4 Comparing and Scaling
advertisement

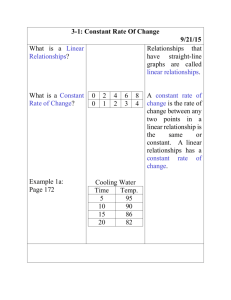
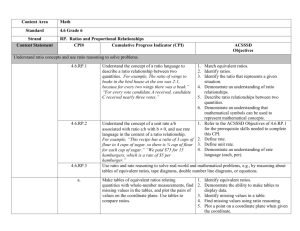
Course Name: 7th Grade Math Unit #4 Unit Title: Comparing and Scaling Enduring understanding (Big Idea): Students will understand how to use ratios, percents and fractions to determine the relationship between quantities. Students will use scaling, proportions, and unit rate to find equivalent ratios and unknown quantities in real world situations. Essential Questions: Which quantities should be compared? Which comparison strategies should be used to make predictions about unknown quantities? How can the comparison be expressed in different but useful ways? BY THE END OF THIS UNIT: Students will know… Students will be able to… How to use proportions, equations and tables to compare quantitative data. How to scale ratios, rates and fractions to make larger or smaller objects relative to the characteristics of the original. Analyze comparison statements made about quantitative data Use ratios, fractions, differences, and percents to form comparison statements given various situations Use tables, graphs and equations to make predictions and useful comparisons Determine point of view and judge the reasonableness of comparison statements. Vocabulary: Proportion, unit rate, rate, rate table, ratio, scale, scaling Unit Resources Mathematical Practices in Focus: Learning Task: Additional Practice Investigation 1- 4 1- Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them 2- Reason abstractly and quantitatively 3- Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others 4- Model with mathematics 5- Use appropriate tools strategically 6- Attend to precision 7- Look for and make use of structure 8- Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning Performance Task: CC Additional Investigations 1.2-3 Project: Paper Pool Investigation and Report Unit Review Game: Proportions Trail https://www.teachingchannel.org/videos/junior-high-mathlesson MathForward: Just How Many Are There? CCSS-M Included: 7.RP.1, 7.RP.2a, 7.RP.2b, 7.RP.2c, 7.G.1 Suggested Pacing: 18 days Standards are listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Course Name: 7th Grade Math Unit Plan Standard 7.RP.1 Investigation 1: Making Comparisons Standard 7.G.1, 7.RP.2a Investigation 2: Comparing Ratios, Percents, and Fractions Standard 7.RP.2b Investigation 3: Comparing and Scaling Rates Standard 7.RP.2a, 7.RP.2c Investigation 4: Making Sense of Proportions Unit #4 Unit Title: Comparing and Scaling Investigation 1.1 Ads That Sell 1.2 Targeting and Audience 1.3 American Records Math Reflection 1 Determine the Most Useful Comparison Strategies Suggested ACE Questions ACE 1-3, 11-16, 34 ACE 4-7, 17-33, 34 ACE 8-10, 36-41 2.1 Mixing Juice 2.2 Sharing Pizza 2.3 Finding Equivalent Ratios Math Reflection 2 Compare the Use of Ratios, Decimals and Percents ACE 1-3, 9-13 ACE 4, 5, 14-18, 22 ACE 6-8, 19-21, 23, 24 3.1 Technology on Sale 3.2 Time, Rate, Distance 3.3 Comparing CD Prices 3.4 What Does Dividing Tell You? Math Reflection 3 Compare Rates Using Graphs, Tables and Equations ACE1-3, 13-18, 33 ACE 4-8, 10, 19-23 ACE 9, 11, 24-26, 34 ACE 12, 27-32 4.1 Setting Up and Solving Proportions 4.2 Everyday Use of Proportions 4.3 Developing Strategies for Solving Proportions Math Reflection 4 Create Multiple Proportions of Equivalence Looking Back and Looking Ahead 1. Comparing Transportation Survey Results 2. Determining the Better Buy 3.Use Comparison Strategies to Interpret Data ACE 1, 2, 15-17, 21-23 ACE 3-5, 18-20, 25, 26 ACE 6-14, 24, 27, 28 Standards are listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Course Name: 7th Grade Math Unit #4 Unit Title: Comparing and Scaling CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Analyze proportional relationships and use them to solve real-world and mathematical problems. Standard: 7.RP.1 Compute unit rates associated with ratios of fractions, including ratios of lengths, areas and other quantities measured in like or different units. For example, if a person walks 1/2 mile in each 1/4 hour, compute the unit rate as the complex fraction 1/2/1/4 miles per hour, equivalently 2 miles per hour. Concepts and Skills to Master: Ability to describe and identify complex fractions Ability to recognize the difference between unit rate and ratio SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge Conceptual Understand ratios as proportional relationships between quantities Understand fractions as a ratio, rate or as a part to whole relationship Understand the relationship between part to whole and part to part Understand the connection between decimals and fractions Procedural Ability to convert fractions to decimals and percents Ability to determine fractional equivalence Ability to identify common factors or multiples of similar figures Academic Vocabulary Ratio, unit rate, compare, describe, explain, relate, quantities, equivalence Suggested Instructional Strategies: Resources: Introduce the concept of ratios by requiring students to write three ratios to represent a jar of marbles that has two colors. This will help the students relate part to part, part to whole and whole to part. Use several real world examples such as boys to girls and girls to number of students in the class. Help students connect arithmetic ratios to algebraic ratios by using variables to represent each quantity in the ratios. Inform the grade level teachers of the comparison language needed for this unit and work together to increase student ability to communicate effective comparative statements. Sample Assessment Tasks Skill-based task In 1990, there were approximately 141,542,000 