6. Immunisation and Vaccination Update
advertisement

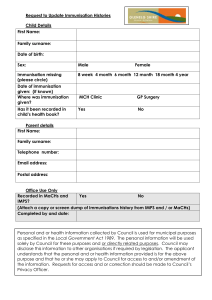
Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust OHP 2c - Procedure for Immunisation Assessment 1. Introduction 1.1 This procedure should be used in conjunction with the following Norfolk & Norwich University Hospital Trust Guidelines: Hepatitis B protection for Health Care Workers and guidance relating to Exposure Prone Procedures Varicella Zoster vaccination for Health Care Workers Trust Guideline for the Immunisation of new and existing health care workers Trust Guideline for the Prevention of TB & Management of TB exposure in HCWs 1.1 This procedure is designed to ensure that all Occupational Health Advisers (OHA) undertake an immunisation and vaccination check correctly in order to protect health care workers from contracting occupational acquired disease and to establish accurate details of the immunity of all health care staff. 1.2 All vaccinations are administered in accordance with the Trust Nursing Policies and Practice. All OHAs must have signed a Patient Group Direction before administering any vaccination. 1.3 All information relating to immunisations is taken from the Dept of Health Immunisation against Infectious Disease 1996 and the 2005/6 updated chapters. 2. Handling and Storage of Vaccines 2.1 Ordering It is the responsibility of all OHAs undertaking clinics to assess vaccine stock levels at the end of each clinic and to order further vaccines from the pharmacy as appropriate using the pharmacy order book which can be located in the surgery at NNUH. On completion of the stock order form please remove the yellow sheet only and take to pharmacy. Do not take the order book to pharmacy. U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust 2.2 Receipt of Vaccines OHAs are responsible for the collection of vaccines previously ordered from the pharmacy, for checking the order for discrepancies, leakage or damage and for recording the date of receipt, vaccine types, quantities, batch numbers and expiry dates on the relevant label and sticking it in the pharmacy order book with the corresponding order counterfoil. Vaccines must be refrigerated immediately on receipt and must not be left at room temperature. Please document on the order counterfoil the time frame between delivery and refrigeration i.e. refrigerated immediately or refrigerated within 15 minutes etc. 2.3 Storage of vaccines All vaccines are Prescription Only Medicines (POMs) and must be stored under locked conditions. Refrigerators must either be lockable or within a room that is locked when not occupied by a member of staff. At NNUH the refrigerators must be locked at the end of the day and the keys locked in the filing cabinet in the office. At Rouen Road the refrigerators must be locked at the end of the day and the keys placed in the key box in the main office. Vaccines must be kept in their original packaging when stored, so that they retain information on batch numbers and expiry dates. The packaging is also part of the protection against light and changes in temperature. Refrigerators must be of pharmaceutical grade and temperature controlled. It is the responsibility of the duty nurse to checked and record the refrigerator temperature at the start of every day on the monitor charts located on the fridge door. All vaccines are sensitive to some extent to heat and cold. Heat speeds up the decline in potency of most vaccines, thus reducing their shelf life. Effectiveness cannot be guaranteed for vaccines unless they have been stored at the correct temperature. Freezing may cause increased reactogenicity and loss of potency for some vaccines. It can also cause hairline cracks in the container, leading to contamination of the contents. Vaccines must not be stored in the door, in the bottom drawers or adjacent to the freezer plate of the refrigerator. If there are temperature variations outside of the recommended +2˚C to +8˚C range, they usually occur in these parts of the U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust refrigerator. Sufficient space should be allowed in the refrigerator so that air can circulate freely. Ice should not be allowed to build up within the refrigerator, as this reduces effectiveness. Annual portable appliance testing (PAT) is performed by the Trust Clinical Engineering team. Cleaning of the inside of the fridge should occur on a monthly basis and be recorded on the temperature monitoring form. In the event of a refrigerator failing, vaccines will be transferred to one of the other Occupational Health refrigerators, labelled/marked to ensure that they are used first. If the failure cannot be identified as occurring within the last 24 hours i.e. over a weekend or public holiday please seek advice from pharmacy prior to disposing of the vaccines. Validated cool boxes (with maximum – minimum thermometers) and cool packs from a recognised medical supply company should be used to distribute or transport vaccines. Individual manufacturers’ instructions should be strictly adhered to. Vaccines must be kept in the original packaging, and placed into a cool box with cool packs as recommended by the manufacturer’s instructions. 