Fuel Load Calculation Cheatsheet: Forestry & Ecology
advertisement

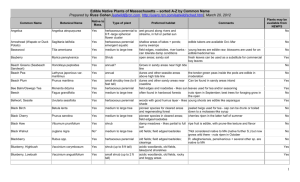
Your Assignment: Fuel Load Calculations Cheatsheet To Do: Use this cheatsheet to calculate the fuel loading for the downed woody debris, litter and duff, and shrub and herbaceous fuels in the two sites. Input the data into the Excel worksheet you were given, and email to lkobziar@ufl.edu before Tuesday of next week. I. Downed woody Debris (from Brown 1974): Computing Tons per Acre: 1, 10 hr size class: 0-3 in: (tons/acre) = (11.64 * n * d2 * s * a * c )/ Nl 100, 1000 hr size classes: 3+ inches: (tons/acre) = (11.64 * ∑d2 * s * a * c )/ Nl Where: c = slope correction factor (From Brown 1974) n = total number of intersections over all sample points (for each of the 1-hr, 10-hr and 100-hr samples) d2 = squared average diameters Page 1 For 1, 10 and 100-hr fuels these have been measured in the field and constants for different species and systems have been derived. For our purposes, use the following (nonslash composite values from Brown 1974): Diameter class (inches) : 0-0.25 d2 (inches2): 0.0151 0.25-1 0.289 1-3 2.76 For 1000-hr fuels (3+ in), the actual diameters of each piece are squared and added together to get ∑d2 s = specific gravity of the materials Approximate Specific gravities for conifers given by Brown (1974) were: Diameter class (inches) : Specific gravity : 0-0.25 0.25-1 1-3 0.48 0.48 0.40 3+Sound 0.40 3+Rotten 0.30 a = the nonhorizontal angle correction factors The correction factor adjusts weight estimates for the fact that all particles do not lie horizontally as assumed in the planar intersect theory. Brown provides the following: 0 to 3 inches: 1.13 3+ inches: 1.00 Nl = the total length of the sampling line These lengths are different for different protocols: FIREMON Sampling Scheme: Fuel Size Class Length of Transect Sampled 1-hr 6ft 10-hr 6ft 100-hr 15ft Page 2 1000-hr 60ft II. Litter and Duff: Litter and Duff loadings are calculated by multiplying the average depth by the bulk density of litter (or duff). Use bulk density values of 2.75 lbs/ft3 for litter and and 5.5 lbs/ft3 for duff. Note that you will need to convert to tons/acre. III. Live and dead herbaceous and woody loads: For each transect, average the two fixed-area plot estimates for live shrub cover, dead shrub cover, live herbaceous cover, and dead herbaceous cover. Find the average shrub height and average herbaceous height. Biomass of live and dead shrubs and biomass of live and dead herbaceous plants are calculated using the equation, B=H*C*BD Where: B = biomass (kg/sq. m) H = height (m) C = percent cover/100 BD = bulk density (kg/cu. m) Bulk density used for the herbaceous and shrub components are 0.8 kg/m3 and 1.8 kg/m3, respectively. Page 3