babies born in the world. About how many births was this per day? Per hour? Per Minute? Textbook Correlation: Investigation 1 MARS Task: E14: Best Buy Graphing Calculator Task: Can You Walk 3 Miles Per Hour? Problem Task Describe a method you could use to estimate how many times your heartbeats in a day, a week, and in a year. Standards are listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Course Name: 7th Grade Math Unit #4 Unit Title: Comparing and Scaling CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Analyze proportional relationships and use them to solve real-world and mathematical problems. Standard: 7.RP.2.a Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities. a) Decide whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship, e.g., by testing for equivalent ratios in a table or graphing on a coordinate plane and observing whether the graph is a straight line through the origin. Concepts and Skills to Master: Ability to graph coordinates interpreted from proportional context Ability to recognize given proportional situations that the two “between ratios” and the two “within ratios” are the same Ability to recognize that two equal ratios represent a proportion and can be represented using ordered pairs and linear representations. SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge Conceptual Understand how to use equations, linear graphs, tables and ordered pairs to represent patterns Understand how to construct proportions to determine proportionality between multiple quantities Understand how to test for equivalence using multiple strategies Procedural Ability to plot patterns in the form of linear representations on a coordinate grid Cross multiply to determine proportionality Ability to continue an arithmetic and geometric sequence Academic Vocabulary Linear, origin, equivalence, ordered pairs, proportional relationship Suggested Instructional Strategies: Resources: Graphing Proportions: Allow students to discuss the difference between inversely and directly proportional prior to completing the problem task below. Assign the students real world problems and solutions. Task: Create, solve and describe a directly and inversely proportional situation using a tables, graphs and equations. Explain the difference between inversely and directly proportional. Performance Based Tasks with Rubrics: Complete performance based tasks from the following link. Use the sample response to help student understanding of rubrics. #1 Amy’s Vacation http://www.oercommons.org/courses/proportionalreasoning/view Sample Assessment Tasks Skill-based task One of the pipes in your house broke. You are trying to decide which plumbing company to call, Wizards or Easy Clean. Wizards charges $75 to make a house call and then $25 per hour until the job is finished. Easy Clean charges $60 to make a house call and then $30 per hour until the job is finished. Using the information above describe the meaning of each ordered pair. 1. (2, 175) 2. (6, 240) Textbook Correlation: Investigation 2, 4 MARS Task: E10: A Golden Crown Graphing Calculator Task: Does the Hand Relate to the Foot? Problem Task Photographs come in several standard print sizes. Some of the most common print sizes are 4x6, 5x7, and 8x10. (Note: The dimensions are given in inches.) Does a proportional relationship exist between these print sizes? Justify your answer using a graph, proportion and table. Standards are listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Course Name: 7th Grade Math Unit #4 Unit Title: Comparing and Scaling CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Analyze proportional relationships and use them to solve real-world and mathematical problems. Standard: 7.RP.2b. Identify the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, graphs, equations, diagrams and verbal descriptions of proportional relationships. Concepts and Skills to Master: Ability to express unit rates using a variety of representations, given a contextual situation SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge Conceptual Understands how to make connections between decimals, fractions and percents represented in real world situations Understands how to make inferences about quantities and develop strategies and techniques to solve for missing values Understands the purpose of expressing values in the form of unit rates Procedural Ability to construct tables, graphs, equations and diagrams to demonstrate proportionality Ability to determine unit rate using proportions Ability to use division to determine unit rate and multiply to determine unknown data Academic Vocabulary Constant, diagrams, independent, dependent, rate tables Suggested Instructional Strategies: Resources: If students are still having difficulty using fraction equivalents rely upon the practice sheet “Ratios and Fractions” to reinforce simplifying and comparing fractions. This is recommended as a warm-up for students that lack fraction foundations. If students haven’t demonstrated mastery at writing finding unit rates rely upon the skills practice sheet “Finding and Using Rates.” Use this as a homework, review or warm-up activity. Go to this site for additional table and graph situations. http://dooleymath.com/Algebra/SystemsOverview.html Sample Assessment Tasks Skill-based task It takes Juan 80 steps on the elliptical machine to go 0.1 of a mile. When his workout is done, he has gone 4 miles. How many steps has she made on the machine? Textbook Correlation: Investigation 3 MARS Task: A21: Sale Graphing Calculator Task: Equations from Unit Rates Problem Task Surrounding the EPIC Center are several parking lots. Parking lot A is charging $4.50 