2.4 Disposal of vaccines All reconstituted vaccines and opened multi-dose vials must be used within the period recommended by the manufacturers and disposed of at the end of an immunisation session by sealing in a ‘sharps’ box. Any out of date stock should be returned to pharmacy for disposal and a record of this should be inserted on a yellow pharmacy order form and identified clearly as returned stock for disposal. 2.5 Anaphylaxis All health professionals responsible for immunisation must attend annual training sessions for resuscitation and the recognition and management of anaphylaxis. An anaphylaxis pack containing two ampoules of adrenalin 1:1000, four 23G needles and four graduated 1 ml syringes and oxygen must be available whenever vaccines U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust are given. In the event of anaphylaxis 0.5 ml of the adrenaline should be administered intramuscularly and repeat after 5 minutes if no improvement in symptoms. Please see Appendix F for anaphylactic reactions and treatment flow chart. All OHAs undertaking vaccination must be familiar with the procedure for contacting the emergency services relevant for that area. 3. The Purpose of Immunisation 3.1 To protect Health Care Workers (HCW) from any occupational risk of contracting communicable disease that is preventable by vaccination. 3.2 To protect patients and colleagues from acquiring vaccine preventable disease from an infected HCW. 4. Definition of HCW 4.1 HCWs who work within a healthcare setting may be directly or indirectly involved with patient care. For the purpose of occupational risk the following categories of HCWs are defined as: New HCW – these people are individuals who are commencing a post for the first time within the NHS and having patient contact, Commencing a post (or training) for the first time that involves EPP procedures or individuals that are returning to work in the NHS after a break. New HCWs who have previously worked in another NHS Trust but had continuous service – to be known as ‘Continuous Service New HCW’ Laboratory workers and other staff who have direct contact with potentially infectious clinical specimens and may be exposed to pathogens in the laboratory. Non clinical staff who may have social contact with patients but not usually of a prolonged or close nature ( e.g. ward clerks, porters, cleaners, admin staff in ward / department areas, maintenance engineers, cleaners) If a job change occurs the immunisation status of an individual should be reviewed to ensure it meets their specific requirements. U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust 5. Prior to Immunisation and Vaccination update 5.1 All health care staff will have their immunity and vaccination history updated in accordance with this procedure. 5.2 All HCW immunisation status will be reviewed when undertaking the preemployment health screening procedure (see OHA 2a). Depending on the post applied for will depend on what immunisation will be required. 5.3 Those roles which require EPP procedures or are considered to be in areas of high risk to TB are required to have their immunisations updated prior to their commencement of employment unless all documentary evidence has been provided. 6. Immunisation and Vaccination Update 6.1 All immunisation and vaccination information must be reviewed, updated and entered onto the green immunisation form / entered onto the NOHS database. 6.2 If vaccines are administered then the vaccine administration form for that particular vaccine should be completed and signed by the Occupational Health Adviser with appropriate consent gained from the individual agreeing to have the vaccination. 6.3 The Occupational Health Adviser must ensure all staff are assessed and comply with the mandatory immunisation requirements of the healthcare post. 6.4 If an individual refuses to have the vaccination then their manager and HR manager for their divisional area should be informed via email. 6.5 If an individual cannot have the vaccination due to a permanent contra-indication then the file should be passed onto the Senior OH Physician who will advise on the most appropriate course of action. 7. Chicken Pox U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust 7.1 All staff who have contact with patients must have their immunity to Varicella assessed and immunisation offered to those health care workers who are not immune. Particular attention should be given to those who work in high risk clinical areas Oncology Haematology Rheumatology OPD Genito urinary medicine Paediatrics Obstetric and Neonatal Intensive Care 7.2 Immunity will be assessed as follows: A definite history of having the disease unless they are HCW who has arrived from a tropical country regardless of history when serological testing will be required. A definite history of shingles Documentary evidence of x2 doses of Varicella Zoster Virus vaccine. If the employee is unsure regarding their immunity the OHA must take a sample of blood for VZV antibody to confirm current immunity status (yellow bottle and sent to Trust Microbiology). 7.3 All healthcare workers who are not immune to Varicella will be offered the chicken pox vaccine. See Trust guideline on the management of varicella zoster for health care workers. See Appendix A 8. Measles Mumps Rubella (MMR) 8.1 All staff who work in clinical areas must have their immunity to Measles, Mumps and Rubella assessed and immunisation offered to those health care workers who are not immune. 8.2 Immunity will be assessed as follows:- U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust Documentary evidence of having received two doses of MMR Positive antibody test for Measles, Mumps and Rubella. History of the disease is NOT evidence of immunity 8.3 If vaccinations are refused then both the manager of the area and HR Divisional manager need to be informed. A serology test for rubella and measles should be taken. If this is negative then it may be necessary to place restrictions on working in certain areas. 8.4 Staff with a known or suspected latex allergy can have the vaccination however the MMR powder should be diluted with water for injection not the reconstitution solution and a 2ml syringe used in place of the syringe provided. The needle should be changed after diluting the powder prior to administering the vaccination. 8.5 If the individual has a permanent contra-indication that prevents them from having the vaccine, then a serology test for rubella and measles should be taken. If this is negative then it may be necessary to place restrictions on working in certain areas. 9. Polio / DTP 6.1 All Staff who may be exposed to polio in the course of their work in microbiology laboratories and clinical infectious disease units are at risk and must be protected. The Department of Health 2006 states that a total of five doses of vaccine at the appropriate intervals are considered to give satisfactory long term protection. Staff regularly handling faecal specimens should be offered a polo booster every 10 years. 10. Pulmonary TB 10.1 Evidence of Immunity As indicated by one of the following: Documented positive tuberculin test (a grade 2 or more Heaf Test or greater than 6mm Mantoux test) in the previous 5 years. Evidence of a BCG vaccination resulting in a pale, flat, circular scar. U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust Documentary evidence of a BCG vaccination. See OHP 5 If no evidence of scar refer for Mantoux +/- BCG appointments. 7.2 High risk areas where staff would require documentary evidence of immunity / scar check by an OH professional prior to employment are described in OHP 5 11. Hepatitis B 11.1 Staff working in a Clinical Environment or who come into contact with blood and body fluids Staff who will come into contact with blood and body fluids will be advised to commence a course of Hepatitis B vaccinations which can be administered by the Centre for Occupational Health. 11.2 Hepatitis B vaccination programme Vaccine: Hep B VaxPro 10 micrograms. Engerix B (vial) may be used if staff are sensitive to Latex, this will need to be ordered through pharmacy. Route: Intramusular injection into deltoid muscle Frequency: Primary course of three doses at day 0, 1 month and 6 months followed by a blood test to check the anti-HBs titre level 8 weeks after the third vaccine has been administered. NB: When taking blood for an antibody level, ensure that consent is gained from the individual to undertake a Hep B Surface antigen and Hep B Core test on the blood if their response to the vaccination is <10 miu/ml. 11.3 In special circumstances (e.g. if a staff member had not been immunised and had a blood exposure incident or if a staff member is starting in employment and doing a high level of EPPs or working in area that is considered high risk for Hepatitis B and has no immunity) an accelerated course may be used (0, 1, 2, 12 months). 11.4 Eight weeks after the third dose the HCW should attend the COH for a blood test to measure their antibody response to the vaccine (anti-HBs titre). The significance of the results and actions required (DoH recommendations) are as follows: U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust Optimal response (>100 mIU/mL). A single booster is required after 5 years without reassessment of titre. Poor response (10-100 mIU/mL). An additional booster dose is required and the titre must be repeated in 8 weeks. If the repeat Titre is satisfactory then a further single booster is required at 5 years without reassessment of titre. Non-responder (<10 mIU/mL). Confirm if Hep B Surface antigen and Hep B core antibody is negative – if so repeat the full course of 3 vaccinations followed by a titre at 8 weeks. If the level remains at <10 mIU/mL then the individual is defined as a non-responders. If level >10 mIU/mL they will require 5 year booster (as above). o If level remains <10 miu/ml then will be classed as a non- responder. o If the HBsAg and / or Hep B Core level is positive, then the file must be passed to a SOHNA / OH Nurse manager so that further testing can be instigated (see section 8.6 + Appendix D for further advice). o If the level becomes >10 miu/ml then the individual will require a 5 year booster as above. 11.4.1 If the OHA receives or makes a telephone call to an individual employee regarding their Hepatitis B status (e.g. to inform / explain poor response / seek consent for HBsAg / HB Core tests or outcome of further tests) then this should be logged on the NOHS system as a journal entry – under the drop down box title ‘Hep B Telephone Call’. If however, the nurse is contacting a specific external company to provide a general update of where employees are on their course and recommendations of those needing to attend further appointments this will be included in the Hep B course pricing. 11.5 HCWs who have been previously immunised but have no record of immunity status should have an anti-HBs titre undertaken and if indicated by the risk assessment performed by COH, given a booster dose of vaccine. If the level is U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust returned <100 miu/ml then a repeat antibody test will be performed at 8 weeks post vaccination. 11.6 Heptiatis B Surafce antigen or Core antibody positive results 8.6.1 If the HBsAg and / or Hep B Core level is positive, the file must be passed to a SOHNA / OH Nurse manager so that further testing can be instigated (see Appendix C for further advice). 11.6.2 Where appropriate ensure that the laboratory is proceeding to undertake the Anti HB Core IgM, HB e antigen and HB e antibody tests to assess the level of infectivity. Consideration should be given as to whether the worker is involved in EPP activities – see OHP 3 for guidance on restriction of these activities when Hepatitis B positive and further testing that is required. 11.6.3 On receipt of the results, it is vital that the individual is seen by an OHP so that information can be given as well as appropriate referral made to GP or Hepatologist. If the employee is an EPP worker viral load testing may need to be undertaken. EPP activity may also need to be suspended. 11.6.4 The SOHNA must ensure that the results are inputted into NOHS system and the appropriate description of infectivity is given (see appendix D). 11.6.5 A 6 monthly report should be pulled from NOHS on all Hepatitis B positive employees within the contracts that are covered. These employees should be contacted to identify if they have remained in the same place of work and also offer general support. This conversation should be logged in their records and followed up with an OHP appointment if their circumstances have changed. 12.0 EPP Members of staff must provide evidence of a United Kingdom accredited laboratory result indicating Hepatitis B antibody level and Hepatitis B Surface antigen and where appropriate Hepatitis C antibodies and HIV antibodies and antigen. The OHA should use the ‘Consent form for Hep B, C and HIV Bloods / EPP Bloods’. This form U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust incorporates the Pre-test discussion issues that need to be considered when undertaking these tests. See procedure for EPP clearance. 13. Hepatitis C and HIV tests for non-EPP workers 13.1 All HCW commencing employment should be offered an opportunity to have Hepatitis C and HIV testing. 13.2 The OHA can offer this test when undertaking the immunisation assessment and should use the Consent form for Hep B, C and HIV Bloods / EPP Bloods. This form incorporates pre-test discussion issues that need to be considered when undertaking these tests. 14. Tetanus 14.1 Staff whose work involves contact with soil i.e. gardeners, maintenance workers will be advised to ensure they are protected against tetanus. Staff will be advised to attend their General Practice for this vaccination to be administered 14.2 The Department of Health recommends the following vaccination programme: A primary course of three doses of 0.5ml adsorbed tetanus vaccine one month between each dose. A reinforcing dose is recommended after the primary course and again ten years after that. There is little justification for boosting with tetanus vaccine beyond the recommended 5-dose regimen. 15. Audit 15.1 This procedure will be audited as indicated by the Centre for Occupational Health. All results will be discussed with the team and changes in practice implemented where needed in line with current best practice. 16. Process for Development 16.1 This procedure has been agreed by the Occupational Health Team and is reviewed regularly. 17. Dissemination U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust 17.1 Copies of this procedure will be held in the Centre for Occupational Health in a computerised format. References Department of Health (2005) Immunisation against Infectious Diseases Health and Safety Executive (2002) Control of Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations. http://www.hse.gov.uk/healthservices/index.htm Department of Health (2006) .Immunisation Against Infectious Disease 3rd edition, (“Green Book”) http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publichealth/Healthprotection/Immunisation/Greenbook/DH_ 4097254 Department of Health (2007) Health clearance for tuberculosis, hepatitis B, hepatitis C and HIV: New Health Care Workers http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/PublicationsPolicyAnd Guidance/DH_073132 Department of Health (2007) Hepatitis B infected healthcare workers and antiviral therapy. http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/PublicationsPolicyAnd Guidance/DH_073164 Expert Advisory Group on AIDS and the Advisory Group on Hepatitis. (1998) Guidance for Clinical Health Care Workers: Protection against infection with Bloodborne viruses. (HSC 1998/063) http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/PublicationsPolicyAnd Guidance/DH_4002766 U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust European Consensus Group on Hepatitis B Immunity. (2000) Are booster immunisations needed for lifelong Hepatitis B immunity? Lancet; 355: 561-565 NHS Management Executive HSG (93)40, Protecting Health Care Workers and Patients from Hepatitis B addendum Sept 96 (EL(96)77) Sept 96. http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Lettersandcirculars/Healthserviceg uidelines/DH_4084234 Depart of Health (2000) HSC 2000/020 Hepatitis B infected Health Care Workers. http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Lettersandcirculars/Healthserviceci rculars/DH_4004553 U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust Appendix A Assessing Immunity to VZV + Indication for Vaccination Does the Health Care Worker (HCW) have a definite history of VZV infection(chicken pox or shingles) or documented evidence of x2 doses of varicella vaccine? Yes Have they come to the UK from a tropical country? No No Yes Consider Immune No further action required VZV antibody test Antibody test result positive? Yes No Are they immuno-compromised e.g steriods / HIV / cancer treatment etc? Yes No Vaccination is contraindicated unless immunosupression resolves Is this a female member of staff? Yes No Offer vaccination Slicylates should be avoided from time of 1st dose to 6 weeks post 2nd dose. 2nd dose should be given 4-8 weeks after first dose Pregnancy should be avoided for 3 months following each vaccination. Are they pregnant or suspect they might be? No Yes Occ Health Defer vaccination until pregnancy finished or pregnancy is not confirmed Routine Follow up serological testing is not routinely required. U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 HCW If rash develops post vaccination see Occuaptional Health prior to patient contact 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust Appendix B U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust Quick Reference Guideline - Occupational Health pre employment standard and additional health clearance checks for New HCWs ALL NEW AND EXISTING HCWS UNDERTAKING EPPS MUST BE SEEN BY OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH (OH) FOR ADDITIONAL HEALTH CLEARANCE CHECKS PRIOR TO EMPLOYMENT UNLESS IVS DOCUMENTED EVIDENCE IS AVAILABLE ALL NEW & EXISTING HCWS MUST BE SEEN BY OH WITHIN THE FIRST WEEK OF EMPLOYMENT TO UNDERTAKE STANDARD & ROUTINE HEALTH CLEARANCE CHECKS UNLESS IVS DOCUMENTED EVIDENCE IS AVAILABLE New Health Care Worker (NHCW) 1.First time with direct patient contact 2.New to post or training involves EPPS 3.Returning to work following a break ( OH to assess) Direct Patient Contact & undertaking EPPS Additional Health Clearance Check to be undertaken prior to employment 1.HIV antibody 2.Heb B surface antigen& antibody 3.Hep C antibody Standard Health Clearance Check for 1.TB 2. Hep B clearance as above Routine Immunisation Check 1. VZV 2. MMR 3. Advise on Diphtheria. Tetanus and Polio Direct Patient Contact & NOT undertaking EPPS Standard Health Clearance Check within first week of employment 1.TB ( if in high risk area clearance required prior to employment) 2. Advice on Hep B 3. Offered test for Hep C & HIV Routine Immunisation Check 1. VZV 2. MMR 3. Advise on Diphtheria. Tetanus and Polio New Health Care Workers who have previously worked in an NHS Trust-continuous service Direct Patient Contact & undertaking EPPS Direct Patient Contact & NOT undertaking EPPS Additional Health Clearance Check to be undertaken prior to employment 1. Hep B surface antigen & antibody 2. Hep C - antibody ( if commenced EPPs after Jan 2003 3. HIV antibody ( if commenced EPPs after 2008) 4. If HCW has been undertaking EPPs prior to Jan 2003 HCW must be offered a test for Hep C & HIV. Mandatory Hep C & HIV not required Standard Health Clearance Check 1.TB (if in high risk area clearance required prior to employment) 2. Advice on Hep B 3. Offered test for Hep C & HIV Standard Health Clearance Check 1. TB 2. Hep B clearance as above Routine Immunisation Check 1. VZV 2. MMR 3. Advise on Diphtheria. Tetanus and Polio U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 Routine Immunisation Check 1. VZV 2. MMR 3. Advise on Diphtheria. Tetanus and Polio 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Laboratory Workers including non technical staff Regularly handle pathogens or potentially infected specimens Standard Health Clearance Check 1.TB ( if in high risk area clearance required prior to employment) 2.Advice on Hep B 3. Offered test for Hep C & HIV Routine Immunisation Checks 1. VZV 2. MMR 3.Advise on Diphtheria. Tetanus and Polio following risk assessment and advice from manager Non Clinical Health Workers Social contact with patients e.g ward clerks porters & cleaners Standard Health Clearance Check 1.TB ( if in high risk area clearance required or work involves social contact) 2. Advice on Hep B Routine Immunisation Checks 1. VZV 2. MMR 3.Advise on Diphtheria. Tetanus and Polio Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust Appendix C Action required on obtaining an anti-HBs level of <10 mIu/ml U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust Appendix C - Action on obtaining an anti-HBs level of <10 mIu/ml Hep B Antibody taken. Result<10 miu/ml Request lab to undertake Hep B Surface antigen (HBsAG) + Hep B Core (HB Core) No HBsAG positive? Yes File to Senior OH Nurse Adviser (SOHNA) HB Core positive? No Yes Repeat primary course (if approraite) or confirm True Non reponder No requirement for Anti core IgM or e status tests as not currently infectious Ensure lab are undertaking Anti HB Core IgM HB e antigen HB e antibody to assess level of infectivity Profile = immune following previous infection. No further action unless patient becomes immunosuppressed No EPP worker? Arrange for DNA viral load tests to be undertaken. 2 samples one week apart (see seperate flow chart for specific EPP guidance) Results back to SOHNA Yes No Anti HB Core IGM Positive? (showing recent infection) Yes No HB e antigen positive and Anti HB e Negative? HBe antigen positive and Anti HB e negative No Yes HBe antigen positive and Anti HB e negative HB e antigen negative and AntiHB e positive? Yes HB e antigen negative and AntiHB e negative? Yes Yes Profile = Recovery of infection High risk of infectivity. Repeat blood test in 4 weeks Referral ASAP to Heaptologist No Profile = Acute infection High risk of infectivity. Repeat blood test in 2-3 months Profile = Chronic infection. High risk of infectivity Profile = Chronic infection. Risk of infectivity Book OHP appt for referral to hepatologist / inform primary care practitioner U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 Profile = Possible Chronic Infection Risk of infectvity Repeat blood test in 4 weeks to ascertain whether seroconversion has occurred 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust Appendix D Nohs Profile Table U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust Outcome of results profiles for Hepatitis B HBsAg Anti-HBs Anti-HBc Anti-HBc IgM HBeAg Anti-HBe Negative Positive (rarely negative) Positive Negative Not Required Not Required Positive Negative Positive or Negative Positive Positive Negative Positive Negative Positive Negative Positive Negative Positive Negative Positive Negative Negative Positive Negative Positive Positive Negative Negative Positive Negative Positive Positive Negative Positive U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3) Positive Centre for Occupational Health Norfolk & Norwich University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust U/procedures & Competences/OHA procedures/pre employment/immunisation Date of issue July 2004 Update Feb 2009 Review due March 2010 09/02/2016 Ref (3)