloud how the scenes give the reader information and work together to create the drama Student Experiences: Explain how stories, dramas, and poems are written in different forms (specifically chapter, scene and stanza) using examples from their book box Use the terms chapter, scene and stanza when writing in reader’s notebook or speaking while conferring with teacher about parts of the text Describe how chapters, scenes, and stanzas give you, the reader, information and work together to create the story, drama, or poem Page 4 of 4