for the first hour and $1.50 for every after following. Parking Lot B is charging $3.50 for the first hour and $2.50 for every hour following. Create tables, graphs and equations to determine which parking lot has the better rate for customers. Write a paragraph to justify your final decision. Standards are listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Course Name: 7th Grade Math Unit #4 Unit Title: Comparing and Scaling CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Analyze proportional relationships and use them to solve real-world and mathematical problems. Standard: 7.RP.2.c Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities. c. Represent proportional relationships by equations. Concepts and Skills to Master: Ability to recognize that multiplicative relationships are proportional For example, if total cost t is proportional to the number of n of items purchased at a constant price p, the relationship between the total cost and the number of items can be expressed as t = pn. SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge Conceptual Understands how to relate corresponding units as fractions and ratios Understands how to interpret real life comparisons and translate the quantities into useful representations Understands which formulas to use when solving for unknown quantities Procedural Ability to use cross products to determine proportionality Ability to use formulas to solve problems Ability to interpret patterns from tables and use the patterns to determine unknown values Academic Vocabulary Constant, relationship, correlation, rate, unit rate, rate table, compare, describe, inverse proportion, direct proportion Suggested Instructional Strategies: Resources: If students haven’t demonstrated mastery at setting up and solving proportions rely upon the skills practice sheet “Solving Proportions.” Use this as a homework or warmup activity. Review formulas Help students visually align corresponding sides, with tracing paper if the figures are not angled in the same direction. It may also be important to color code each edge to help visual learners. https://www.teachingchannel.org/videos/visualizinggeometry-lesson Sample Assessment Tasks Skill-based task 15 m Textbook Correlation: Investigation 4 Graphing Calculator Task: The Golden Rectangles Problem Task Determine the missing measurements in the given similar triangles. 9m 15 m x 12 m y x = _______________ y = _______________ Standards are listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. The Iditarod is a 1,159-mile sled dog race from Anchorage, Alaska to Nome, Alaska. Susan Bucher is a four-time winner of the race. Her average time was about 11 days. Find her average rate in miles per day. Use a diagram, formula, substitution, and inverse operations to determine her average rate per day. Course Name: 7th Grade Math Unit #4 Unit Title: Comparing and Scaling CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Draw, construct and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships between them. Standard: 7.G.1 Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including computing actual lengths and areas from a scale drawing and reproducing a scale drawing at a different scale. Concepts and Skills to Master: • Ability to describe and identify ratios and proportions • Ability to reproduce scale drawing at a different scale SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge Conceptual Understands the difference between similar and congruent figures Understands the rules of angle relationships such as complementary and supplementary angles Understands the difference between area and perimeter and how the scale factor impacts dimensions of the image Procedural Ability to determine corresponding parts of similar figures Ability to set up proportions and use cross products to determine missing values Ability to determine proportionality using ratios and cross products Ability to isolate the variable and solve two step equations Ability to construct geometric figures using ordered pairs Academic Vocabulary Scale drawing, scale factor, dilation, enlargement, reduction, congruence, similarity, corresponding parts Suggested Instructional Strategies: Resources: Help students revisit the concept of similar figures and proportionality using tools such as a protractor. Use actual measurements to demonstrate the difference between congruent and similar. Revisit fraction equivalence to help students correlate corresponding lengths, sides, widths, and parts. Use cross products to demonstrate proportionality. Students should know supplementary, vertical, complementary, alternate interior and alternate exterior angles. This will improve their ability to identify corresponding parts of geometric figures. Sample Assessment Tasks Skill-based task If you visit the Museum of Science and Industry in Chicago, you are able to examine a scale model of a human heart that is large enough to walk through. The height of the scale model is 16 feet. The scale used is 1 ft: 9/32 in. What is the height of the actual heart? Textbook Correlation: Comparing and Scaling Labs MARS Task: E09:Triangular Frameworks Graphing Calculator Task: Scaling the Geometry Problem Task If given the dimensions of the builder’s floor plans and the actual dimensions of the actual house, explain how you can determine the scale factor. Design a sample floor plan and actual dimensions to explain how you would determine the scale factor. Use corresponding parts to create equations, tables and proportions when possible as evidence of your understanding how to scale ratios. Standards are listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes.